![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Fabry disease |
Cause: alpha-galactosidase A deficiency -> accumulation of ceramide trihexoside. Inh: X-linked recessive Symp: peripheral neuropathy of hands/feet, angiokeratomas, cardiovascular/renal disease.
|
|
|
Gaucher disease |
Most common sphingolipidosis. AR. Cause: Glucocerebrosidase (beta-glucosidase) deficiency -> accumulation of glucocerebroside. Symp: Hepatosplenomegaly, pancytopenia, Treat: recombinant glucocerebrosidase. |
|
|
Niemann-Pick disease |
Cause: sphingomyelinase deficiency -> accumulation of sphingomyelin. AR. Symp: Progressive neurodegeneration, hepatosplenomegaly, “cherry-red” spot on macula, foam cells (lipid laden macrophages) |
|
|
Tay-Sachs |
Cause: Hexominidase A deficiency -> G2 ganglioside accumulation. AR. Symp: progressive neurodegeneration, developmental delay, lysosomes with onion skin, cherry red spot on macula, no hepatosplenomegaly |
|
|
Krabbe disease |
Cause: Galactocerebrosidase deficiency -> galactocerebroside accumulation. AR. Symp: Peripheral neuropathy, developmental |
|
|
Metachromatic leukodystrophy |
Cause: Arylsulfatase A deficiency -> cerebroside sulfate accumulation. AR. Symp: Central and peripheral demyelination |
|
|
Hurler syndrome |
Cause: alpha-L-iduronidase deficiency -> heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate accumulation. AR. Symp: gargoylism, developmental delay, corneal clouding, airway obstruction, hepatosplenomegaly |
|
|
Hunter syndrome |
Cause: Iduronate sulfatase deficiency -> heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate accumulation. XR. Symp: mild Hurler+aggressive behavior, no corneal clouding |
|
|
What shingolipidoses are more common among Ashkenazi jews? |
Tay-Sachs, Niemann-Pick, some forms of Gaucher disease. |
|
|
What is lipoprotein lipase and where it can be found? |
Enzyme that degrades TG circulating in chylomicrons and VLDLs. Found on vascular endothelial surface |
|
|
Draw circulation pathways of dietary fat and cholesterol |

|
|
|
What does hormone-sensitive lipase do? |
Degrades TG stored in adipocytes |
|
|
What is LCAT? |
Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase. It catalyzes esterification of 2/3 of plasma cholesterol |
|
|
Statins mechanism of action |
Competitively and reversibly inhibit HMG-CoA reductase |
|
|
What is CETP? |
Cholesterol ester transfer protein, mediates transfer of cholesterol esters to other lipoprotein particles. |
|
|
Regulation of HMG-CoA reductase |
Insulin (+) |
|
|
Where does energy (ATP) come from after a meal? |
Glycolysis and aerobic respiration |
|
|
What hormone is active after a meal and what processes does it contribute to? |
Insulin. Stimulates storage of lipids, glycogen, proteins. |
|
|
Where does energy come from between meals (fasting state)? |
Glycogenolysis (major); hepatic gluconeogenesis, release of FFA from adipose tissue (minor). |
|
|
What hormones are active in a fasting state and what processes do they contribute to? |
Glucagon and epinephrine stimulate use of fuel reserves. |
|
|
How blood glucose level is maintained in 1-3 days of starvation? |
Hepatic glycogenolysis; adipose release of FFA; liver and muscle start to use FFA to save glucose; hepatic gluconeogenesis from peripheral alanine and lactate, from adipose tissue glycerol and propionyl-CoA. |
|
|
What TG components can contribute to gluconeogenesis? |
Odd chain fatty acids -> propionyl-CoA -> succinyl-CoA |
|
|
How fast glycogen reserves deplete? |
After day 1 of starvation |
|
|
What conditions can lead to overproduction of ketone bodies and why? |
In prolonged starvation and diabetic ketoacidosis, oxaloacetate is depleted for gluconeogenesis. In alcoholism, excess NADH shunts oxaloacetate to malate. Both processes cause a buildup of acetyl-CoA, which shunts glucose and FFA toward the production of ketone bodies. |
|
|
What is the source of energy for organism after day 3 of starvation? |
Adipose stores (ketone bodies become the main source of energy for the brain). After these are depleted, vital protein degradation accelerates, leading to organ failure and death. Amount of excess stores determines survival time. |
|
|
Carnitine deficiency |
Inability to transport LCFAs into the mitochondria, resulting in toxic accumulation. Causes weakness, hypotonia, and hypoketotic hypoglycemia. |
|
|
What fruity odor of breath indicates to? |
Fruity odor, or acetone odor, of the breath indicates to high level of ketone bodies. |
|
|
Draw FA synthesis pathway |

|
|
|
Draw FA degradation pathway |

|
|
|
FA oxidation regulation |
Rate-limiting enzyme is carnitine acyltransferase I, (-) by malonyl-CoA |
|
|
FA synthesis regulation |
Rate-limiting enzyme is acetyl-CoA carboxylase, (+) by insulin, citrate; (-) glucagon, palmitoyl-CoA. |
|
|
Cholesterol synthesis regulation |
Rate-limiting enzyme is HMG-CoA reductase, (+) insulin, thyroxine, (-) by cholesterol, glucagon. |
|
|
Von Gierke disease |
Glycogen storage disease type I. Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency. AR. Symp: severe fasting hypoglycemia, ↑↑ glycogen in liver, ↑ blood lactate, hepatomegaly. Treatment: frequent oral glucose/cornstarch; avoidance of fructose and galactose. |
|
|
Pompe disease |
Glycogen storage disease type II. Lysosomal alpha-1,4-glucosidase (acid maltase) defificency. AR. Symp: Cardiomyopathy and systemic findings leading to early death. |
|
|
Cori disease |
Glycogen storage disease type III. Debranching enzyme alpha-1,6-glucosidase deficiency. AR. Milder form of type I with normal blood lactate levels. Gluconeogenesis is intact. |
|
|
McArdle disease |
Glycogen storage disease type V. Skeletal muscle glycogen phosphorylase (myophosphorylase) deficiency. AR. Symp: ↑ glycogen in muscle, but cannot break it down, leading to painful muscle cramps, myoglobinuria (red urine) with strenuous exercise, and arrhythmia from electrolyte abnormalities. |
|
|
Symptoms of ammonia intoxication |
Tremor (asterixis), slurring of speech, somnolence, vomiting, cerebral edema, blurring of vision. |
|
|
Causes of hyperammonemia |
Can be acquired (e.g., liver disease) or hereditary (e.g., urea cycle enzyme deficiencies). |
|
|
Treatment of hyperammonemia |
Limit protein in diet. Benzoate or phenylbutyrate (both of which bind amino acid and lead to excretion) may be given to ↓ ammonia levels. Lactulose to acidify the GI tract and trap NH4+ for excretion. |
|
|
How can excess amount of NH4+ |
Excess NH4+ depletes alpha-KG, leading to inhibition of TCA cycle. |
|
|
N-acetylglutamate deficiency |
Required cofactor for carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I. Absence of N-acetylglutamate → hyperammonemia. Presentation is identical to carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency. However, ↑ ornithine with normal urea cycle enzymes suggests hereditary N-acetylglutamate deficiency. |
|
|
Draw urea cycle |
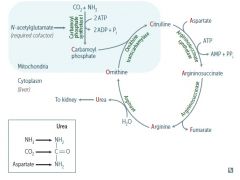
|
|
|
Draw transport of ammonia by glutamate and alanine |
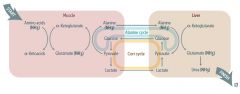
|
|
|
What is the most common urea cycle disorder? |
Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency |
|
|
What happens to excess carbamoyl phosphate in OTC deficiency? |
It is converted to orotic acid (part of pyrimidine synthesis pathway |
|
|
OTC deficiency, findings |
↑ orotic acid in blood and urine, ↓ BUN, symptoms of hyperammonemia. No megaloblastic anemia (vs. orotic aciduria). Often evident in the first few days of life, but may present with late onset. XR. |
|
|
Cause of cystinuria, mode of inheritance, epidemiology. |
Hereditary defect of renal PCT and intestinal amino acid for Cysteine, Ornithine, Lysine, and Arginine (COLA). Excess cystine in the urine can lead to precipitation of hexagonal cystine stones. AR. Common (1:7000). |
|
|
Cistinuria treatment |
Urinary alkalinization (e.g., potassium citrate, acetazolamide) and chelating agents ↑solubility of cystine stones; good hydration. |
|
|
How diagnosis of cistinuria is confirmed? |
Positive urinary cyanide-nitroprusside test (the addition of fresh sodium cyanide formed by sodium nitroprusside to a sample of urine gives rise to a stable red-purple color in the presence of cystine). |
|
|
Different types of homocystinuria and appropriate treatment |
(1) Cystathionine synthase deficiency (treatment: ↓ methionine, ↑ cysteine, ↑ B12 and folate in diet); (2) ↓affinity of cystathionine synthase for pyridoxal phosphate (treatment: ↑↑ B6 and ↑ cysteine in diet); |
|
|
Homocystinuria findings |
↑↑ homocysteine in urine, intellectual disability, osteoporosis, tall stature, kyphosis, lens subluxation (downward and inward), thrombosis, and atherosclerosis (stroke and MI) |
|
|
Draw homocysteine metabolism |

|
|
|
What phenylketones do you know? |
Phenylacetate, phenyllactate, phenylpyruvate |
|
|
PKU symptoms |
Intellectual disability, growth retardation, seizures, fair skin, eczema, musty body odor. Tyrosine becomes essential. Excess phenylketones in urine. Screened for 2-3 days after birth (normal at birth because of maternal enzyme during fetal life) |
|
|
PKU treatment |
↓Phe, ↑Tyr in diet. Avoid the artificial sweetener aspartame, which contains Phe |
|
|
Maternal PKU |
Develops as a result of a lack of proper dietary therapy during pregnancy in women with PKU. Findings in infant: microcephaly, intellectual disability, growth retardation, congenital heart defects |
|
|
Causes of PKU |
(1) phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency, (2) tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency (malignant PKU). AR. Incidence 1:10,000. |
|
|
Alkaptonuria cause |
Homogentisate oxidase deficiency. AR. |
|
|
Alkaptonuria findings |
Benign disease. Dark connective tissue, brown pigmented sclerae, urine turns black on prolonged exposure to air. May have debilitating arthralgias (homogentisic acid is toxic to cartilage). |
|
|
What is the structure of cystine? |
It is made of two cysteines connected by a disulfide bond. |
|
|
Maple syrup urine disease, cause and symptoms |
Blocked degradation of branched aminoacids (Isoleucine, Leucine, Valine) due to ↓α-ketoacid dehydrogenase (B1). Causes ↑α-ketoacids in the blood, especially those of leucine. Causes severe CNS defects, intellectual disability, and death. AR. Urine smells like maple syrup/burnt sugar. |
|
|
Maple syrup urine disease treatment |
Restriction of leucine, isoleucine, and valine in diet, and thiamine supplementation. |
|
|
Phe derivates |

|
|
|
Trp derivates |

|
|
|
His derivates |
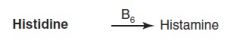
|
|
|
Glutamate derivates |
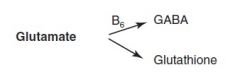
|
|
|
Glycine derivates |

|
|
|
Arginine derivates |

|

