![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
normal lysosome function
|
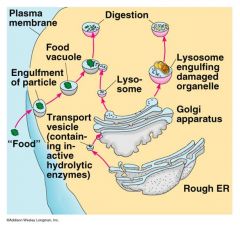
turnover; breakdown molecules to recycle and use again
bud off golgi; target damaged organelles and fuses with organelle; mixes with contents and digestion occurs |
|
|
how are hydrolases activated in a lysosome
|
drop in pH; stimulated by an ATP-dependent proton pump
|
|
|
how do hydrolases get into lysozyme lumen in the first place?
|
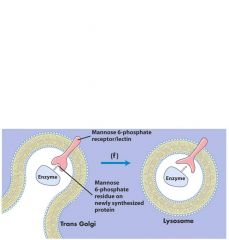
Lyosomal enzymes possess a mannose-6-phosphate residue that is recognized by a specific luminal receptor (lectin)
|
|
|
Sphingolipids; first fatty acid added to serine in synthesis
|
palmitate
|
|
|
Sphingolipid nomenclature
|
‘G’ = ganglioside
Second letter indicates number of NANA molecules: M=1, D=2, T=3, Q=4 Subscript number = 5 - #neutral sugars |
|
|
Gaucher's disease; accumulation of glucocerebrosides due to a deficiency in B-glucocerebrosidase; causes hepatosplenomegaly
|
|
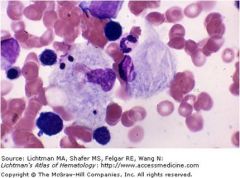
|
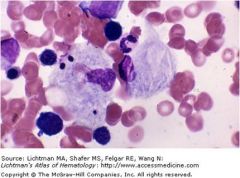
Gaucher cells; macrophages that look like crumbled tissue paper; accumulation of glucocerebroside due to a deficiency in B-glucocerebrosidase
|
|
|
why would enzymes w exposed mannose groups be used in tx of gaucher's diseases
|
macrophage mannose receptor; macrophages have mannose receptors which play a role in immune response; recognize mannose groups present on bacteria, viruses and fungi; this trick is exploted into tricking the macrophage into taking up the recombinant enzyme; by putting a high mannose chain on it the macrophage thinks its a bug; brings it right into the lysosome which deposits active enzyme cargo BUT its >200K year; large cost to the therapy
|
|
|
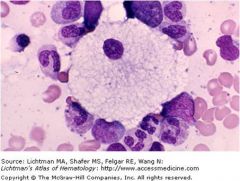
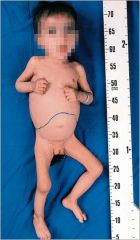
Niemann Pick dz; deficient sphingomyelinase = sphingomyelin accumulates
progressive neurodegeneration hepatosplenomegaly, cherry red spot on macula, foam cells |
|
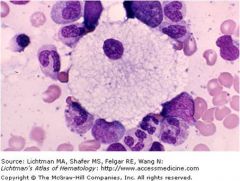
|
Foam cell in Niemann Pick dz; no sphingomyelinase = sphingomyelin accumulates
|
|
|
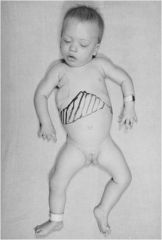
GM1-Gangliosidosis (Pseudohurler syndrome - used to think it was a mucopolysaccharidoses);
|
|
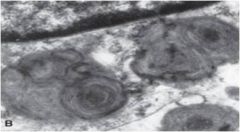
Tay Sachs
|
Hexoaminidase A deficiency, GM2 ganglioside builds up = motor weakness, hypotonia, massive startle response (hyperacusis). Retinal cherry-red spots. Blindness, spasticity, dysphagia, seizures. Macrocephaly by 18 months. Demented and decerebrate by 3 years. Death by age 5.
→Sandhoff may co-present with visceromegaly, but not Tay-Sachs |
|
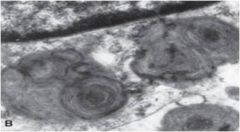
|
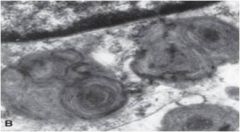
Whorled lysosomes in Tay-Sachs or Sandhoff
|
|
|
Tay Sachs vs Sandhoff
|
HexA deficiency = tay sachs
Hex A + B deficiency = Sandhoff Both present same way w/ cherry red spot, but additional visceromegaly in Sandhoff bc globosides are nonneural tissue |
|
|
Krabbe Disease
|
White matter destruction via galactocerebrosidase deficiency = accumulation of galatocerebrosides; demyelination results in symptoms of Irritability, crying, vomiting, hyperesthesia, peripheral neuropathy within 6 months. Flexed upper and extended lower extremities, seizures. Blindness, loss of bulbar functions. Death from hyperpyrexia, respiratory complications or aspiration by 2 years.
|
|
|
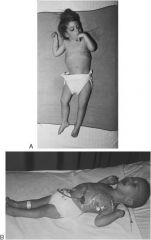
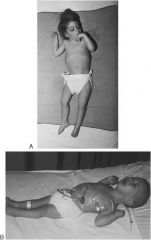
Krabbe disease; symptoms of leukodystrophies; no galactocerebrosidase = accumulation of galactocerebrosides = demyelination
note spastic posture indicative of leukodystrophies |
|
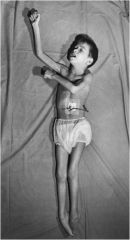
Metachromatic leukodystrophy
|
deficieincy in arylsulfatase = accumulation of sulfatides = demyelination = leukodystrophy spastic/hyotonia presentation due to peripheral neuropathies
|
|
|
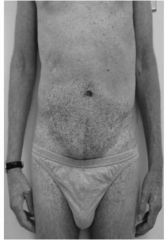
Angiokeratoma in Fabrys disease
Symptoms appear during first decade. Severe pain in the extremities (acroparesthesia) lasting hours to days. Characteristic angiokeratomas appear on lower part of abdomen, buttocks and scrotum in majority of patients. Renal, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease (e.g. hearing loss, strokes). |
|
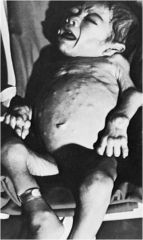
Farbers Disease
|
Lipogranulomas throughout body
ceramide accumulation due to ceramidase deficiency |
|
|
Mucopolysaccharidoses
|
Defieincy of enzymes required for glycosaminoglycan (mucopolysaccharide) degradation
ALL AR inheritance except Hunter syndrome (XR) |
|
|
unbranched homopolysccharide example
|
cellulose
|
|
|
branched homopolysaccharide
|
glycogen
|
|
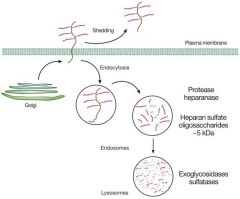
Maintnenace of the ECM requires constant turnoff; failure of the enzymes to maintain this = accumulation = mucopolysaccharidoses
|
|
|
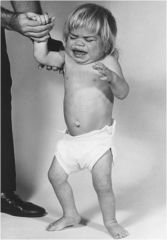
|
Hurler phenotype; corneal clouding and COARSE facial features
"Hunters see clear" |
|
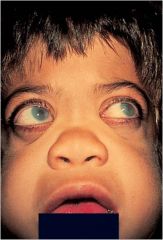
Hurler-Scheie Spectrum
|
Mild (Scheie) to severe (Hurler); screen for urine GAGs looking for molecule at the non-reducing end
|
|
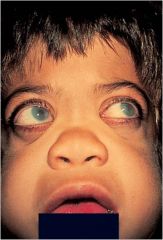
Hurler Syndrome
|
Deficiency in alpha-L-iudronidase leads to accumulatoin of heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate = mucopolysaccharidoses
Developmental delay, gargoylism, airway obstruction, corneal clouding, hepatosplenomegaly |
|
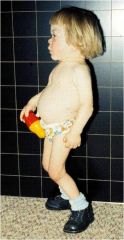
Mucolipidoses
|
Deficiency of n-acetylglucosamine phosphotransferase; hurler like phenotype; death in first decade of life
|
|
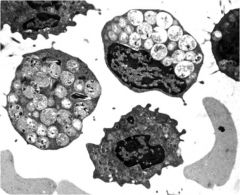
|
Prominent vacuole like inclucions in peripheral lymphocytes in I-cell patients
M6P = zip code to lysosomal hydrolases can't get into lysosome in golgi; the hydrolases get secreted into secretory vesicles = elevated SERUM hydrolases |
|
|
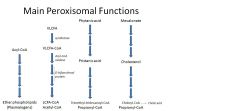
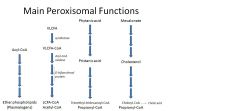
Peroxisomes
|
anaolic and catabolic functions; mainly involved in lipid metabolism - B-oxidize VLCFA (everything else in mitochondria)
synthesize plasmalogens (parts of cell membranes and myelin); lack their own DNA, are encoded by the nuclear genome |
|
|
peroxisome biogenesis
|
like mitochondria but lack their own dna; import all their own enzymes in contrast to mitochondria
|
|
|
|
|
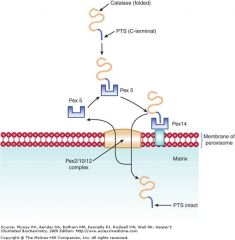
Peroxins (Pex)
|
Necessary for importing enzymes into peroxisomes;
|
|
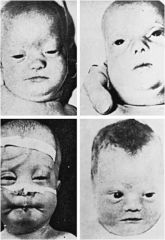
Zellweger syndrome
|
perixosomal biogenesis disease; VLCFA accumulation; analyze blood cells for plasmologens
impaired neural migration, delayed myelination hypotonia & seizures deafness ocular abnormalities (cataracts & retinitis pigmentosa leading to blindness) |
|
|
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
|
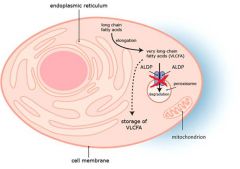
deficient ALDP = peroxisomal VLCFA transporter = accumulation of VLCFAs in brain
dx = elevated plasma vlcfa in presence of normal plasmalogens (lorenzos oil normalizes plasma VLCFAs but has no curative or preventive effects) |
|
|
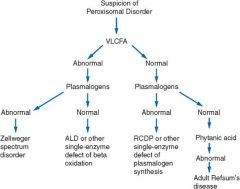
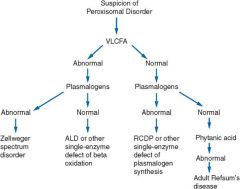
Diagnostic evaluation of peroxisomal disorders
|
|
|
adult refsums disease
|
normal plasmalogens -> accumulation of phytanic acid
|

