![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Explain what a GTPase is and it's cycle?
|
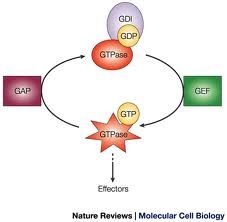
|
|
|
What are GEF's? What do they do?
|
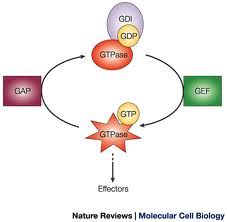
Guanosine Exchange Factors
completely exchange GDP for GTP |
|
|
What are GAP's, what do they do?
|
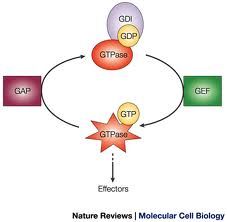
GTPase Activating Protein
|
|
|
Protein synthesis elongation begins when 70S initiation complex is ______________.
|
Protein synthesis elongation begins when 70S initiation complex is completed.
|
|
|
Protein synthesis elongation begins when 70S ___________ ___________ is completed.
|
Protein synthesis elongation begins when 70S initiation complex is completed.
|
|
|
Protein synthesis ____________ begins when 70S initiation complex is completed.
|
Protein synthesis elongation begins when 70S initiation complex is completed.
|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
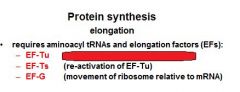
Which protein synthesis EF's are GTPase's?
|
EF-Tu and EF-G
|
|
|
What protein synthesis EF is a GEF?
|
EF-Ts
|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
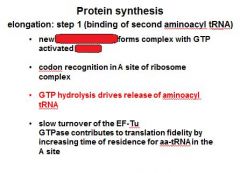
How does the proofreading in the A site of the ribosome work?
|
The slow GTP hydrolysis on EF-Tu while in the site allows for time to proofread.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
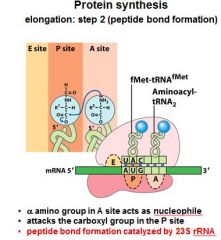
|
|
|
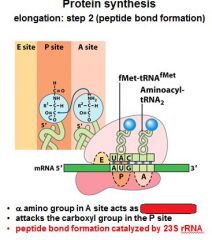
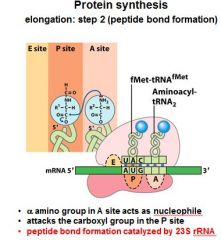
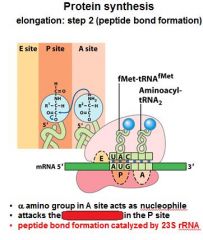
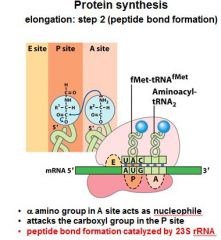
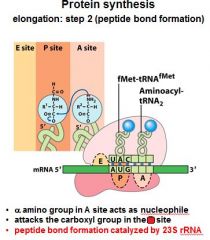
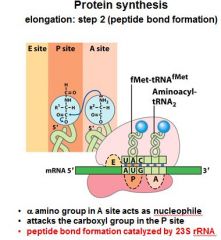
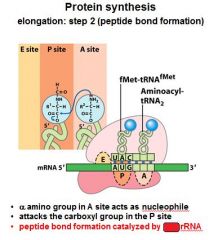
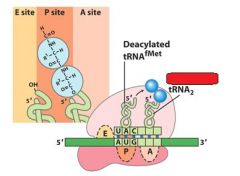
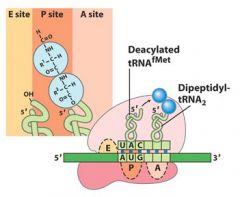
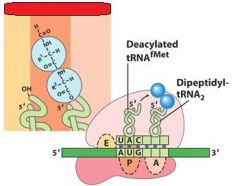
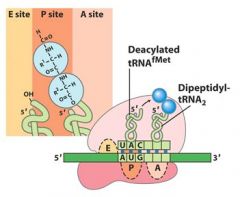
What do you notice in the A,P, and E sites after the formation of the peptide bond between the A and P sites?
|
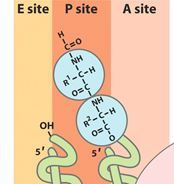
That the tRNA's have shifted and the one in the P site is now partially in the E site, and the one in the A site is now partially in the P site.
|
|
|
After the peptide bond formation between the __ and __ sites, there is an uncharged tRNA left in the __ site.
|
After the peptide bond formation between the P and A sites, there is an uncharged tRNA left in the P site.
|
|
|
After the peptide bond formation between the P and A sites, there is an ____________ tRNA left in the P site.
|
After the peptide bond formation between the P and A sites, there is an uncharged tRNA left in the P site.
|
|
|
After the ______________ _____________ formation between the P and A sites, there is an uncharged tRNA left in the P site.
|
After the peptide bond formation between the P and A sites, there is an uncharged tRNA left in the P site.
|
|
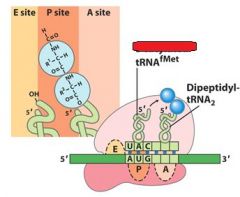
|
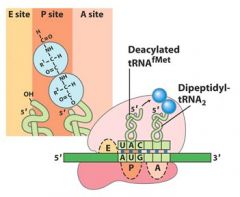
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|

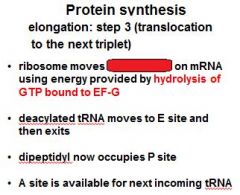
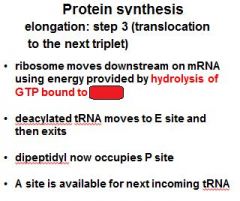
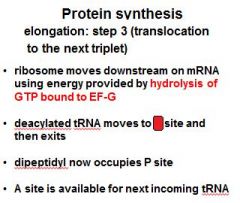
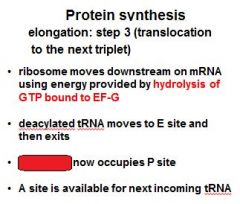
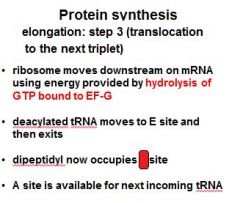
Three steps of protein synthesis elongation:
1) binding of second aminoacyl tRNA 2) peptide bond formation 3) ????????????? |

Three steps of protein synthesis elongation:
1) binding of second aminoacyl tRNA 2) peptide bond formation 3) translocation to the next triplet |
|
|
Three steps of protein synthesis elongation:
1) binding of second aminoacyl tRNA 2) ?????????? 3) translocation to the next triplet |
Three steps of protein synthesis elongation:
1) binding of second aminoacyl tRNA 2) peptide bond formation 3) translocation to the next triplet |
|
|
Three steps of protein synthesis elongation:
1) ?????? 2) peptide bond formation 3) translocation to the next triplet |
Three steps of protein synthesis elongation:
1) binding of second aminoacyl tRNA 2) peptide bond formation 3) translocation to the next triplet |
|
|
What are the three steps of protein synthesis elongation:
|
Three steps of protein synthesis elongation:
1) binding of second aminoacyl tRNA 2) peptide bond formation 3) translocation to the next triplet |
|
|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|
|
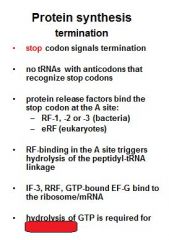
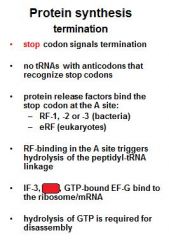
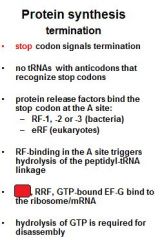
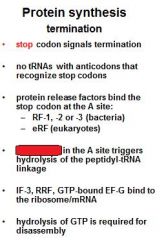
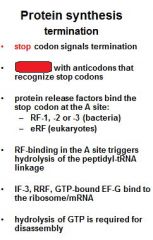
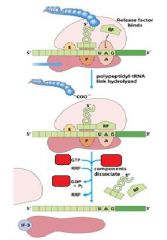
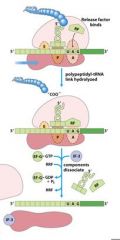
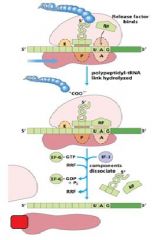
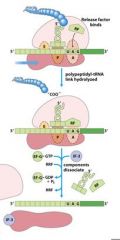
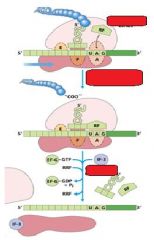
Which release factors associate with the stop codons?
|
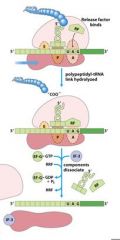
RF1 and RF3
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
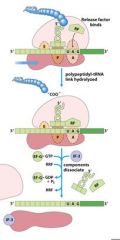
|
|
|
The energy released from _____-GTP blows up the ribosome complex.
|
EFG
|
|
|
What is the RRF?
|
ribosomal recycling factor
|
|
|
___________________ inhibits protein synthesis by binding in the A site and causing the premature release of the polypeptide.
|
Puromycin inhibits protein synthesis by binding in the A site and causing the premature release of the polypeptide.
|
|
|
Puromycin inhibits __________________ by binding in the A site and causing the premature release of the polypeptide.
|
Puromycin inhibits protein synthesis by binding in the A site and causing the premature release of the polypeptide.
|
|
|
Puromycin inhibits protein synthesis by binding in the __ site and causing the premature release of the polypeptide.
|
Puromycin inhibits protein synthesis by binding in the A site and causing the premature release of the polypeptide.
|
|
|
Puromycin inhibits protein synthesis by binding in the A site and causing the _______________ release of the polypeptide.
|
Puromycin inhibits protein synthesis by binding in the A site and causing the premature release of the polypeptide.
|
|
|
Puromycin inhibits protein synthesis by binding in the A site and causing the premature release of the ____________.
|
Puromycin inhibits protein synthesis by binding in the A site and causing the premature release of the polypeptide.
|

