![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
aldose
|
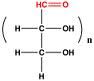
An aldose is a monosaccharide (a simple sugar) that contains only one aldehyde (-CH=O) group per molecule.
|
|
|
ketose
|
A ketose is a sugar containing one ketone group per molecule.
|
|
|
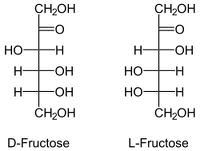
D and L designation in monosaccharides are determined by?
|
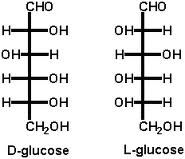
The configuration about the chiral center most distant from the carbonyl carbon.
|
|
|
The formation of cyclic monosaccharides by the reaction between alcohol and aldehyde
|
hemiacetal
|
|
|
furanoses
|
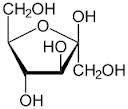
5 member ring compounds
|
|
|
what is a carbohydrate anomer?
|
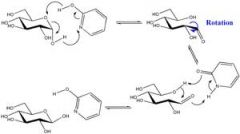
isomeric forms of monosaccharides that differ only in their configuration about the hemiacetal or hemiketal carbon
|
|
|
The formation of cyclic monosaccharides by the reaction between alcohol and ketone forms a ............?
|
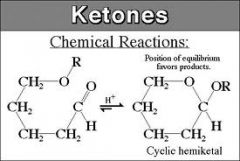
hemiketal
|
|
|
identify the alpha anomer of a cyclic sugar?
|
the OH goes down on the anomeric carbon
|
|
|
what defines the beta anomer of glucose?
|
when the OH group goes up on the anomeric carbon
|
|
|
what is the anomeric carbon?
|
the carbonyl carbon when the carbohydrate is in ring form.
|
|
|
mutarotation
|
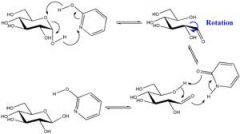
the alpha and beta anomers interconvert in aqueous solution
|
|
|
reducing sugars
|
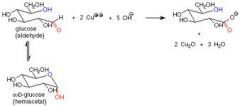
sugar rings with no other molecule attached to the anomeric carbon
|
|
|
what two carbohydrates contribute to the starch structure?
|
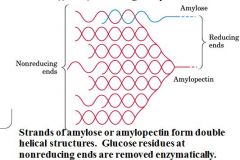
|
|
|
whate are the monomer(s) of glycogen? what is the linkage? is it branched?
|
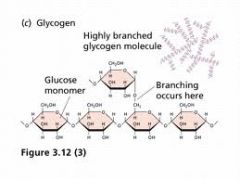
the monomer is glucose with alpha1-4 and alpha1-6 linkage, branched
|
|
|
Dextrans are _______ and ______ polysaccharides.
|
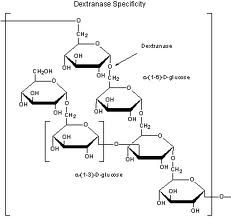
bacterial and yeast
note (alpha 1-6 linkage and alpa 1-3 linkage) |
|
|
Draw cyclic beta-D-glucose?
|
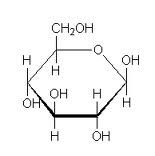
|
|
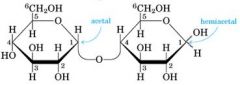
which monomer (if any) has the reducing end?
|

the right monomer of glucose
|
|
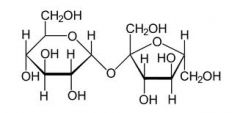
what is this molecule?
|
sucrose
|
|
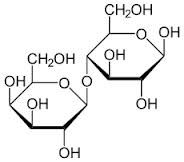
what is this molecule?
|
lactose which is Gal and Glc
|
|
|
Draw linear D-glucose
|
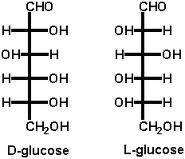
|
|
|
draw linear D-fructose?
|
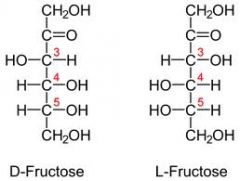
|
|
|
draw D-gluconate
|
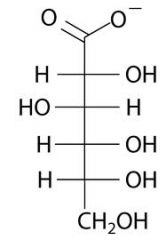
|
|
|
draw D-gluconate
|
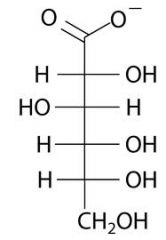
|
|
|
what are the monomers of lactose? and the linkage?
|
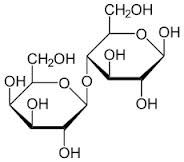
Gal beta1-4 Glc
|
|
|
what are the monomers of sucrose? and the linkage?
|
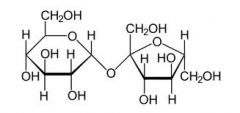
Fru 2beta-alpha1 Glc Glc 1alpha-beta2 Fru
|
|
|
what are prostaglandins?
|
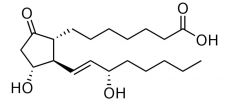
A prostaglandin is any member of a group of lipid compounds that are derived enzymatically from fatty acids and have important functions in the animal body. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring
|
|
|
basic triacylglycerol structure?
|
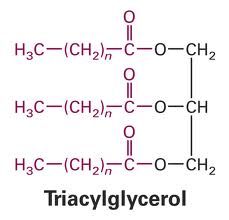
|
|
|
draw a hemiacetal reaction?
|
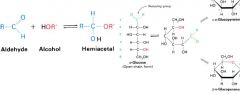
|
|
|
draw a hemiketal reaction?
|
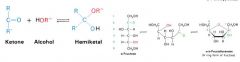
|
|
|
Sugars as reducing agents!!!
|
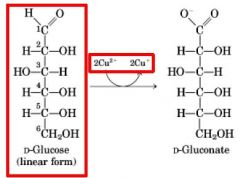
|
|
|
beta sugars have the OH group _____ from the anomeric carbon?
|
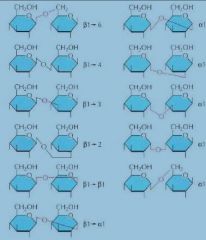
|
|
|
alpha sugars have the OH group _______ on the anomeric carbon
|
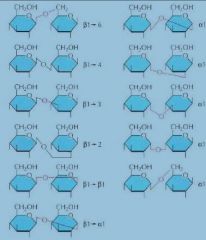
down
|
|
|
waxes are ???????
|
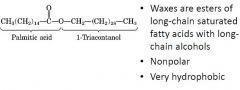
|
|
|
Glycerophospholipid general structure?
|
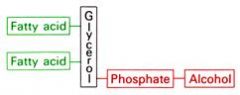
|
|
|
Shingolipid basic structure?
|
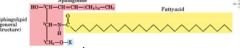
the blue x is a charged head group
|
|
|
cholesterol basic structure?
|
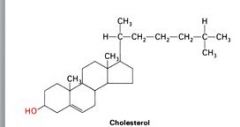
|
|
|
Name the three subclasses of sphingolipids?
|
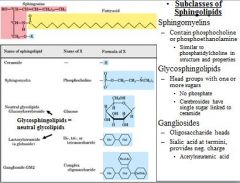
|
|
|
degradation of phospolipids and sphingolipids?
|
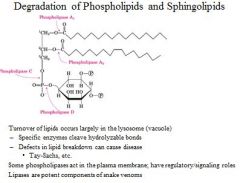
|
|
|
phospolipid general structure?
|
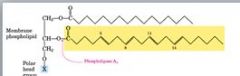
|
|
|
function of:
prostoglandins thromboxanes leukotrienes |

|
|
|
Arachidonic acid structure and pathway?
|
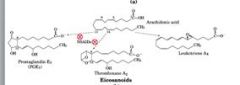
|
|
|
Cholesterol basic structure?
|

|
|
|
Most important sterol?
|
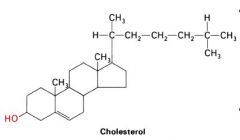
|
|
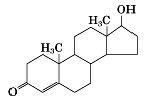
|
testosterone structure
|
|
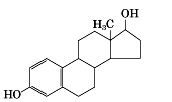
|
estradiol structure
|
|
|
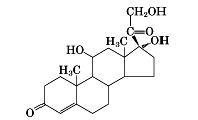
cortisol structure
|
|
|
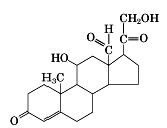
aldosterone structure
|
|
|
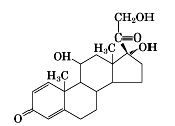
prednisolone structure
|
|
|
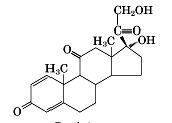
prednisone structure
|
|
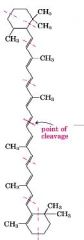
what is this structure? it is used to produce?
|
b-carotene structure breaks down into vitamin A/retinol
|
|
|
beta-carotene breaks down into _________?
|
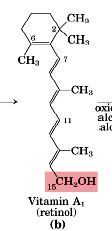
vitamin A/retinol
|
|
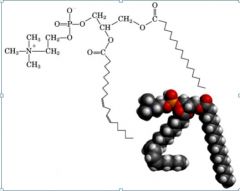
|
phosphotidylcholine
|
|
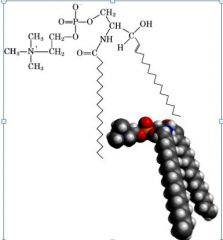
|
sphingomyelin
|
|
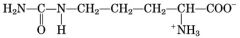
|
citrulline
|
|
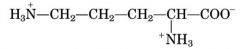
|
ornithine
|
|
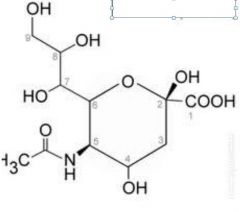
|
sialic acid
|
|
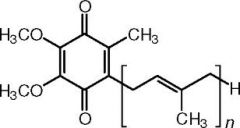
|
ubiquinone and isoprene unit
|
|
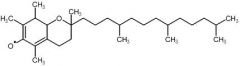
what is this molecule?
|
vitamin E
|
|
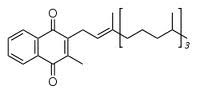
|
vitamin K
|
|
|
what is the phospholipid basic structure?
|
xxxx
|

