![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Allosteric proteins
|
contain distinct regulatory sites and have multiple functioning sites and display cooperativity.
|
|
|
Examples of covalent modification include
|
phosphorylation. acetylation. ubiquination.
|
|
|
The most common strategy(ies) for enzymatic regulation are:
|
multiple enzyme forms, allosteric control, reversible covalent modification, and proteolytic activation
|
|
|
An allosteric interaction between a ligand and a protein is one in which:
|
the binding of a molecule to a binding site affects the binding properties of another site on the protein.
|
|
|
In hemoglobin, the transition from T state to R state (low to high affinity) is triggered by:
|
oxygen binding.
|
|
|
The fundamental cause of sickle-cell disease is a change in the structure of:
|
hemoglobin.
|
|
|
A small molecule that decreases the activity of an enzyme by binding to a site other than the catalytic site is termed a(n):
|
allosteric inhibitor.
|
|
|
Allosteric enzymes:
|
usually have more than one polypeptide chain.
|
|
|
How do a nucleotide and a nucleoside differ?
|
A nucleotide is a nucleoside with a phosphate ester linked at the sugar 5' residue.
|
|
|
In the trinucleotide pApCpG, where is the free OH group?
|
at the 3' end
|
|
|
The feature(s) of DNA deduced by Watson and Crick included
|
two antiparallel polynucleotide chains coiled in a helix around a common axis. the pyrimidine and purine bases lie on the inside of the helix. the bases are nearly perpendicular to the axis.
|
|
|
A major component of RNA but not of DNA is:
|
uracil.
|
|
|
The difference between a ribonucleotide and a deoxyribonucleotide is:
|
deoxy- has an –H instead of an –OH at C-2.
|
|
|
The phosphodiester bonds that link adjacent nucleotides in both RNA and DNA:
|
join the 3' hydroxyl of one nucleotide to the 5' hydroxyl of the next.
|
|
|
By definition, the 5' end of a DNA or RNA strand:
|
has no nucleotide attached to the 5' hydroxyl.
|
|
|
The DNA oligonucleotide abbreviated pATCGAC:
|
has 6 phosphate groups.
|
|
|
In a double-stranded nucleic acid, cytosine typically base-pairs with:
|
guanine.
|
|
|
For the oligoribonucleotide pACGUAC:
|
the nucleotide at the 5' end has a phosphate on its 5' hydroxyl.
|
|
|
The Watson-Crick base pairing scheme for an A–T base pair includes:
|
a hydrogen bond between a keto oxygen and an extracyclic amino group.
a hydrogen bond between two ring nitrogen atoms. |
|
|
In the Watson-Crick structure of DNA, the:
|
the two strands are antiparallel.
|
|
|
In the Watson-Crick model of DNA structure:
|
the distance between two adjacent bases in one strand is about 3.4 Å.
|
|
|
In the Watson-Crick model of DNA structure (now called B-form DNA):
|
the bases occupy the interior of the helix.
|
|
|
In double-stranded DNA:
|
the two strands have complementary sequences.
|
|
|
Adenine, Purine
|
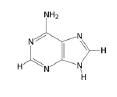
What is the name of this nucleotide
|
|
|
Guanine, Purine
|
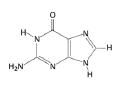
What is the name of this nucleotide?
|
|
|
Cytosine, Pyrimidine
|
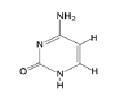
What is the name of this nucleotide
|
|
|
Uracil, Pyrimidine
|
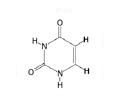
What is the name of this nucleotide
|
|
|
Thymine, Pyrimidine
|
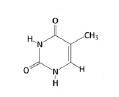
What is the name of this nucleotide?
|
|
|
A form, B form, Z form
|
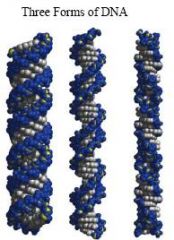
name the three froms of DNA
|
|
|
Name the forces in DNA
|
H bonds between bases, hydrophobic bases in the middle, phosphates near water, stacking of bases (Van der Waals)
|
|
|
Functions of Nucleic Acids include:
|
Information molecules (DNA, RNA), Energy Metabolism (ATP), Anabolism (UDP-Glucose),
|
|
|
Ribose
|
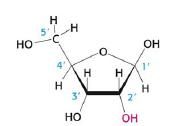
This is:
|
|
|
Deoxyribose
|
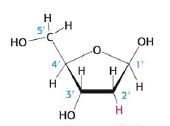
This is:
|

