![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Biomolecule
|
molecules synthesized by living organisms
|
|
|
macromolecule
|
polymers of certain biomolecules
|
|
|
enzyme
|
biomolecular catalyst
|
|
|
metabolism
|
the sum total of all reactions in a living organism
|
|
|
homeostasis
|
the ability of living organisms to regulate their metabolism regardless of their internal/external environments
|
|
|
polypeptide
|
polymer of amino acids
|
|
|
peptide
|
a polymer of up to 50 amino acids
|
|
|
protein
|
a polymer of more than 50 amino acids
|
|
|
oligopeptide
|
a polymer of up to 50 amino acids
|
|
|
peptide bond
|
amide linkage between adjacent amino acids
|
|
|
standard amino acids
|
20 amino acids commonly found in polypeptides - consist of R groups, an amine group, and a carboxyl group attached to an alpha carbon
|
|
|
sugar
|
basic unit of a carb
|
|
|
monosaccharide
|
simple sugar consisting of a single sugar molecule
|
|
|
polysaccharide
|
polymer of sugar molecules containing more than 20 monosaccharide units
|
|
|
glucose
|
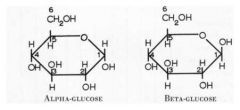
6 carbon aldohexose sugar
|
|
|
cellulose
|
a polymer of glucose with beta 1,4 glycosidic bonds
|
|
|
nucleotide
|
5 carbon sugar
nitrogenous base phosphate groups |
|
|
purine
|
bicyclic nitrogenous base
|
|
|
pyrimidine
|
monocyclic nitrogenous base
|
|
|
nucleic acid
|
polymer of nucleotides linked together by phosphodiester bonds
|
|
|
transcription factor
|
a class of proteins that bind to specific regulatory DNA sequences to regulate gene expression
|
|
|
response element
|
specific regulatory DNA sequence that transcriptions factors bind
|
|
|
signal molecule
|
molecule that binds to a receptor protein
|
|
|
RNA interference
|
mediated by siRNA to function as an antiviral defense
|
|
|
nucleophile
|
atom or group with an unshared pair of electrons that is involved in the displacement reaction
|
|
|
electrophile
|
an electron-deficient species
|
|
|
Leaving group
|
the outgoing nucleophile that leaves with its electron pair
|
|
|
anhydride
|
a molecule with two carbonyl groups linked through an oxygen atom
|
|
|
energy
|
the ability to do work
|
|
|
coenzyme
|
small molecules that function in association with enzymes as carriers of small molecular groups
|
|
|
glycolysis
|
a 10-reaction pathway that degrades glucose to two pyruvates to generate energy
|
|
|
systems biology
|
study of living organisms as integrated systems
|
|
|
reductionism
|
the belief that complex processes can be understood by examining their simpler parts
|
|
|
Salt bridges
|
ionic interactions between positively charged amino acid side groups
|
|
|
Solvation spheres
|
shells of water molecules formed by water around solutes
|
|
|
Amphipathic/amphiphilic
|
contains hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts (polar and nonpolar)
|
|
|
Crenation vs hemolysis
|
crenation - shrinking that results from hypertonic solution. Shriveled in plant cells, plasmolyzed in plant
hemolysis - swelling that may cause bursting from hypotonic solution. lysed in animals, turgid in plants |
|
|
Buffers
|
resist pH changes with the addition of H+ or OH- via Le Chatlier's Principle
|
|
|
Acidosis vs alkalosis
|
changes in pH of blood
Acidosis is below 7.35 Alkalosis is above 7.45 |
|
|
Micelle
|
formed when amphipathic molecules are mixed with water with the polar surface exposed to water and the nonpolar surface internalized
|
|
|
State functions
|
Traits that are independent of the state path
|
|
|
Coupling
|
Pairing of a non-spontaneous reaction with a spontaneous one to give a net negative Gibbs
For example the hydrolysis of ATP is coupled to bind glucose to phosphate |
|
|
Isoelectric point
|
pH at which charge is 0
|
|
|
Relationship between pH vs pKa and acid vs conjugate base concentration
|
When pH = pKa, concentration of acid is equivalent to conjugate base
|
|
|
MOTIFS
|
Supersecondary structure
|
|
|
Oligomer vs Protomer
|
Oligomers are polymers of protomers (polypeptide units)
|
|
|
Allostery
|
Regulation of protein binding by the binding of effector to a protein's allosteric site
|
|
|
Modulation
|
altering of a protein's shape as a result of allosteric regulation
|
|
|
IUP
|
Intrinsic Unstructured Proteins - lack of tertiary structure in isolated polypeptide form
|
|
|
Natively Unfolded Proteins
|
Proteins that have no ordered structure under physiological conditions
|
|
|
Taut vs Relaxed
|
Taut state is tense. Favored with low pH, high CO2 and high BPG concentrations. Increases affinity for Oxygen (causes cooperative binding)
|

