![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Notes
- Digestion tips |
- food has to enter somehow, digested, processed, exited. Also helps w diagrams too
|
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Description |
- defined by presence of 5 features of development
1) Dorsal, hollow Nerve Cord 2) Notochord (cellular hydroskeleton, prevents distortion of body) 3) paired Pharyngeal Pouches 4) Gland or Tissue that concentrates iodine 5) Post Anal Tail |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Subphyla |
- there are 3, we only looked at 1
- Subphylum Vertebrata |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Perch - External Anatomy |
- Fusiform body shape (streamlined when swimming)
- Scales (note direction, overlapping, decreases resistance) - 2 openings on Ventral surface 1) Anus (larger/anterior) for waste 2) Urogenital (smaller/posterior) |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Perch - Lateral Surface |
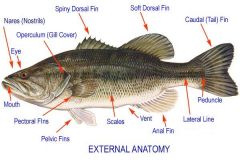
- Operculum: protection, covers gills
- Lateral LIne system: modified scales for sensory - divided in 3 parts 1) Head: terminal mouth: 4 nasal apertures - 2 anterior - 2 posterior 2) Trunk - post to opculum, 2 pectoral fins - post and ventral Pelvic Fins 3) Tail - caudal fin |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Perch - detailed lateral diagram |
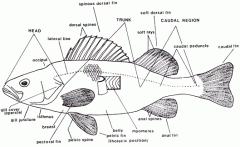
|
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Perch - Internal Anatomy |
- Skeletal muscles divided in two: Axial & Appendicular
- Muscle system has "W" called Myomeres - Myomeres separated by Myosepta - Horizontal Septum divides dorsal & ventral myomeres |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Perch - Digestive |
> Mouth, ends at Cloaca or external environment via Anus
>digestive tract divided into Oral Cavity (mouth), pharynx (throat), esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine >accessory organs associated w/ tract: teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder - herbivores need bacteria and protozoa to break down cellulose |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Mammal Teeth |
- Molars: flat surface for crushing
- Premolars: shearing/cutting - Incisors: chisel shaped, biting - Canines: pointed teeth (seen in carnivores) |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Perch - Internal Features |
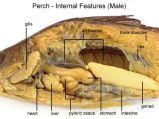
- esophagus: short tube leads from oropharynx to stomach
- Stomach: U-shaped tube, has Pyloric Caeca (finger like tubes) surrounding to aid in digestion - Intestine: starts at stomach, directly to anus - LIver: anterior (front of stomach) - Pancreas: along ventral portion of intestine - Spleen: post dorsal to stomach |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Perch - Photo guide |

|
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Perch - Photo Guide 2 |
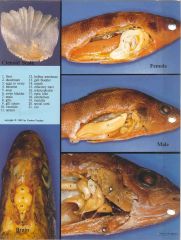
|
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Perch - Osmoregulatory |
2 approaches for osmoregulation:
1) Osmoconformers: do not adjust/isosmotic 2) Osmoregulators: not isosmotic and regulate their internal solute concentration (perch is one) - Kidneys lie dorsal to swim bladder - two small ducts connect to form ureter - Ureter and gonoduct empty via urogenital opening - Urinary bladder, separate sac in males, incorporated in oviducts of females - bladder small in perch, urine removed asap. |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Perch - Reproductive |
- Testes (males): pair of white long bodies below air bladder
- Ovaries (females): lie between intestine & air bladder - Egg exits via Urogenital opening, behind anus |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Perch - Repiratory |
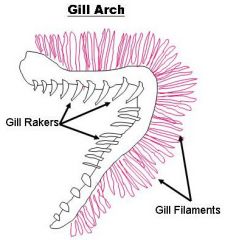
- Gills (behind operculum) attached to ea four pairs of Branchial Arches
- Gill Rakers are on ant surface of Gills - Perch has 2 sets of filaments (and/post) - Counter Current System: blood flow is opposite of water over the gills > 2 line highway, blood goes one way, O2 enriched water goes other way |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Perch - Circulatory System |
- Vertebrates have a closed circulatory system
> heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, and blood - Perch has low pressure single type system - Transverse septum (membrane) separates Pericardial & abdominal cavities. - fish heart (post to ant, in blood flow direction) 1) Sinus venosus: recv's blood from cardinal veins) 2) Atrium (thicker than Sinus Venosus) 3) Ventricle (thick muscular structure, valve prevents backflow) 4) Bulbus Arteriosus (enlarged portion of Ventral Aorta> how blood flows from heart to gills) |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Rat |
all mammals: have hair & mammary glands
- Rat - Tetrapod, Digitgrade (walks on toes) - has scales on tail & has claws |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Rat: Anatomy |
4 regions
1) Head - External Nares on nose and eyes protected by Upper & Lower eyelids - Pinna: external ear fold, directs sound into ear - Vibrisse: sensory hairs 2) Neck 3) trunk (ant thorax) & post abdomen - treats or nipples: evident on ventral side in females - female has 3 openings: urethral opening (ant), Vaginal orifice (just below), Anus posterior - Male has: urethra, urogenital tract in penis, Scrotum which has testes 4) Tail |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Rat - Internal Anatomy |
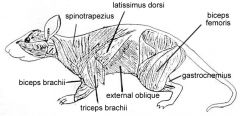
- External Oblique: outer layer of body wall
- Internal Oblique: just beneath external oblique - Transverse oblique: 3rd layer and innermost (EIT) - Rectus Abdominus: muscle running ant-post along midventral line - Latissiums Doris: fan shaped tissue runs from arm to midventral line over ribs - Appendicular muscles: triceps, biceps, |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Rat - Digestive System - Oral Cavity |
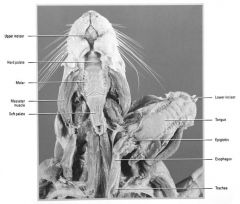
Salivary Glands:
- Parotid Gland (beneath ear) - Submaxilary glands (ventral to parotids), inseparable from Sublingual Glands - Extraorbital Lacrimal Gland forms tears Oral Cavity - large incisor teeth, molars, tongue, hard palate - DOES NOT HAVE: canines or premolars |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
The Rat - Digestive System Abdominal Cavity - Membranes |
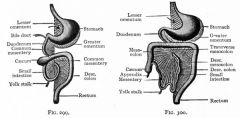
Abdominal & Thoracic Cavity separated by Diaphragm
- Organs or viscera, suspended by Coelom - Ab cavity & viscera covered by membrane Peritoneum Membranes: 1) Mesentery Proper: peritoneal membrane extends from dorsal body wall to Viscera 2) Falciform Ligament: tissue extends from Ventral Body wall / diaphragm to Liver 3) Parietal Peritoneum: Shiny membrane (lines body wall of abdominal cavity) 4) Visceral Peritoneum - shiny membrane (covers viscera) 5) Greater Omentum - Extends from greater curvature of stomach to spleen 6) Lesser Omentum - Extends from lesser curvature of stomach to liver |
|
|
Digestive System
The Rat - Digestive System - Passages & Stomach portions |
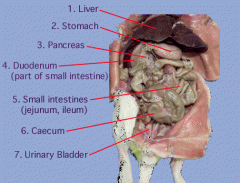
- food passes mouth down to esophagus to stomach
- Stomach has 3 areas 1) Cardia Portion (entrance from esophagus) 2) Fundic Portion (large middle area) 3) Pyloric Portion (constricted posterior end) - Stomach opens into Deudenum through Pyloric Sphincter - Rugae are folds in stomach (allow for expansion) |
|
|
Digestive System
The Rat - Digestive System - Small & Large Intestine Areas (3 & 4) |
Small:
1) Duodenum: stomach empties into here, first section 2) Jejunum: middle section 3) Ileum (final section) - Pancreas straddles small intestine and if you cut open small intestine you would see Villi Large Intestine: 1) Caecum (blind sac near ileum) 2) Ascending COlon 3) Transverse Colon 4) Descending Colon |
|
|
Digestive System
The Rat - Osmoregulatory |
- Ureter exits kidney at depression - Hilus
- Ureter carries urine into Urinary Bladder - Urethra, ducts that lead from the bladder to exterior - Male, urethra travels through penis |
|
|
Digestive System
The Rat - Reproductive System Male |
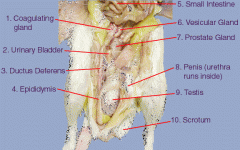
- Male has scrotum: sac of skin, resides externally
- Inside are Testes - Epididymis, C-shaped around testes Epididymis has 3 regions 1) Caput Epididymis (head) 2) Corpus Epididymis (mid) 3) Caudal Epididymis (tail) - Sperm cells travel through epididymis into Vas Deferens, which runs to Urethra, inside penis - Prostate glands are on either side of bladder. - Vesicular & Coagulating glands (associated w/ bladder) secrete seminal fluid, which carries sperm |
|
|
Digestive System
The Rat - Reproductive System Female |
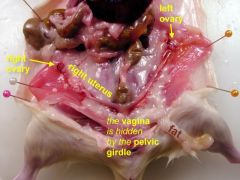
- has pair of ovaries (post to kidneys)
- small highly coiled Oviducts, lead from ovaries to uterus - Left and right Cornua (horns) of uterus unite to form Vagina |
|
|
Digestive System
The Rat - Respiratory System |
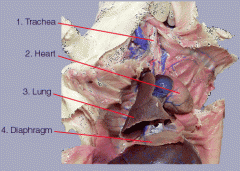
- Thoracic Cavity contains heart & lungs
- Parietal pleura is membrane lining thoracic cavity - Visceral Pleura lines lungs - 1 lobe for left lung, 4 lobes for right lung - Trachea> branches into Bronchus > leads to Bronchioles (in lungs) |
|
|
Digestive System
The Rat - Circulatory |
- High pressure Double Circulatory System
- 2 circuits of blood flow: Systemic and Pulmonary - Deoxygenated Blood goes from body to lungs (gets oxygenated)> Pulmonary - Oxygenated blood returns to heart, pumped to body (Systemic) |
|
|
Digestive System
The Rat - Heart |
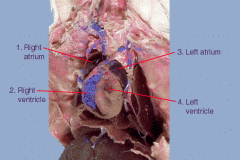
- 4 chambers
- L & R Ventricles (hard to distinguish) - L & R Atrium (distinguishable) - dark ear shaped structure 3 Main BV bring Deoxygenated Blood to heart 1) R. Superior Vena Cava 2) L Superior Vena Cava 3) Inferior Vena Cava - R & L SVC bring De-O2 blood to heart R/L sides of neck - IVC brings De-O2 blood to heard from lower part of body - De-O2 blood in R. Atrium pumps to R. Vent though Tricuspid Valve - Blood pumped from R. Ventricles through Pulmonary Semilunar Valve into Pulmonary Trunk> divides R/L Pulmonary arteries going to lungs. - O2-Blood returns from Lungs via L. Atrium via L. Pulmonary Veins - From L. Atrium blood enters L.Vent through Bicuspid Valve |

