![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Prokaryotic Cells |
cell has no nucleus or membrane |
|
|
prokaryotic cell |
cell has 2 domains Archea Bacteria |
|
|
Eukaryotic Cells |
cells has a nucleus and membrane bound organelles |
|
|
Eukaryotic Cells |
cell has one domain; Eukarya |
|
|
Eukarya |
domain has 4 kingdoms protists fungi plants animals |
|
|
coccus
|
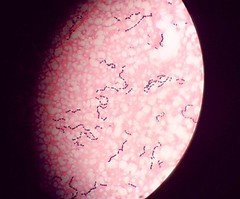
round i.e. streptococcus pyogenes
|
|
|
bacillus |
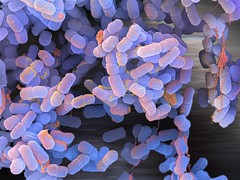
rod i.e E. Coli |
|
|
sprillium
|

spiral i.e trepanema phillidum
|
|
|
Cynobacteria |
photosynthetic bacteria and contains chlorophyll |
|
|
Nucleus |
DNA is found here |
|
|
Nucleolus |
spot found inside the nucleus |
|
|
mitochondria
|
ATP is produced here
|
|
|
Ribosomes
|
protein synthesis
|
|
|
cellwall
|
thick wall made of cellulose
|
|
|
large central vacuole |
70% of the cell used for storage |
|
|
Plastids |
a double membrane bound organelle involved in sythesis and storage of food |
|
|
chloroplast
|
contain chlorophyll for photosythesis
|
|
|
Amyloplasts |
contains starches |
|
|
Chromoplast
|
contains pigment
|
|
|
Oscillatoria |

chlorophll |
|
|
Gloeocapsa |
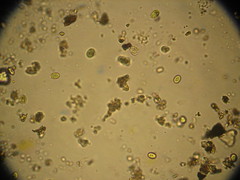
|
|
|
Bacillus |
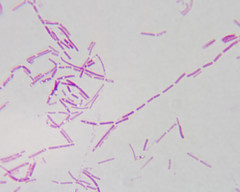
|
|
|
Onion |
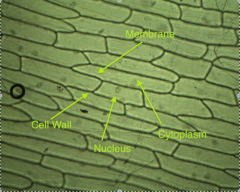
|
|
|
Potato |
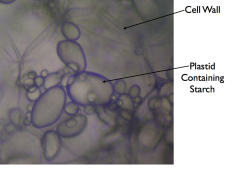
Amyloplasts |
|
|
Elodea |
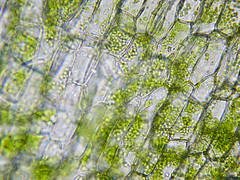
cell wall chloplast |
|
|
Red Pepper |
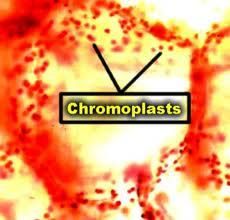
|
|
|
Human Cell |
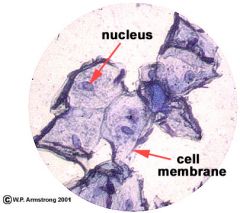
|
|
|
Passive Transport |
transport that does not require energy |
|
|
Active transport |
transport that requires energy |
|
|
Diffusion |
movement from high concentration to low concentration |
|
|
Rate of Diffusion |
increase temp increase rate
|
|
|
concentration gradient |
difference in concentration |
|
|
rate of diffusion |
size increase rate decreases |
|
|
Dialysis |
diffusion across a semipermeable membrane
|
|
|
osmosis |
diffusion of water
|
|
|
solution |
a soild dissoloved in a liquid |
|
|
hypertonic |
greater solute concentration |
|
|
hypotonic |
low solute concentration |
|
|
isotonic |
equal sloute concentration |
|
|
pure water |
0ppt |
|
|
salt water |
33ppt |
|
|
fresh water |
0-2ppt
|
|
|
human tissue |
9ppt |
|
|
hemolysis |
cell burst |
|
|
cienation |
cell shrinks |
|
|
Turgar Pressure |
internal pressure in plant cells; makes cell rigid and self supporting |
|
|
plasmolysis |
loss of turgar pressure; cell wilts |
|
|
Non-vascular plants |

no vascular system small plants i.e. mosses |
|
|
seedless vascular plants |

vascular system spores instead of seeds i.e. fern trees few cells w/ coating |
|
|
Gymnosperms |
seeds on cones conifers- pines, firs, spruce blade cypress- taxodium distichum |
|
|
angiosperms |
largest group flowering plants___reproduction |
|
|
Monocots & Dicots |
2 groups of angiosperms |
|
|
monocots |
1 catelydon in the seed |
|
|
dicots |
2 catelydon in the seed |
|
|
monocot |
parallel leaf veins |
|
|
dicots |
net veins |
|
|
monocot
|
multiples of 3 leaves
|
|
|
dicot
|
multiples of 4 or 5 leaves
|
|
|
types of leaves |
blades per leaf simple leaf compound leaf |
|
|
simple leaf |
1 blade |
|
|
compound leaf |
more than 2 blades |
|
|
leaf arrangment |
leaves per blade |
|
|
Alternate leaves |
1 leaf per node |
|
|
opposite leaves |
2 per node |
|
|
whorled leaves
|
more than 2 leaves
|
|
|
types roots
|
tap root
fiberous root |
|
|
tap root |
dominate 1 root |
|
|
fiberous root |
many equal sized roots |
|
|
root |
underground water absorbation & nutients holds plants in soil stores carbohydrates i.e cypress kness |
|
|
stem |
connects roots & leaves |
|
|
leaves
|
goes through photosynthesis
|
|
|
dermal tissue |
specialized cells/ guard cells |
|
|
epidermis
|
outer most layers & job is to protect
|
|
|
ground tissue |
not dermal or vascular |
|
|
parenchyma cells
|
potato
large thin wall living cell |
|
|
schlerenchyma cell |
small thick walled dead cells |
|
|
chloronchyma cells
|
contain chlorophyll found in leaf mesophyll
|
|
|
vascular tissue |
transporting tissue around the cell |
|
|
xylem
|
large thick walled hallow cell
transports water works by capillary action dead cell |
|
|
phloem |
living cells small thin walled living cells transports carbohydrates use active transport |
|
|
cambium |
meristcmatic tissue plant stem cell forms xylem & phloem |
|
|
stomata (stoma) |
pores in leaf gas exchange formed by guard cell |
|
|
monocot root |
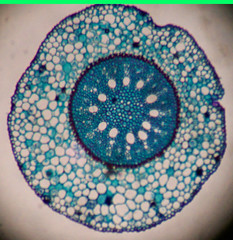
|
|
|
monocot stem |

|
|
|
dicot root |
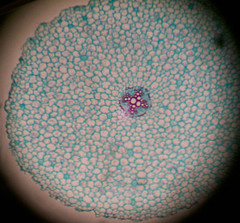
|
|
|
dicot stem |
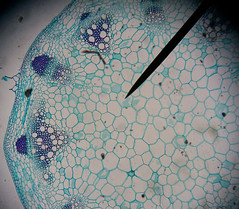
|
|
|
dicot leaf |
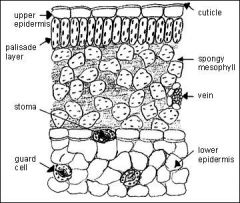
|
|
|
dicot stem |
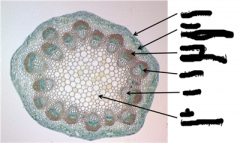
|
|
|
dicot root |
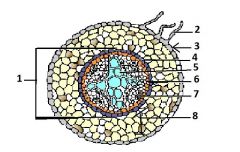
|
|
|
monocot stem |
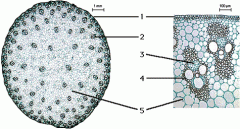
|
|
|
monocot root |
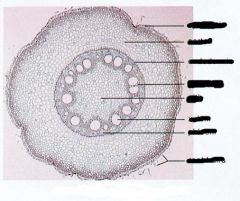
|
|
|
dicot middle |
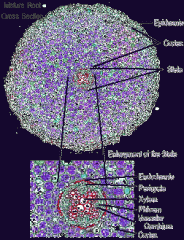
|

