![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Inheritance |
-The transfer of traits from parent to offspring dna(genotype)→rna→protein→trait→phenotype |
|
|
Trait |
A measurable or observable characteristic of a cell/organism, result of the expression of different alleles |
|
|
Alleles |
Alternative forms of a gene; most genes have 2 types, dominant and recessive |
|
|
Locus |
Segment of dna that has information controlling some aspect of the structure or function of an organism -alleles govern variations of the same characteristic and occupy corresponding loci (locations) on homologous chromosomes |
|
|
Genotype |
Genetic makeup of an organism, often expressed as symbols -dominant homozygous, AA, always observed in the form of a trait -dominant heterozygous, Aa, dominant trait is expressed -recessive homozygous, aa, only time recessive trait is expressed |
|
|
Phenotype |
Physical appearance of an organism, determined by genotype |
|
|
Multiple genes on one chromosome |
Genes must be at the same location on a pair of homologous chromosomes to be considered alleles |
|
|
Mendel's principles of inheritance |

Principle of segregation: alleles separate before gametes are formed; alleles remain intact during meiosis and recessive alleles are not "lost" and can reappear in subsequent generations -one allele per gametes |
|
|
Mendel's principles of inheritance |

Independent assortment: alleles on nonhomologous (different) chromosomes are randomly distributed into gametes -gametes receive alleles based on where the chromosomes are located during separation -contributes to genetic recombination |
|
|
Linked genes |
Genes on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together in successive generations -an exception to the principle of independent assortment -some genetic recombination occurs as a result of crossing over events as well |
|
|
Dominant traits |
Always expressed, represented by capital letters |
|
|
Recessive traits |
Only observed if both alleles code for the same trait, represented by lower case letters |
|
|
Types of genotypes |
Homozygous- both alleles for a trait are the same Heterozygous- alleles for a trait are different |
|
|
Punnett square |
Predicts the ratios of offspring with a particular genotype or phenotype resulting from the combinations of gametes from two parents; predicts the outcome of a cross |
|
|
Monohybrid (parental) cross |

Homozygous dominant alleles x homozygous recessive alleles = 4/4 heterozygous genotype, 4/4 dominant phenotype |
|
|
Heterozygous (F1) cross |

Heterozygous alleles x heterozygous alleles = 1/4 homozygous dominant genotype, 2/4 heterozygous genotype, 1/4 homozygous recessive genotype, 3/4 dominant phenotype, 1/4 recessive phenotype |
|
|
Test cross |

Determines the genotype of an individual who has a dominant trait by mating the individual with one who has the recessive trait then looking for a recessive offspring |
|
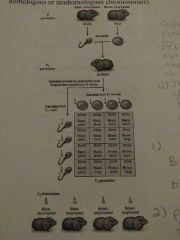
Dihybrid cross |
Mating between individuals with different alleles at two loci (on homologous or nonhomologous chromosomes) |
|
|
Independent events |
One event does not affect the outcome of the other event; chance has no memory |
|
|
Product rule |
Probabilities of independent events are multiplied Ex: if the offspring of two individuals has a 1/4 chance of having hazel eyes, there is a 1/16 chance for them to have two children with hazel eyes since 1/4 * 1/4 = 1/16 |
|
|
X-linked genes |
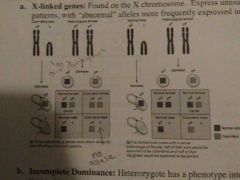
Found on the x chromosome, express unusual inheritance patterns with abnormal alleles more frequently expressed in male offspring; y chromosome is smaller than x chromosome and does not have corresponding alleles for some traits, so a female will have one dominant allele that will mask the recessive allele, but if the male only has a recessive allele that will be expressed |
|
|
Incomplete dominance |
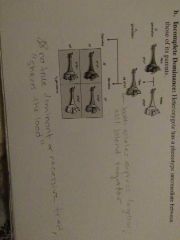
Heterozygote has a phenotype intermediate between those of its parents |
|
|
Codominance |
Heterozygote simultaneously expressed the phenotypes of both types of homozygotes Ex: speckled chickens |
|
|
Multiple alleles |
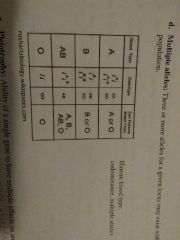
Three of more alleles for a given locus may exist within a population Ex: blood type |
|
|
Pleiotrophy |
Ability of a single gene to have multiple effects of an organisms phenotype; single gene affects multiple traits |
|
|
Polygenic inheritance |
Multiple independent pairs of genes may have similar and additive effects on the same characteristic (height, body shape, etc); multiple genes work together to affect one trait |
|
|
mutation |
change in the nucleotide sequence |
|
|
spontaneous mutations |
result from errors in base pairing during dna replication |

