![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Gene pool |
The gene pool is the set of all genes, or genetic information, in any population, usually of a particular species |
|
|
|
Allele frequency |
Allele frequency is the relative frequency of an allele at a particular locus in a population, expressed as a fraction or percentage |
|
|
|
Normal distribution |
a function that represents the distribution of many random variables as a symmetrical bell-shaped graph. |
|
|
|
Microevolution |
evolutionary change within a species or small group of organisms, especially over a short period. |
|
|
|
Directional selection |
directional selection is a mode of natural selection in which an extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, causing the allele frequency to shift over time in the direction of that phenotype |
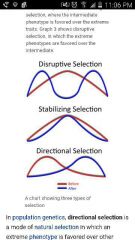
|
|
|
Distributive selection |
describes changes in population genetics in which extreme values for a trait are favored over intermediate values |
|
|
|
Gene flow |
Gene flow is the transfer of alleles or genes from one population to another |
|
|
|
Gene drift |
is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms. |
|
|
|
Bottle neck effect |
Population bottlenecks occur when a population's size is reduced for at least one generation. |
|
|
|
Founder effect |
the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population |
|
|
|
Sexual selection |
mode of natural selection where members of one biological sex choose mates of the other sex to mate with |
|
|
|
Reproductive isolation |
a collection of mechanisms, behaviors and physiological processes that prevent the members of two different species that cross or mate from producing offspring, or which ensure that any offspring that may be produced are sterile. |
|
|
|
Speciation |
the evolutionary process by which reproductively isolated biological populations evolve to become distinct species |
|
|
|
Behavior isolation |
helps members of the same species identify each other as proper mates. |
|
|
|
Geographic isolation |
population of animals, plants, or other organisms that are separated from exchanging genetic material with other organisms of the same species. Typically geographic isolation is the result of an accident or coincidence. |
|
|
|
Temporal isolation |
this is a mechanism that prevents species from mating because they breed at different times |
|
|
|
Convergent evolution |
organisms not closely related independently evolve similar traits as a result of having to adapt to similar environments |
|
|
|
Coevolution |
change in the genetic composition of one species in response to a genetic change in another. |
|
|
|
Extinction |
the state or process of a species, family, or larger group being or becoming extinct. |
|
|
|
Adaptive radiation |
a process in which organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species into a multitude of new forms, particularly when a change in the environment |
|
|
|
Punctuated equilibrium |
a theory in evolutionary biology which proposes that once species appear in the fossil record they will become stable |
|

