![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hooke
|
Scientist (last name) who looked at cork and coined the term 'cell'
|
|
|
Leeuwenhoak
|
Scientist (last name) who looked at pond water and discovered protists
|
|
|
Schleiden
|
Scientist (last name) who found that all plants are made of cells
|
|
|
Schwann
|
Scientist (last name) who found that all animals are made of cells
|
|
|
Virchow
|
Scientist (last name) who observed that all cells come from pre-existing cells (cell division)
|
|
|
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic
|
2 main types of cells
|
|
|
Eukaryotic
|
Type of cell that has membrane-bound organelles
|
|
|
Prokaryotic
|
Type of cell that lacks membrane-bound organelles, such as nucleus
|
|
|
Single circular chromosome
|
Form of DNA found in bacteria
|
|
|
Proteins & phospholipids
|
The two types of organic molecules found in the cell membrane
|
|
|
Nucleus
|
control centerof the cell
|
|
|
Chromatin
|
Long thin strands of DNA found in the nucleus
|
|
|
Golgi Body or Golgi Apparatus
|
the organelle that packages items before they leave the cell (two names for it)
|
|
|
Lysosomes
|
organelles containing digestive enzymes
|
|
|
Vacuoles
|
organelles which store nutrients, food, water
|
|
|
Chloroplasts
|
plant cell organelle used in photosynthesis
|
|
|
Cilia & Flagella
|
Two types of structures on the outer surface of a cell to help the cell move
|
|
|
Lipid Bilayer
|
Structure formed when phospholipids arrange themselves in 2 layers because nonpolar tails cannot touch water
|
|
|
cytoskeleton
|
the framework within the cytoplasm of a cell
|
|
|
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
|
a series of highly folded membranes in the cytoplasm with ribosomes attached to it
|
|
|
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
|
a series of highly folded membranes in the cytoplasm WITHOUT ribosomes attached to it
|
|
|
Fluid Mosaic model
|
Name of current model of cell membrane
|
|
|
Nucleolus
|
Organelle found inside of the nucleus that makes ribosomes and RNA
|
|
|
Cell Theory
|
All organisms made of 1 or more cells; cells are the basic unit of structure and function for all living organisms; All cells come from pre-existing cells
|
|
|
Cell membrane or Plasma membrane
|
Outside of a cell that maintains homeostasis (two names)
|
|
|
Semi-permeable
|
Ability of the cell membrane to control what materials enter/exit the cell (one word)
|
|
|
Cytosol
|
Fluid portion of the cytoplasm in a cell
|
|
|
Virus
|
A small infectious agent that only replicates when inside the living cells of another organism (host)
|
|
|
Cell wall & Chloroplasts
|
Two parts of a plant cell NOT found in an animal cell
|
|
|
Plants, Animals, Fungi, Protists
|
Four groups of organisms with eukaryotic cells
|
|
|
Phospholipid
|
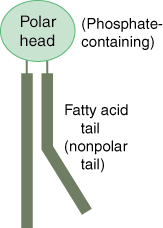
Molecule with a polar head with two nonpolar tails; makes up the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane
|
|
|
46
|
Number of chromosomes in human body cells
|
|
|
Bacteria
|
only type of organism made of prokaryotic cells
|
|
|
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
|
organelle that serves as a transport system for proteins throughout the cell
|
|
|
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
|
organelle that serves as a production and transport system for carbohydrates and lipids throughout the cell
|
|
|
Mitochondria
|
This organelle is nicknamed the powerhouse of cell and makes ATP for the cell to use as energy
|
|
|
Chlorophyll
|
The green pigment found inside chloroplasts
|
|
|
Centriole
|
This organelle is found only in animal cells and it aids in cell division
|
|
|
Receptor protein
|
type of protein found in the cell membrane that gathers information about the cell's surroundings
|
|
|
Microfilaments & Microtubules
|
The two types of protein polymers that make up cytoskeleton
|
|
|
Marker protein
|
type of protein found in the cell membrane, nicknamed name tag of cell
|
|
|
Transport or Channel protein
|
type of protein found in the cell membrane, nicknamed passageways of cell (two names)
|
|
|
Vesicle
|
Organelle produced by Golgi body that sends proteins throughout the cell
|
|
|
Bacteria
|
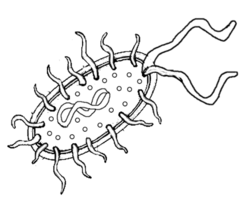
Organism pictured here; does not contain a nucleus
|
|
|
Animal cell
|
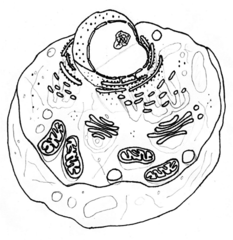
Type of cell pictured here; does not contain a cell wall
|
|
|
Plant cell
|
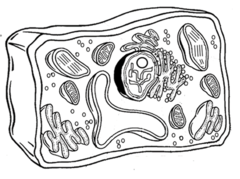
Type of cell pictured here; contains both a nucleus and a cell wall
|
|
|
Multicellular
|
Term describing organisms composed of more than one cell
|
|
|
Unicellular
|
Term describing organisms composed of just one cell
|
|
|
Cholesterol
|
molecule made up of four rings of hydrogen and carbon atoms; helps maintain the fluidity of the cell membrane
|
|
|
Central Vacuole
|
The largest organelle in the plant cell; functions to maintain the proper pressure within the plant cell to provide structure and support for the growing plant.
|
|
|
Micrometer
|
Metric unit used to measure cells
|
|
|
Plasmids
|
Accessory rings of DNA in bacteria
|
|
|
Nucleoid
|
Region of a bacterial cell which contains the single, circular chromosome
|
|
|
Endosymbiosis
|
Process in which a prokaryotic cell lived inside another cell and become part of it, forming eukaryotic cells
|

