![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) |
-stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce hormones -pituitary |
|
|
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone |
-Stimulates the thyroid -Pituitary |
|
|
Human Growth hormone |
-hormone that promotes bone/cell growth -Pituitary |
|
|
Follicle Stimulating Hormone |
-stimulates ovaries and testes, produces sex cells |
|
|
Luteinizing hormone |
-causes ovulation and development of corpus luteum |
|
|
Prolactin |
-production of breast milk |
|
|
Oxytocin |
-causes uterine contractions and stimulates breast milk production |
|
|
Thyroxin |
-increase metabolic rate |
|
|
Calcitonin |
-Lowers blood calcium by storing it in the bones |
|
|
Parathormone |
-increases blood calcium by releasing calcium from the bones |
|
|
Insulin |
-lowers blood sugars |
|
|
Glucagon |
-increases blood sugar |
|
|
Melatonin |
-biorhyththym, sleep cycle |
|
|
Epinephrine |
-causes fight or flight response through the medulla |
|
|
Cortisol |
-Increases lipid breakdown |
|
|
Estrogen |
-activates the development of female secondary sex hormones |
|
|
Progesterone |
-stimulates the uterus for pregnancy -Pituitary |
|
|
Testosterone |
-stimulates development of male secondary sex cells |
|
|
Diabetes |
when the body doesn't produce enough insulin to function |
|
|
Goiter |
caused by a lack of iodine, a mass that appears on the thyroid making it hard to breathe |
|
|
Hypothyroidism |
Not enough thyroxin is produced causing tiredness and a constant feeling of being cold |
|
|
Hyperglycemia |
When the levels of glucose in the bloodstream is too high |
|
|
Homeostasis |
an internal balance maintained through a series of checks and adjustments |
|
|
Negative Feedback loop |
occurs when a change is detected and action is taken to bring it back within normal limits |
|
|
Positive Feedback loop |
where a small change is detected and amplified |
|
|
Temporal lobe |
Lobe responsible for hearing and speech interpretation, located on the lower front |
|
|
Occipital lobe |
Lobe that interprets the things we see, located on the back |
|
|
Frontal lobe |
Lobe that makes decisions about information received and behavioral lobe, located on the upper front |
|
|
Parietal lobe |
Lobe that regulates sensory information, located on the upper back |
|
|
Medulla Oblongata |
responsible for vital body functions, also the information crossroads. Small round part in front of the spinal cord. |
|
|
Cerebellum |
Responsible for muscle coordination and balance. Round part behind spinal cord. |
|
|
Pons |
Responsible for message transmission. Large round part above medulla. |
|
|
Midbrain |
Relay for sight and sound, small patch above the pons and below the thalamus. |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
controls the autonomic nervous system and the internal organs of the body. Small lump in the center of the brain. |
|
|
Thalamus |
forms a sensory relay center on the way to the cerebrum, controls level of consciousness, middle of the brain |
|
|
Meninges |
Protective membranes surrounding the brain. Dura, Pia, Arachnoid. |
|
|
Reflex arc |
Receptor, sensory nerve, association nerve, motor nerve, effector |
|
|
Reaction |
action in response to an interpretation by the brain to a stimulus, when the brain realizes whats happening |
|
|
Reflex |
action that is taken at the spinal cord level, automatic response to move away |
|
|
Gyrus |
Bumps on the brain |
|
|
Neurotransmitter |
a chemical released by a nerve cell which transmits an impulse from a nerve cell to another nerve |
|
|
Corpus callosum |
A bundle of nerves in the brain |
|
|
All or none response |
when a neuron reacts completely or not at all |
|
|
Neurilemma |
a thin sheath around a nerve axon |
|
|
Depolarization |
when sodium ions begin to flood into a nerve through the openings |
|
|
Repolarization |
the openings begin to close off, no longer allowing sodium to pass through |
|
|
Cerebrum |
responsible for voluntary movement and thoughts |
|
|
Utricle |
structure in the ear responsible for head position |
|
|
Rods |
Responsible for the detection of light in the eye |
|
|
Lacrimal |
structure that floods the eye to clear it on any foreign substances |
|
|
Choroid |
responsible for absorbing excess light in the eye |
|
|
myopia |
near-sightedness, the eye is too long. |
|
|
hyperopia |
Far sightedness, eye focuses light on the back of the retina |
|
|
cones |
Help detect colors in the eye |
|
|
Tapetum |
Colorful layer in the animal eye that helps make it easier to see in the dark. |
|
|
Pinna |
amplifies sound by funneling it from a large area to a narrow one |
|
|
Auditory canal |
carries sound waves to the tympanic membrane |
|
|
eustachian tube |
air filed tube of the middle ear that equalizes pressure |
|
|
tinnitus |
ringing in the ears that could be either acute or chronic. Normally caused by infection |
|
|
conjunctivitis |
infection of the conjuctiva, pink-eye |
|
|
Utricle/Saccule |
helps maintain balance. on the floor of the utricle is a small patch of hair cells, when the head is tilted they're stimulated by a jelly like fluid |
|
|
Semicircular canals |
three canals that help maintain balance, when the head moves, theres a liquid throughout these canals that moves and are detected. Up/down, sideways, around. |
|
|
Iris |
regulates the amount of light entering the eye |
|
|
Vitreous humour |
maintains the shape of the eyeball and permits light transmission to the retina |
|
|
Nucleic acids |
Thymine, Nitrogen Base, Nucleotide, Phosphate Group, Adenine, Double Helix, Ribose, Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil |
|
|
Lipids |
Oils, Cell Membranes, Saturated, Waxes, Synthesized Hormones, Storage of Energy, Fats, Glycerol, Waterproofing, Phospholipids, Cholesterol, Tryglycerides, Sterols, Atherosclerosis, Unsaturated, Insoluble, LDL, HDL, Fatty Acids |
|
|
Proteins |
Amino Acids, Peptide Bonds, Quaternary, Denature, Collagen, Fibrin, Ribosomes, Structural Components, Enzymes, Coagulation, Linear, R group, Antibodies, Hemoglobin, Keratin |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Isomers, Saccarides, -ose, Storage of Energy, Sugars, 1:2:1 |
|
|
Covalent bonding |
when electrons are shared between atoms to achieve stability |
|
|
Isotopes |
an atom with a different number of neutrons than most of the atoms of the same tipe |
|
|
Cellulose |
the type of carbohydrate the body uses for roughage or fiber |
|
|
animals store their energy as: |
glycogen |
|
|
Monosacchride |
simple sugars |
|
|
Hemoglobin |
protein that carries oxygen through the blood |
|
|
Enzymes |
protein that speeds up metabolic rates in the body |
|
|
Antibodies |
protein that helps the body fight against diseases |
|
|
A sugar, a phosphate and a nitrogen base make up a: |
Nucleotide |
|
|
difference between DNA & RNA |
1. Contains ribose 2. Single stranded 3. Contains uracil |
|
|
why is RNA needed to act as the messenger? |
Because the DNA is too large to leave the nucleus through its pores |
|
|
Hydrogenation |
when hydrogen molecules are used to saturate organic compounds |
|
|
Dehydration synthesis vs. hydrolysis |
bonds are formed through the removal of water vs. bonds are broken through the addition of water |
|
|
Purine vs Pyrimidine |
2 rings in their structure vs. only one ring in their structure |
|
|
Denature vs Coagulation |
proteins or nucleic acids are temporarily deformed vs. permanently deformed |
|
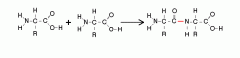
|
Protein chain |
|
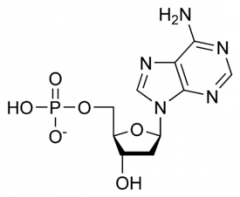
|
Nucleotide |
|
|
Transcription |
The process of producing mRNA from DNA is called |
|
|
6CO2+ 12H2O+Sun= C6H1206+6O2+6H2O |
Photosynthesis |
|
|
Light dependant |
a water molecule is split and the oxygen is released into the air. The hydrogen goes into the carbon fixation phase |
|
|
Carbon fixation |
the hydrogen and energy stored from the first stage combine with carbon to produce glucose |
|
|
C6H12O6+6O2=6CO2+6H2O+Energy |
Cellular respiration |
|
|
Glycolysis |
when glucose is broken down into two pyruvic acid molecules without the presence of oxygen |
|
|
Catalyst |
substance capable of speeding up a chemical reaction |
|
|
Substrate |
an ion attaching to an enzyme |
|
|
Active site |
the site where the lock and key process occurs, where the substrate and the enzyme join |
|
|
Induced fit |
when a substrate changes shape to properly fit an enzyme |

