![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Calvin Cycle |
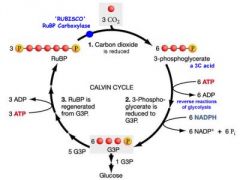
4 steps: carbon fixation, reduction, release of one molecule of G3P and regeneration of the starting molecule, ribulose bisphosphate. Does not require light |
|
|
4 different trophs |
autotrophs: plants which, sustain themselves, make food from photosynthesis, and do not consume organic molecules derived from other organisms Photoautotrophs: use the energy of light to produce organic molecules. Chemoautotrophs: prokaryotes that use inorganic chemicals as their energy source. Heterotrophs:consumers that feed on plants or animals or decompose organic material |
|
|
light reactions |
electron excited by photon(light) giving it high potential energy. goes down electron transport chain and produces ATP. The electron is excited again by another photon, giving it more potential energy and generates NADPH |
|
|
photosystems |
consists of a number of light harvesting complexes surrounding a reaction center complex. Contains various pigment molecules bound to proteins. Understand the differences between photosystem I and II |
|
|
electromagnetic spectrum/energy |
Sun contains electromagnetic energy. Energy travels in waves varying in wavelength. visible light is only a small part of the spectrum, which is the full range of electromagnetic wavelengths. |

