![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
112 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Taxon |
A Taxonomic group at any level |
|
|
-phyta |
Ending for plant phyla |
|
|
-opsida |
Ending for plant class |
|
|
-ales |
Ending for plant orders |
|
|
-aceae |
Ending for plant families |
|
|
Taxonomy |
Identification, classification, & naming of organisms |
|
|
Systematics |
Identification, classification, & naming of organisms as well as its evolutionary history |
|
|
Theophrastus |
"Father of Botany" Greek 1st person to write down a classification in a permanent & logical form He used gross morphological characteristics |
|
|
Carl Linnaeus |
Swedish 1753 He published "Species Plantarum" (The Kinds of Plants) Beginning of ALL scientific plant names |
|
|
Binomial Nomenclature |
Latin 2 words make up a species name |
|
|
Authority |
The person who publishes the new name first |
|
|
Who's Authority is L. |
Carl Linnaeus |
|
|
I.P.N.I. Stands for |
International Plant Names Index |
|
|
The International Botanical Congress meets every ______ to vote on name changes |
6 years |
|
|
I.C.B.N is published by whom |
International Botanical Congress |
|
|
What are the rules of naming plants |
All new names must be PUBLISHED 1st to name the plant gets priority All names must have a description in Latin Type specimen must be designated |
|
|
Type Specimen |
Usually a dried, pressed plant or preserved animal that is reresentative of a species |
|
|
Where are Type specimens archived |
Museums or Herbarium |
|
|
Where is the larges collection of type specimens and how many do they have? |
Paris, France 8.8 Million |
|
|
Meristems |
Cells that retain potential to divide |
|
|
Primary Growth |
Herbacecous From apical moisten (No wood) |
|
|
Secondary growth |
From lateral meristems Wood |
|
|
What are the 3 primary meristems made by the Apical Meristem |
Protoderm (Dermal) Ground meristem (ground) Procambium (Vascular) |
|
|
What is the functions of Dermal tissue |
Protection & gas exchange |
|
|
What is the functions of Ground Tissue |
Photosynthesis, storage, & support |
|
|
What is the functions of Vascular tissue |
Water & sugar transport Support & storage |
|
|
Parenchyma |
Living, thin walls Photosynthetic cells & food storage cells |
|
|
Collenchyma |
Living, uneven thick walls Elastic support for stem & leaves |
|
|
Sclerenchyma |
Dead at maturity, evenly thick walls (look completely empty) |
|
|
What are the 2 types of Sclerenchyma |
Sclerids Fibers |
|
|
Where do tree rings happen |
In areas where tree experience hot/cold & dry/wet seasons |
|
|
Apples are native to _____ |
Kazakhstan |
|
|
In the early 1800 in America what we're Apple's used for; and why |
Apple cider bc they did not trust the water to drink. Very few were grown to eat bc most were bitter |
|
|
In the time of Jonny Appleseed why were fruit trees important |
Settlers needed to plant fruits so they could show that they were going to settle on the land. This is how the Settelers were able to keep the land. |
|
|
At the time of prohibition how did Apple farmers rebrand apples |
An apple a day keeps the doctor away They marketed them for eating |
|
|
Vascular cambium |
Lateral meristem Can result in wood |
|
|
Vascular tissue in roots and stems |
Vascular cylinder or vascular bundles |
|
|
Vascular tissue in leaves |
Veins |
|
|
Xylem |
Dead at maturity Transports water & minerals |
|
|
Apoptosis |
Programmed cell death |
|
|
Pholem |
Sugar transport |
|
|
Where is Dermal Tissue found |
In the epidermis of the roots, stem, & leaves |
|
|
Stomata |
Pores for gas exchange |
|
|
Guard cells |
Surround the stoma Form in pairs They can open to allow Carbon Dioxide in Can close to regulate water loss |
|
|
Trichomes |
"Hairs" on the surface |
|
|
Cork cambium |
Capable of producing the lateral meristem (Part of the bark) |
|
|
Cuticle in the epidermis do what |
Form a continuous layer on the outside |
|
|
What do you call Trichomes on the roots |
Root Hairs |
|
|
What are the 3 main functions of a root |
Anchorage Storage Conduction (transportation) |
|
|
Primary root |
First root to emerge from the embryo |
|
|
Taproot |
The one that goes the deepest Can be the first root |
|
|
Adventitous roots |
Primary routes in short-lived new Roots develop from the bottom of the stem Monocots Fibrous roots |
|
|
Root cap |
Made of parenchyma Tip of root |
|
|
Mycigel |
Root lubricant Secreted by the root cap |
|
|
What are the 3 major regions of a root |
Region of cell division Region of elongation Region of maturation |
|
|
What is a major function of root hairs |
Increase surface area for absorption |
|
|
True or false ground meristem produces the cortex |
True |
|
|
Amyloplast |
Organell that stores starch Think chloroplast without green pigment |
|
|
Plasmodes mata |
Numerous cell conects ?other? |
|
|
Apoplectic movement |
Substances that can move through the air space and the cell walls (In the cortex) |
|
|
Symplastic movement |
Substances can move through the cytoplasm & plasmodesmata (In the cortex) |
|
|
Casparian strip |
It stops water Surrounds each cell and a band of ligands and suberin Location: cortex (Think empty green boxs with rubber bands around them) |
|
|
True or false a Apoplectic movement is passive |
True So plants can NOT control it |
|
|
Prop root |
Support especially in wet or windy habitats |
|
|
What is another name for air roots |
Pneumatophores They stick up out of the water |
|
|
Symbiosis |
A relationship where both organisms benefit |
|
|
In the relationship of fungus on plant roots what do each get out of it |
Plans get an increase uptake and water minerals Fungus gets sugars provided by the plants |
|
|
What are the main functions of a stem |
Support & conduction |
|
|
What is the main function of leaves |
Photosynthesis |
|
|
Nodes |
Where 1 or more leaves arise |
|
|
Internodes |
The area between nodes |
|
|
Apical meristems are produced by ______ |
The overlapping of leaves |
|
|
True or false shoots have pericycle |
False |
|
|
What do leaf primordia become |
Leaves |
|
|
What do Bud primordia become |
Lateral shoots |
|
|
What is primordial |
A word given to the structure that is in its earliest stage of differentiation |
|
|
True or false Bud scales and leave scars look the same on all plants |
False They differ from species to species and can be used to help identify plants |
|
|
What are bundle scars |
Dots in the leaf scar where are vascular bundles were attached |
|
|
What are Lenticels on Woody stems |
Openings for gas exchange (replace the stomata) |
|
|
True or false in shoots dicots have piths |
True |
|
|
True or false in shoes monocots have piths |
Fales |
|
|
Vascular bundles are also known as |
Fascicles |
|
|
Interfacicdar regions |
Regions between the bundles |
|
|
Cuticle in Tilia (Basswood) are |
Layers of wax or fat |
|
|
What do you call a compound leaf with no rechis |
Plamately compound leaf |
|
|
What do you call a compound leaf with rachis |
Pinnately compound leaf |
|
|
A leaf with only 1 bundle is called |
Simple leaf |
|
|
What are the 3 basic parts of a leaf |
Blade, peticle, & stipule |
|
|
True or false in a Barrel Cactus the stem is where photosynthesis occurs |
True |
|
|
True or false spines are leaves |
True They are used for defense |
|

In compound leaves what is the area called from the node to the rachis (Black section in photo) |
Petiole |
|

In compound leaves what is the area where the leaves Branch off from called (Circled in red in the photo) |
Rachis |
|
|
How to you tell if it is a simple or compound leaf |
Buds are in the axile of a leaf Leaflets do not buds |
|
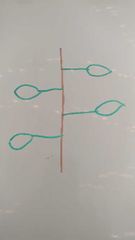
What do to call it when there is 1 leaf per node |
Alternote leaves |
|

What do you call it when there are 2 leads per node |
Opposite leaves |
|
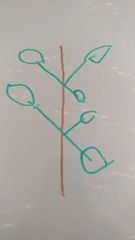
What do you call it when there are 3 leads per node |
Whorled leaves |
|
|
Leaf trace |
Vascular tissue extending from the vascular cylinder |
|
|
Leaf trace gap |
The gap in the vascular tissue caused by leaf trace |
|
|
Where is the spongy parenchyma on horizontal leaves |
The bottom (the lower surface) |
|
|
True or false the Palisade parerichyma has more chloroplasts than the spongy parerichyma on horizontal leaves |
True This is bc the Palisade parerichyma gets more sunlight than the spongy parerichyma |
|
|
Mid rib |
Main vein in leaves |
|
|
Where can the epidermis be on a leaf |
It can be on 1 or both sides |
|
|
Mesophytes |
Plants with "medium" water needs (Usually with more stomata on lower surface) |
|
|
Hydrophytes |
Plants requiring lots of water ?other? |
|
|
Xerophytes |
Plants adapted to avid habitats (Dessert plants have more stomata, often sunken) |
|

What is the arrow pointing to (root) |
Cortex |
|

What is the arrow pointing to (root) |
Cortex |
|

What is the arrow pointing to (root) |
Pith |
|
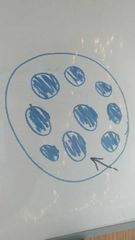
What is the arrow pointing to (root) |
Ground Tissue You cannot identify whether there is a cortex or pith in this example |
|

What is the red arrow pointing to |
Stipule |
|

Not done |
Need to get labels |
|
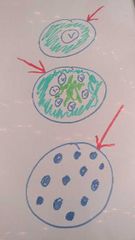
What are the arrows pointing to |
Dermal tissue |

