![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Ingestion occurs when |
The mouth takes in good |
|
|
|
Digestion involves |
The breakdown of food by both chemical and mechanically |
|
|
|
Peristalsis |
Food movement by means of alternate waves of contraction and relaxation of muscle in the organ walls |
|
|
|
5 basic processes involved in Digestion |
Ingestion, digestion, movement, absorption, elimination |
|
|
|
What does the esophagus do? |
Moves food from pharynx to stomach |
|
|
|
What does the mouth do in the digestive process |
Teeth chew food Tongue tastes food |
|
|
|
What does the Pharynx do in the digestive process? |
Passageway for food and air Participated in swallowing |
|
|
|
Gastrointestinal Tract Wall: What are the 4 layers? |
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, serosa |
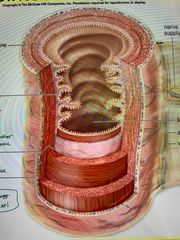
|
|
|
Gastrointestinal Tract Wall: what is the Mucosa? |
Inner mucous membrane layer that is modified according to the digestive organ |
Mucus, lubricant |
|
|
Gastrointestinal Tract Wall: what is the Submucosa? |
Broad band of loose connective tissue that contains nerves, blood, and lymphatic vessels |
Immune! |
|
|
Peristalsis Vs Segmentation |
Peristalsis moves food in one direction and segmentation pushes food back and forth to break down food. |
|
|
|
What is Chyme? |
Mixture of stomach acid and food |
|
|
|
What is hydrochloric acid? |
Produces a pH of about 2, breaks down large bits of food |
|
|
|
Gastrointestinal Tract Wall: what is the Muscularis? |
Two layers of smooth muscle |
Muscle contractions - mix and propelle |
|
|
Gastrointestinal Tract Wall: what is the Serosa? |
Thin, outermost tissue that is the visceral peritoneum |
Connective tissue |
|
|
What do proteins breakdown into? |
Amino acids |
|
|
|
What do carbs breakdown into? |
Sugars |
|
|
|
What do lipids breakdown into? |
Fat, triglycerides>glycerin > fa’s |
|
|
|
What is segmentation? |
Digestive enzymes breaking down protein, carbs, and fats |
|
|
|
What are the 3 saliva glands? |
Sublingual glands, parotid glands, and submandibular glands |
|
|
|
How does food move through through the esophagus? |
Gravity and peristalsis |
|
|
|
What is the stomachs function? |
Food storage, digestion, regulation of delivery |
|
|
|
What does the small intestine do? |
digests food and absorbs nutrients
|
|
|
|
What is the gall bladder? |
stores and concentrates bile |
|
|
|
What does the pancreas do? |
Secretes digestive enzymes into small intestine and secretes bicarbonate into small intestine to neutralize stomach acid |
|
|
|
What does the liver do? |
Produces bile and performs various functions associated with processing and storing nutrients |
|
|
|
What does the large intestine do? |
Absorbs nutrients and stores waste material |
|
|
|
What is the Rectum? |
Passageway for feces |
|
|
|
What does the anus do? |
Expells undigested material |
|
|
|
What does salivary glands do? |
Moistens food, bicarbonate maintains pH, amylase digest starch, lysozyme inhabits bacteria |
|
|
|
Disorders: What is Diverticular Disease? |
In the large intestine, polyps on the colon. When inflamed, it is diverticulitis |
|
|
|
Disorders: Cholera |
Infections bacterial disease in the small intestines. Typically caused by infected water supply. |
|
|
|
Disorders: Celiac Disease |
An immune reaction to eating gluten, a protein. |
|
|
|
Disorders: Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
Its a catch all Ongoing Inflammation of all or part of the digestive tract Examples: Crohns, Ulcerative colitos |
|
|
|
Eating Disorders: Anorexia Nervosa |
Psychological disorder characterized by severe fear of becoming obese |
|
|
|
Eating Disorders: Bulimia Nervosa |
Individuals binge and purge to maintain their weight |
|
|
|
Eating Disorders: Muscle dysmorphia |
Person thinks their body it too small, become preoccupied with diet and body building |
|

