![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
103 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Science |
System of understanding phys. world thru research |
|
|
Research |
Objective collection of data - observable facts |
|
|
Scientific method |
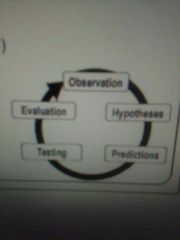
Objective & repeatable process used to gain knowledge 1. Observe 2. Hypothesize (inductive) 3. Deduce predictions (deductive) 4. Test w. empirical evidence 5. Evaluate |
|
|
Scientific theory |
Well substantiated explanation using facts, laws, tested hypotheses |
|
|
Are scientific theories ever proven? |
No, no matter how much evidence you have |
|
|
Law |
Generalization of how some aspect behaves under stated circumstances. Explains what will happen, not why/how |
|
|
Religion |
Understanding world through historical belief |
|
|
Philosophy |
Understanding world through rational argument |
|
|
Steps to scientific research |
Results presented in paper, paper undergoes peer review, published in primary literature |
|
|
Pseudoscience |
Doesn't adhere to scientific method but claims to be scientific - uses anecdotal evidence, cherry picking, scientific language, ad ignorantiam |
|
|
Applied research |
Attempts to solve practical problems or bring a product to market |
|
|
Fundamental research |
Science focused on expanding knowledge of universe |
|
|
What is life? |
Something that can metabolize, reproduce, evolve |
|
|
4.6 BYA |
Sun and planets allegedly form |
|
|
4.6-3.9 BYA |
Meteoritic bombardment and volcanic activity create reducing atmosphere |
|
|
3.9 BYA |
Reducing atmosphere (high hydrogen, no free oxygen, thick with water vapor) |
|
|
3.9 BYA onward |
First cells appear |
|
|
Miller and Urey constructed... |
Early earth atmosphere (formed organic compounds of inorganic) |
|
|
RNA |
Self replicates Self splices Catalyzes Possess genotype and phenotype |
|
|
Protobiont |
Aggregate of abiotically produced organic molecules surrounded by membrane like structure |
|
|
First cells were.... |
Chemoautotrophs, rely on chemosynthesis to produce glucose from chemicals like sulfer and methane |
|
|
Stromatolites 3.5 BYA |
First photoautotrophs. Rock like structures comprised of layering photosynthetic bacteria and sediment over time. Oldest known fossils. |
|
|
History of life |

|
|
|
Stromatolites are imp bc |
saturated the atmosphere w oxygen |
|
|
Endosymbiotic model |
Eukaryotic model Proposed by Lynn Margulis Small prokaryotes enter host as prey or parasites Host gain selective advantage Host and endosymbionts become single organism |
|
|
Evidence for endosymbiotic model |
Organelles.... Biochem homologous to prokaryotes Replicate via binary fission, like them Possess own DNA |
|
|
3 domains of life (bacteria, eucarya, archaea) |
By 2.1 BYA firmly estab. |
|
|
Oldest multicellular lineage? |
1.5 bya |
|
|
Why the multicellular evolution? |
Specialized cells |
|
|
Phanerozoic Eon division |
Cenozoic, mesozoic, paleozoic |
|
|
Lass mass extinction? |
Cretaceous period, in the mesozoic era, in the phanerozoic eon 65 mya |
|
|
Cambrian explosion |
Diversification of animals. 550 mya |
|
|
Geologic timescale |

|
|
|
Cenozoic era division? |
Quaternary, Neogene, Paleogene |
|
|
Mesozoic era division? Age of what? |
Dinosaurs. 250 mya
Cretaceous, jurassic, Triassic |
|
|
Paleozoic era division? |
Permian, Carboniferous, Devonian, Silurian, Ordovician, Cambrian |
|
|
Cenzoic era age of what? |
Mammals |
|
|
Cambrian explosion caused by |
Inc in o2 in atmosphere Hox genes Diversifying selection |
|
|
Evolution |
Change in allele freq over time |
|
|
Locus |
Specific location of a gene, DNA seq on a chromosome |
|
|
Pop. |
Group of interbreeding individuals |
|
|
Gene pool |
Total aggregate of alleles in a pop |
|
|
How do pops evolve |
Migration (gene flow) Mutation Genetic drift Selection |
|
|
Genetic drift |
Random change in allele frq over time |
|
|
Selection |
Mechanism that shapes adaptations via differential reproductive success amongst different genotypes |
|
|
Selection greatly enhanced when |
Overpop of offspring - more choices |
|
|
Modes of selection |
Stabilizing Disruptive Directional |
|
|
Hardy Weinberg theorem |
P+q=1 Allele genotype freq |
|
|
Where does genetic variation come from |
Mutation - substitution, insertion Meiosis Crossing over Random fertilization of gametes |
|
|
Where do new species come from |
A new breeding pop Reduced gene flow btwn new and original pop Time Leads to reproductive isolation Adaptive radiation |
|
|
Adaptive radiation |
Rapid species diversification thru single common ancestor |
|
|
Drift most effective in |
Small pops |
|
|
How does reproductive isolation evolve |
Prezygotic barriers 1. Premating 2. Postmating prezygotic Postzygotic barriers |
|
|
Prezygotic barriers Postzygotic |
Impede fertilization Prevents successful reproduction of offspring |
|
|
Prezygote barriers |
Habitat isolation, temporal, behavioral, mechanical, gametic (cricket example) |
|
|
Post zygote barriers |
Reduced hybrid viability Reduced hybrid fertility Hybrid breakdown |
|
|
Species |
Abstract construct that defines groups |
|
|
Biological species concept |
Species are groups of actually or potentially interbreeding natural pops that are reproductively isolated from other such groups Doesn't apply to fossils, asexual orgs, |
|
|
Allopatric speciation |
Geographic separation restricts gene flow (river, valley) |
|
|
Sympatic speciation |
No geographic sep; biological factors reduce gene flow |
|
|
Anagenesis |
Gradual change from one species into another |
|
|
Cladogenesis |
Branching of one or more new species from a parent species |
|
|
Gradualism |
Speciation occurs gradually over time |
|
|
Punctuated eq |
Speciation occurs by periods of rapid change followed by stasis; leaves impression of fossil record gaps |
|
|
Microevolution |
Evo within a pop or species on a generational timescale |
|
|
Macroevolution |
Evolution across species on a geological timescale |
|
|
Systematics |
Study of biological diversity and it's origins |
|
|
Phylogenetics |
Tool used to study evolutionary history |
|
|
Phylogeny |
Pattern of lineage branching |
|
|
Internal node |
Last common ancestor |
|
|
Terminal node |
Extant species |
|
|
Synapomorphy/homology |
A characteristic present in an ancestral species and shared by its evolutionary deacendents Shared derived new |
|
|
Methods fossil aging |
Radioactive decay, index fossils, magnetism in rock |
|
|
Rock types |
Igneous-cooled magma, abs. Aging Sedimentary- most fossils Metamorphic- radiometrically dated |
|
|
Molecular clock |
Tech used to relate molecular differences between two lineages to their absolute time since divergence |
|
|
Homoplasy/analogous |
Structures appear similar, formed independently |
|
|
Convergent evo |
Two distinct traits form independently (analogous/homoplasy) |
|
|
Binomial |
Official name of every species Consists of genus and species Order family genus species |
|
|
Plesiomorphy |
Ancestral character (old) |
|
|
Autopomorphy |
Unique derived |
|
|
Outgroup |
Reference group to help uncover evolutionary relationships within the group on interest (ingroup) |
|
|
Monophyletic |
Group consisting of ancestor and all descendants |
|
|
Paraphyletic |
Group consisting of single ancestor and most descendants |
|
|
Polyphyletic |
Group consisting of multiple ancestors |
|
|
Cladogram |
Branch length arbitrary |
|
|
Phylograms |
Branch length indicates # of diffs |
|
|
Ultra metric |
Length reps time since divergence |
|
|
Parsimony |
Least evo events likely correct |
|
|
Parsimony can be misleading due to |
Homoplasy/analogous traits |
|
|
What are phylogenies good for |
Rep changes not found in fossil rec |
|
|
Viruses |
Cause disease across all domains Not life, just gene in protein coat Lack metabolic machinery |
|
|
First virus |
Tobacco mosaic virus tmv |
|
|
Viral structure |
Genetic material Capsid (shell) Capsomer (functional unit of shell) Membrane |
|
|
Types of virus |
Helical, icosahedral, envelope, complex |
|
|
Viral classification |
Baltimore or ictv |
|
|
Lytic / lysogenic |
1. Virulent, death imminent 2. Temperate, death eventual |
|
|
Prions |
Misfolded proteins, replicate thru touch |
|
|
Viroids |
No protein coat, can be parasites of other viruses |
|
|
What are prokaryotes |
Single celled, archaea and bacteria No membrane No mitosis Flagellated |
|
|
Shapes of prokaryotes |
Spherical rod spiral |
|
|
Prokaryotes repro thru |
Binary fission Genetic recombination |
|
|
Archaea |
Introns, histones, extreme enviros |
|
|
Bioremediation |
Removal of pollutants using prokaryotes |

