![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Nucleus |
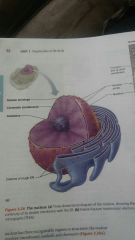
Control center of the cell, transmits genetic info & provides instruction for proteins synthesis |
|
|
|
Cell cycle |
The series of changes a cell goes through from the time it is formed to the time it reproduces. |
|
|
|
Interphase |

Period before cell division. 4 subphases: *G1- vigorous growth, synthesizing proteins rapidly & metabolically active *G0- permanently cease dividing *S- DNA replication *G2- preparation of division |
|
|
|
Cell division |
Essential for body growth & tissue repair. -2 events- *Mitosis: division of the nucleus. 4 stages= PMAT- Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, & Telophase. *Cytokinesis: begins during late Anaphase & ends after mitosis. A contraction ring made of actin filaments draws the plasma membrane inward to form a clevage furrow & pinches the cell apart. 2 daughter cells are formed, each containing a nucleus identical to the original. |
|
|
|
DNA Polymerase |
Means many parts. Is needed to make DNA. |
|
|
|
Helicase |
Unwinds DNA & exposes the bases. |
|
|
|
Protein synthesis |
DNA is the blueprint. |
|
|
|
Gene |
Segment of with blueprint for one polypeptide. |
|
|
|
Transcription |
Exact copy of DNA. |
|
|
|
Translation |
The instructions that DNA enforces to RNA to form protein. |
|
|
|
RNA types |
-3 types: *messenger RNA (mRNA)- carries instructions for building a polypeptide from gene in DNA to ribosomes in cytoplasm. *ribosomal RNA (rRNA)- forms funcional ribosomes, which are the sites of protein synthesis. Together w/ tRNA translates messages from mRNA. *transfer RNA (tRNA)- binds to amino acids & pair with bases of codons of mRNA at ribosomes to begin process of Protein synthesis. |
|
|
|
Tissue |

Group of cells similar in structure & function. - 4 types: *Epithelial *Nervous *Muscle *Connective |
|
|
|
Nervous tissue |
Internal communication. Brain, spinal cord, nerves. |
|
|
|
Muscle tissue |
Contracts to cause movement. Muscles attached to bones (skeletal), muscles attached to heart (cardiac), muscles of wall's of hollow organs (smooth). |
|
|
|
Epithelial tissue |
Forms boundaries between different environments, protects, secretes, absorbs, filters. Lining of the digestive tract organs and other hollow organs, skin surface (epidermis). Avascular (contains no blood cells) but innervated (supplied by nerve fibers), can also regenerate. -2 major groups: *1= simple cell with 1 layer/ nucleus *>1= stratified cell with more than 1. |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, protects, binds other tissues together. Bones, tendons, fat and other soft padding tissue. |
|
|
|
Epithelial tissue types (epithelium) |

2 types: *covering & lining epithelium- on external & internal surfaces. *glandular epithelium- Secretory tissue in the glands. |
|
|
|
Epithelial cell shapes |
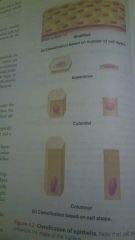
-Squamous cell (squam= scale)- flattened & scale like. -Cuboidal cell- boxlike, approximately as talk as they are wide -Columnar cell- talk & column shaped. |
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelium |

|
|
|
|
Simple Cuboidal epithelium |

|
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelium |
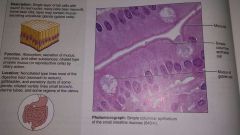
|
|
|
|
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium |
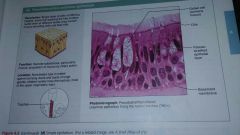
|
|
|
|
Stratified squamous epithelium |
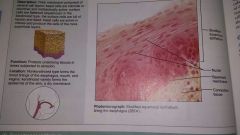
|
|
|
|
Transitional epithelium |
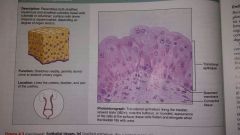
|
|
|
|
Glandular epithelia |
1 or more cells that makes & secretes aqueous (water- based) fluid. Site of product release is the endocrine (internal & ductless) or exocrine (external w/ ducts). Both from the pancreas. Endocrine makes hormones by exocytosis & exocrine secretes the substances. |
|
|
|
Modes of secretion |
*Merocrine glands- exocytosis (merely secrete) ex.spit out, sweat, produced by pancreas, sweat & saliva glands. *Holocrine glands- rupture of accumulated product ex.oil glands of the skin. |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Is abundant in the human body. Major functions are to bind & support, protect, insulate, storing reserved fuel, transporting substances. 4 classes: *connective tissue proper- loose, dense ex fat & fibrous tissue of ligament. *cartalige *bone * blood |
|
|
|
Structural elements of Connective tissue |
*Ground substance- unstructured material fills space bt cells & contains fibers. Composed if fluid, protein & proteoglycans. Protein core + large polysaccharides (chondroitin sulfate & hyaluronic acid) trap water I different amounts; forming a substance that varies from a fluid to a viscous gel. *Fibers- 3 kinds- collagen, elastic & reticular in the dermis. |
|
|
|
Connective tissue cells |
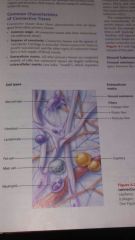
*Blasts- immature cells, actively mitoyic, secrete ground substance & fibers. Connective tissue proper= fibroblasts, cartilage= chondroblast, bone= osteoblast. *Cyte- mature cells, maintain matrix health. *Fat cells- store nutrients *White blood cells- neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes- connected with tissue response too injury. Neutrophil is the first in line against infection. Lymphocytes provide you with immunity- T cell (immunity)& B cell (antibodies). *Mast cell- produces heparin ( blood thinner), histamine (vaso constrictor->closes lungs & throat) *Macrophage- (large eaters) 2nd in defense, white blood cell that defends you against foreign objects. |
|
|
|
Connective tissue proper: loose connective tissue, areolar |
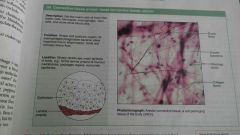
|
|
|
|
Connective tissue proper: loose connective tissue, adipose |
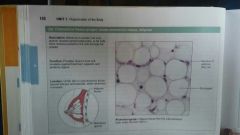
|
|
|
|
Connective tissue proper: loose convective tissue, reticular |
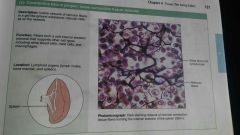
|
|
|
|
Muscle tissue |
Highly cellular, well vascularized tissues that are responsible for body movement. 3 types- skeletal, cardiac, & smooth muscles. |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle |
Attached to the bones of the skeleton. Form flesh of the body,& as they contract they pull on bones or skin causing body movement. Long, cylindric with obvious striations. |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle |
Only found in the walls of the heart. Contractions help propel blood thru blood vessels. Striated, intercalated discs. |
|
|
|
Smooth muscle |
Found mainly in the walls of hollow organs- digestive tract, urinary tract, uterus, blood vessels. Squeezes substances thru organs by alternately contracting & relaxing. No striations, spindle shaped. |
|
|
|
Neurons |
Basic unit of the nervous system. Transmits electrical signals from sensory receptors & effector. Brain, spinal cord & nerves. |
|
|
|
Membranes |
3 types- *cutaneous- the skin *mucous (mucosae)- lines all body cavities that open to the outside of the body ex digestive & respiratory. *serous (serosae)- found in closed ventral cavities ex mesothelium & areolar tissue. |

|
|
|
Steps to tissue repair |
1. Inflammation 2. Organization restores blood supply. 3. Regeneration & fibrosis. |
|
|
|
Layers of skin |
*epidermis- superficial, outer layer, protective shield of the body. *dermis- middle layer, tough & leathery composed of dense connective tissue; blood vessels, arteries, & glands are located here. *hypodermis- deepest layer,subcutaneous, also called superficial fascia, not technically part of skin, consist mostly of adipose tissue. |
|
|
|
Cells of the epidermis |

*keratinocytes- produce fiberous protein keratin. *melanocytes- melanin pigment of the skin. *dendritic (langerhans)- activate immune system. *tactile (merkel)- touch receptors. |
|
|
|
Layers of the epidermis |
*stratum basale (basal layer)- deepest layer, attached to dermis, takes time to heal if damaged. *stratum spinosum (prickly layer)- several cell layers thick, keratinocytes contain melanin & dendritic cells. *stratum granulosum (granular layer)- thin, cells fill with keratin, nuclei & organelles disintegrate & accumulate keratohylaine granules & lamellar granules. *stratum lucidum (clear layer)- in thick skin, translucent, dead keratinocytes. *stratum corneum (horny layer)- outermost layer, protect the skin from abrasions & penetration. |
|
|
|
Dermis |
Strong, flexible connective tissue. 2 layers- *papillary- areolar connective tissue with collagen, contain free nerve endings, capillary loops, meissner's corpuscles; touch. *reticular- thick, provides stretch recoil proper. |
|
|
|
Skin color |
*melanin- yellow to reddish brown- brown to black, responsible for most skin color *carotene- yellow to orange, seen in palms & soles of feet. *hemoglobin- pinkish hue off fair skin, appears in mucous membrane & nail beds. |
|

