![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
127 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
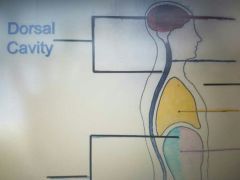
Dorsal Cavity |
Or posterior has two subdivisions the cranial and spinal cavities. |
|
|
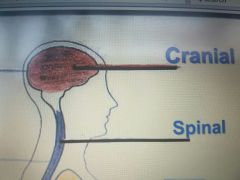
Cranial Cavity |
The space inside the bony skull. The brain is well protected because it occupies the cranial cavity. |
|
|
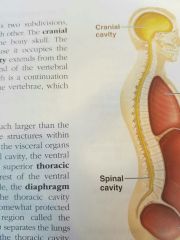
Spinal Cavity |
Extends from the cranial cavity nearly to the end of the vertebral column. The spinal cord which is a continuation of the brain, is protected by the vertabrae, which surround the spinal cavity. |
|
|
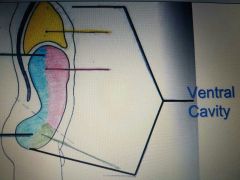
Ventral Cavity |
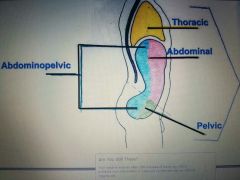
Contains all the the structures within the chest and abdomen, that is, the visceral organs in that region. Thoracic and Abdominopelvic (when subdivided the abdominal and pelvic). |
|
|
|
Thoracic Cavity |
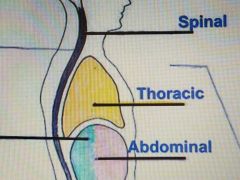
Referring to the chest; the organs (lungs, heart, and others) are somewhat protected by the rib cage within this cavity. |
|
|
|
Diaphragm |
-Any partition or wall separating one area from another. -The thoracic cavity is separated from the rest of the ventral cavity by this dome-shaped muscle. |
|
|
|
Mediastinium |
A central region that separates the lungs into right and left cavities in the thoracic cavity. Housing the heart, trachea, and several other visceral organs. |
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic Cavity |
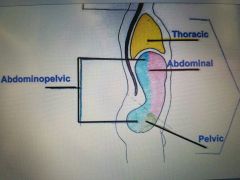
The cavity inferior to the diaphragm when subdivided into the abdominal and pelvic cavities. |
|
|
|
Abdominal Cavity |
Superior cavity containing the stomach, liver, intestines, among other organs. |
|
|
|
Pelvic Cavity |
Inferior to the abdominal cavity it contains the reproductive organs, bladder, and rectum. |
|
|
|
Superior (directional term) |
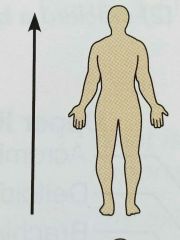
(Cranial/Cephalad) Toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above |
The forehead is superior to the nose |
|
|
Inferior (directional term) |
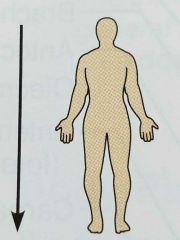
(Caudal) Away from the head end toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below |
The naval is inferior to the breastbone |
|
|
Ventral (directional term) |
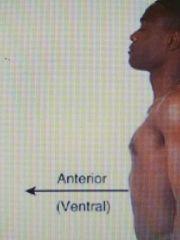
(Anterior) towards the front of the body; in front of |
The breastbone is anterior or ventral to the spine |
|
|
Dorsal ( directional term) |
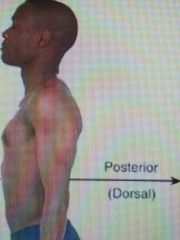
(Posterior) Toward or at the backside of the body; behind |
The heart is posterior to the breastbone |
|
|
Medial ( directional term) |
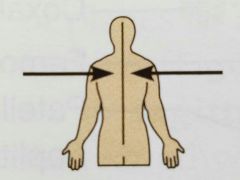
Toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of |
The heart is medial to the arm |
|
|
Lateral ( directional term) |
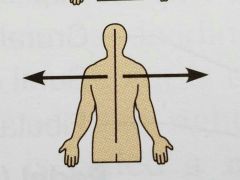
Away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of |
The arm is lateral to the chest |
|
|
Intermediate ( directional term) |
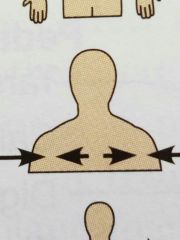
Between a more medial and more lateral structure |
The collarbone is intermediate between the breastbone and the shoulder |
|
|
Proximal ( directional term) |
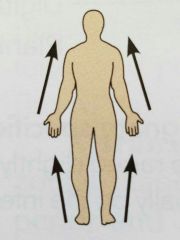
Close to the origin of the body part poor the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk |
The elbow is proximal to the wrist (meaning that the elbow is closer to the shoulder or attachment point of the arm than the wrist is ) |
|
|
Distal ( directional term) |
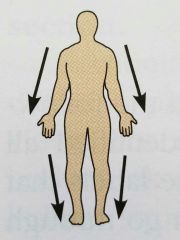
Farther from the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk |
The knee is distal to the thigh |
|
|
Superficial ( directional term) |
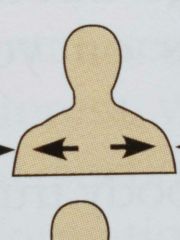
(External) Toward or at the body surface |
The skin is superficial to the skeleton |
|
|
Deep (directional term) |
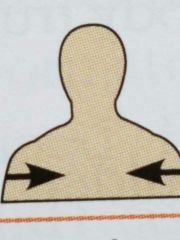
Away from the body surface more internal |
The lungs are deep to the rib cage |
|
|
Sagittal Plane |
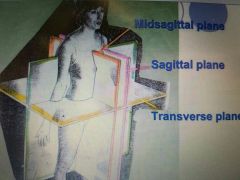
Cut along the lengthwise, or longitudinal, plane of the body, dividing the body into right and left parts. |
|
|
|
Midsagittal ( Median ) |

If the cut is down the median plane of the body and the right and left parts are equal in size |
|
|
|
Cornal ( Frontal Plane) |

A cut along a lengthwise plane that divides the body or an organ into anterior or posterior parts |
|
|
|
Transverse Plane |

A cut along a horizontal plane, dividing the body or organ into superior and inferior parts |
The belt |
|
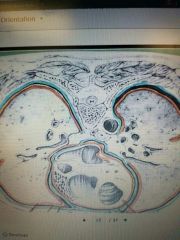
Outer Orange |
Visceral Pleural Membrane |
|
|
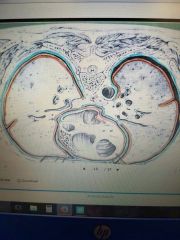
Outer Blue |
Parietal Pleura Membrane |
|
|
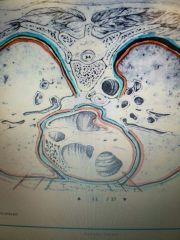
Inner Orange |
Visceral Pericardium Membrane |
|
|
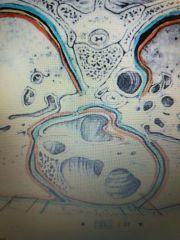
Inner Blue |
Parietal Pericardium Membrane |
|
|
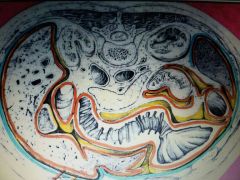
Serous Membrane: Outer Orange Line |
Visceral Peritoneum Membrane |
|
|
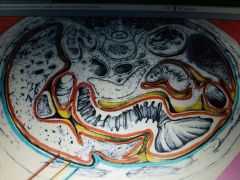
Serous Membrane: Outer Blue Line |
Parietal peritoneum membrane |
|
|

|
Eyepiece |
|
|
|
Body |
|
|

|
Stage |
|
|

|
Light Source |
|
|

|
Knobs to move stage |
|
|

|
Arm |
|
|

|
Coarse or Fine Adjustment |
|
|

|
Stage |
|
|

|
Condenser |
|
|

|
Diaphragm |
|
|

Green Line |
Slide Clip |
|
|

Red Line |
4x Scanning Lens |
|
|

Yellow Line |
10x Low power lens |
|
|

Yellow Line |
Nosepiece |
|
|

Blue Line |
40x High power lens |
|
|

White Line |
100x Oil Immersion Lens |
|
|
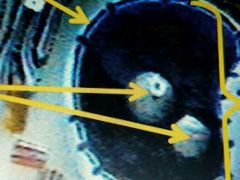
Top left arrow |
Nuclear Membrane |
|
|

Two middle arrows |
Nucleolus |
|
|
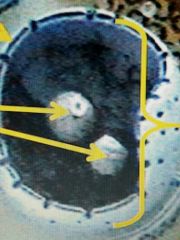
The whole |
Nucleus |
|
|
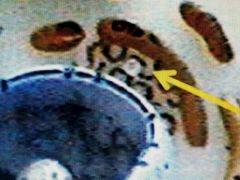
The right arrows |
Ribosomes |
|
|

Left arrow/dark space |
Chromatin |
|
|
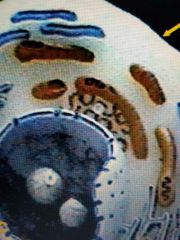
Very outer/arrow |
Cell membrane |
|
|
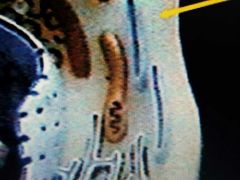
White |
Cytoplasm |
|
|

The spots |
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum |
|
|
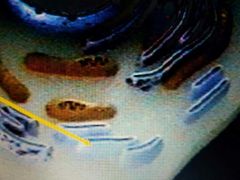
|
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum |
|
|
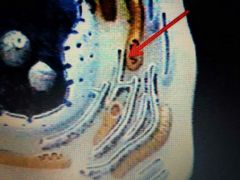
|
Mitochondria |
|
|

|
Centrioles |
|
|

|
Golgi Apparatus |
|
|

|
Lysosomes |
|
|
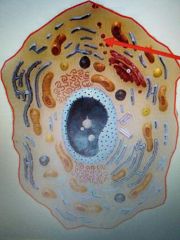
|
Vesicles |
|
|
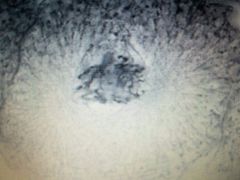
|
Prophase |
|
|
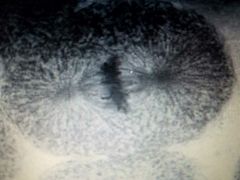
|
Metaphase |
|
|
|
Anaphase |
|
|
|
Telophase |
|
|
Epithelial Tissue |
Simple Squamous |
|
|
Epithelial Tissue |
Simple Columnar |
|
|
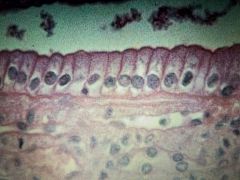
Epithelial Tissue |
Simple Columnar |
|
|

Epithelial Tissue |
Stratified Squamous |
|
|
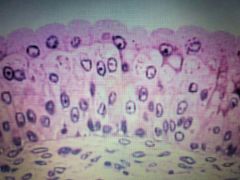
Epithelial Tissue |
Transitional |
|
|
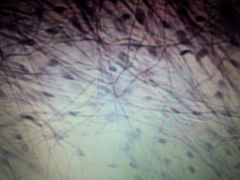
Connective Tissue |
Loose (Areolar) |
|
|
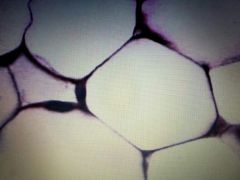
Connective Tissue |
Adipose |
|
|
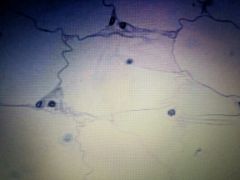
Connective Tissue |
Adipose |
|
|

Connective Tissue |
Bone |
|
|
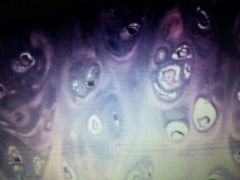
Connective Tissue |
Hyaline Cartilage |
|
|

Muscle Tissue |
Skeletal muscle tissue |
|
|
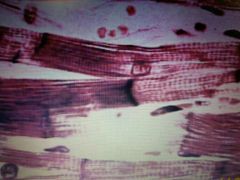
Muscle Tissue |
Cardiac muscle tissue |
|
|
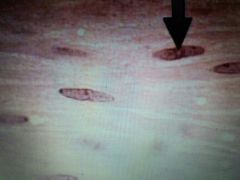
Muscle Tissue |
Smooth muscle tissue |
|
|
Nervous Tissue |
Motor Neuron |
|
|
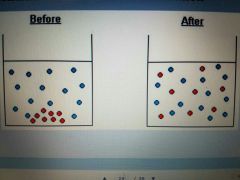
Passive Transport Diffusion |
Movement of particles or molecules from greater concentration to a lesser concentration |
|
|
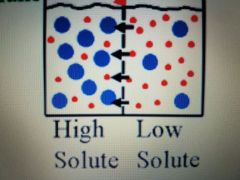
Osmosis |
-Movement of water from greater concentration to a lesser concentration across semipermeable membrane -Diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane |
|
|
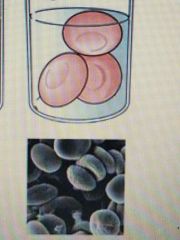
A solution that is less concentrated than the intracellular fluid (cell swells) |
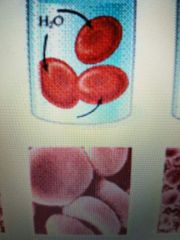
Hypotonic |
|
|
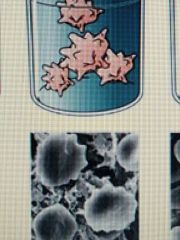
A solution that is more concentrated than the intracellular fluid (cell shrinks) |
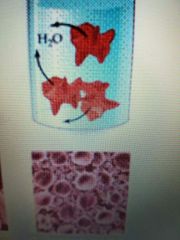
Hypertonic Solution |
|
|
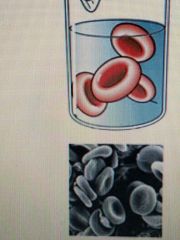
Solution and cell concentration is the same |

Isotonic Solution |
|
|

|
Frontal Bone |
|
|
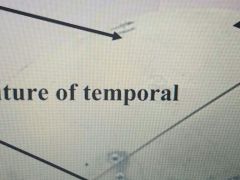
Arrow |
Coronal suture of frontal |
|
|
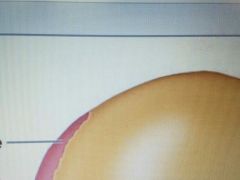
Red |
Parietal Bone |
|
|
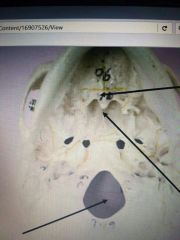
Top Arrow |
Palatine Bone |
|
|

|
Hyoid Bone |
|
|
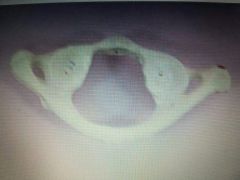
|

Atlas 1st Vertebrae |
|
|
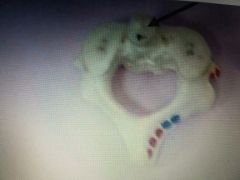
|

Axis 2nd vertebrae |
|
|

|
Odontoid process of axis |
|
|

|

Lumbar Vertebrae |
Lumber Moose |
|

|

Thoracic vertabrae |
Giraffe |
|

|

Cervical vertabrae |
|
|
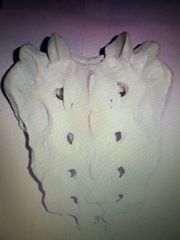
|
Sacrum |
|
|

|
Coccyx |
|
|
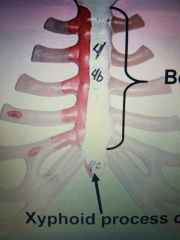
As a whole |
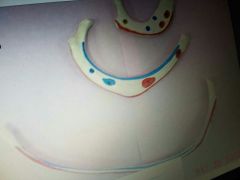
Sternum |
|
|
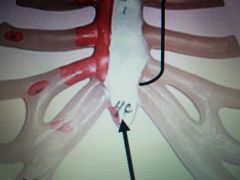
Bottom Arrow |
Xiphoid or Xyphoid process of the sternum |
|
|
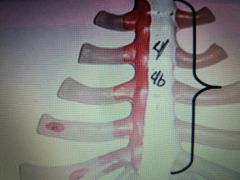
|
Body of sternum |
|
|

|
Manubrium of sternum |
Bow Tie |
|
|
Ribs |
|
|
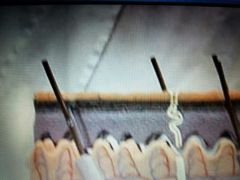
From purple area up |
Epidermis |
|
|
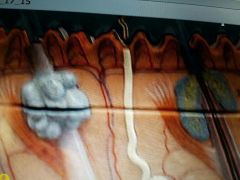
|
Dermis |
|
|
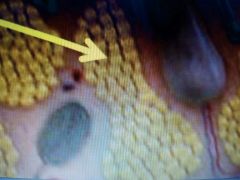
|
Adipose |
|
|
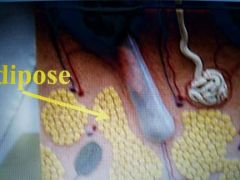
|
Subcutaneous |
|
|
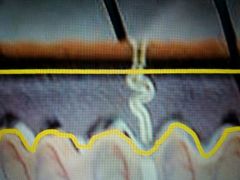
Top part |
Stratum corneum |
|
|
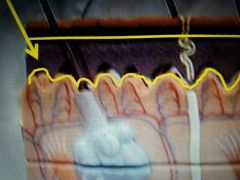
Bottom |
Stratum Basale |
|
|
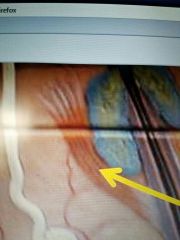
|
Arrector pilli |
|
|
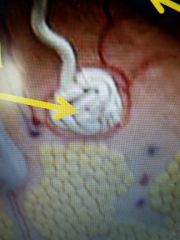
|
Sweat gland |
|
|

|
Hair Shaft |
|
|
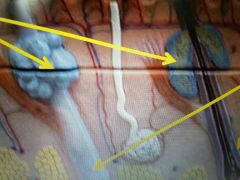
Top two arrows |
Sebaceous Gland |
|
|
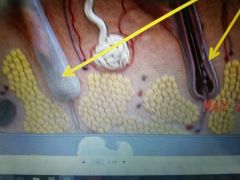
|
Hair Follicle |
|
|

|
Long Bone |
|
|
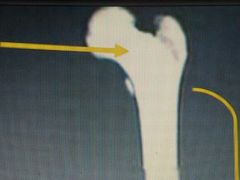
|
Proximal Epiphysis |
|
|
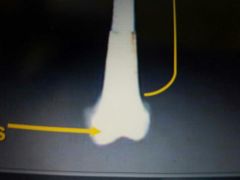
|
Distal epiphysis |
|
|
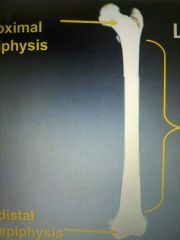
The body of this bone? |
Diaphysis |
|
|
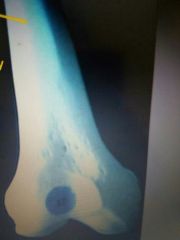
|
Compact bone |
|
|
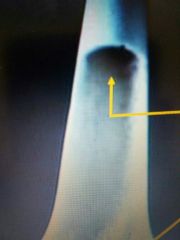
|
Medullary Cavity |
|
|
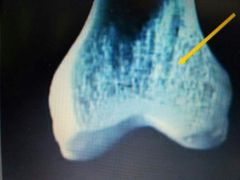
|
Spongy Bone |
|
|
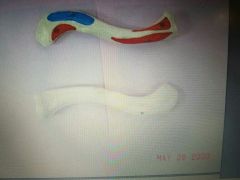
|
Clavicle |
|
|

|
Scapula |
|
|

|
Spine of Scapula |
|
|

Anterior |
Acromion process of scapula |
|
|
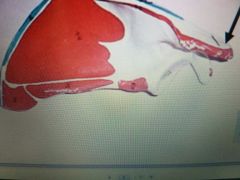
Posterior |
Acromion process of scapula |
|
|

Anterior |
Coracoid process of scapula |
|
|
Posterior |
Coracoid process of scapula |
|

