![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the principle of original horizontality?
|
Sediments accumulate as nearly flat lying layers. Therefore, when sedimentary strata are significantly tilted from horizontal, they must have been disturbed after they were laid down
|
|
|
What is the principle of lateral continuity?
|
when it is initally laid down, a layer of sediment deposidted between two moments in time extends laterally in all directions. Lateral continuity is the basis for correlating strata that can no longer be directly traced from one location to another due to subsequent erosion or burial. Note that this does not imply that layers extend infinitely.
|
|
|
What is the law of superposition?
|
Sedimentary layers are deposited in a time sequence, with the oldest on the bottom and the youngest on the top. In other words, sediments accumulate by piling up, therefore the stuff at the bottom of the pile must have been in place before the stuff on the top could be deposited.
|
|
|
What are the three types of unconformities?
|
Disconformity: an unconformity that separates parallel layers of sedimentary rock
Nonconformity: an unconformity in which older igneous or metamorphic rocks are eroded and overlain by sedimentary rocks Angular unconformity : an unconformity in which sedimentary layers below the surface are not parallel with the layers above the surface |
|
|
What is the principle of cross cutting relationships?
|
A geologic feature that cuts another is the younger of the two features.
|
|
|
How does one use Isochron Diagrams?
|
If there are multiple specimens, plot all of them and trace back each of the half lives of the various specimens (e.g: take the half life 0 from specimen 1,2,3 to the y axis, then take half life 1 from speicment to 1,2,3 to the y axis, repeat) The spot where they meet is the original amount of daughter isotope.
|
|
|
When looking at the intersection of a concordia diagram and an intersection?
|
The radiometric age of the rock
|
|
|
How do you describe rocks based on roundness?
|

|
|
|
How does one describe rocks based on sorting?
|
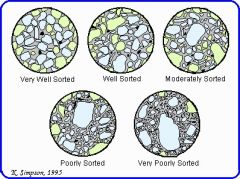
|
|
|
How does one classify grains through wentworths scale?
|

|
|
|
What do grain sizes tell us about energy level?
|
A sluggish trickle can carry silt but not gravel. Coarser sediment grains imply higher energy when they were deposited.
|
|

What is this sedimentary structure?
|
Current Ripple Cross Lamination
|
|

What is this sedimentary structure?
|
Trough Cross Lamination
|
|

What is this type of sedimentary structure?
|
Wave Ripple Cross Lamination
|
|

What is this type of sedimentary structure?
|
Hummocky Cross Lamination
|
|

Fill out
|
From bottom to top
A -> E -> B -> C -> D |
|
|
How are Phyogenies organized?
|
Into nested clades. The father comes from the base and the son/daughter is at the tip. A father can only split into to bases.
|
|
|
How do you interpret ancestral relationships from a phylogenic tress?
|
Things on the same branch are closer related than things on different branches. Something in the middle is as closely related to both the father and it's son, but closer to the father.
|
|
|
How do evaporites form?
What are some examples? |
Although all water bodies on the surface and in aquifers contain dissolved salts, the water must evaporate into the atmosphere for the minerals to precipitate. For this to happen, the water body must enter a restricted environment where water input into this environment remains below the net rate of evaporation. This is usually an arid environment with a small basin fed by a limited input of water. When evaporation occurs, the remaining water is enriched in salts, and they precipitate when the water becomes oversaturated.
calcite, gypsum and anhydrite, halite, sylvite, carnallite, langbeinite, polyhalite, and kanite. |
|
|
How do clastic carbonates form?
What are some examples? |
carbonate minerals can from by direct precipitation, but more often, they are secreted by organisms.
Mineral calcite, dolomite, aragonite |
|
|
What is the duhnam classification system?
|
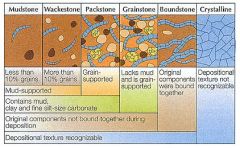
|
|
|
What is Walther's law?
|
The vertical sucession of facies in a continuous stratigraphic succession reflects the lateral arrangement of depositional environments at any one moment in time. In other words, the same thing that goes from the left to right, happens up and down.
|
|
|
What is the rock age of the Lake Sommerville field trip?
|
Eocene
|
|
|
What do the lithologies and sedimentary structures of the Lake Sommerville indicate about the depositional setting?
|
That the top layer was probably a river or a stream because of the lack of S2. The rest of the layers were intermitten layers of either shallow oceans beaches or swamps.
|
|
|
What do the lithologies and sedimentary structures tell us about sea level during the ecoene at lake sommerville spill way?
|
That the sea level rose and fell over time. It wasn't constant.
|
|
|
What is the effect of tilt on seasonality and climate?
|
Since the earth changes it tilt as it rotates, it will change 23.5 degrees from one season to the next. When the tilt makes it closer to the sun, the part of the world is warmer. When the tilt is away from the sun it is colder. Thus it creates seasons. The position of the area also has to do with the climate, it's warmer at the equator because it is almost always full on to the sun, whereas it is colder in the poles because it is almost always full away from the sun
|
|
|
What is the effect of eccentricity on the seasonality and climate?
|
The farther away, the less heat is transfered. Also the orbit is more an ellipse, there fore when it is closest to the sun it is warmer than it is farther. However eccentiricty has less effect than tilt.
|
|
|
What is the effect of precession on the seasonaility and climate?
|
Precession (wobble) is how in sync tilt and eccentiricy are. If they are in sync (e.g. the tilt is away and it is far from the sun) it makes a very cold winter, but if they are out of sync (e.g. the tilt is close and it is far from the sun) it makes a mild winter
|
|
|
What is IODP?
|
Integrated Ocean Drilling Program, goal is to explore the geologic structure and history of earth's ocean basins.
|
|
|
What are the pirmary sources for deep sea sediments?
|
biogenic (marine plankton), terrigenous (sand and clay size particles dervied from weathering and erosion of exposed land) and authigenic (sediements that precipiatete directly from sea water typically at or near the ocean floor)
|
|
|
What lithologies are seen in the cores at IODP?
|
It is almost all calcium carbonate (chalk) with some dust storms particles thrown in
|
|
|
What do the O and C isotope rations tell us? From what kind of organisms do we get the isotope data?
|
We get the isotopes from marine plankton organisms that make their shells out of calcium carbonate and opaline silica. Increasing values of O istoopes indicate colder conditions
Increasing C isotopes indicate greater influxes of biotic activity |
|
|
Benthic vs Planktonic?
|
planktonic means they lived in surface waters
Benthic means they lived on the sea floor |
|
|
What does the isotope data from the cores indicate about clmate changes aross the PETM?
|
It went from high to frozoen to nromal temp
|

