![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
•Which is TRUE of dominant alleles? A.Always the most common trait B.Always the best trait to have C.Replaces the recessive allele expression D.None of the above are TRUE |
C.Replaces the recessive allele expression |
|
|
•There is a gene for flower color wherethe dominant allele F is blue and the recessive allele f is white. What is this individuals genotype? FFA. Heterozygous B. Homozygous dominant C. Homozygous recessive D. Heterozygous dominant |
A. Homozygous dominant |
|
|
•Describe the relationships amongchromosomes, DNA, genes and alleles |
Chromosomes are made of DNA, DNA contains genes, 2 alleles (versions) of each gene (one from mom, one from dad). |
|
|
Why did Gregor Mendel Choose pea plants as his experimental organism? |
. They Are to grow .Develop quickly . Easy to control mating .Produces many offspring .Many traits appear in 2 forms |
|
|
Distinguishbetween dominant and recessive |
Dominant- If present, always expressed and masks the recessive trait. Recessive- traits are masked, homozygus for these traits to be expressed. |
|
|
•Distinguish between heterozygous andhomozygous |
Heterozygus - 2 different alleles Homozygus- 2 of the same alleles |
|
|
Distinguishbetween phenotype and genotype |
Genotype= genetic express actual alleles in genome Phenotype=what we see, physical characteristics |
|
|
DefineP, F1 and F2 generations |
P generation- Parental F1 generation-1st offspring children of P F2 generation- 2nd generation children of F1 |
|
|
Whatis a monohybrid cross |
Inheritance pattern involving a single gene (cross looking for one trait) |
|
|
Whatare the genotypic and phenotypic ratios expected in the offspring of amonohybrid cross |
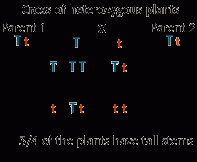
10
Phenotypic 3:1 Genotypic 1:2 |
|
|
Whatis a test cross and why is it useful |
crossing a known parent (homozygus recessive) against an unknown parent - determines if unknown parent is homozygus dominant or heterozygus. Based on offspring |
|
|
Whatis the law of segregation |
2 alleles for each gene will separate into different gametes |
|
|
•A woman who has type O blood has a sonwith type O blood. Who below CANNOT bethe father? A.A man with type A blood B.A man with type O blood C.A man with type AB blood D.A man with type B blood |
C.A man with type AB blood |
|
|
Why do males and females expressrecessive X-linked alleles differently? |
Each female has apair of X chromosomes, whereas a male has only one X chromosome. Any trait amale has on its X chromosome will be expressed. Recessive alleles on an Xchromosome of a female may be masked by dominant alleles on its homologous Xchromosome. |
|
|
•In determining the inheritance mode of adisorder, which factors below can cause problems? A.Humans typically have only a few children B. Co-dominance or incomplete dominanceC.Protein interactions or epistasis D.All of the above |
D.All of the above |
|
|
What is a dihybrid cross |
Crossing 2 individuals and look at how 2 traits are expressed in the offspring. Cross 2 heterozygus individuals |
|
|
What phenotypic ratios are expected forthe offspring of a dihybrid cross? |
9:3;3:1, combination of all possible traits |
|
|
What is the product rule? |
Chance of an individual events occurring is equal to the product of the individual chances that the even will occur . |
|
|
How do patterns of inheritance differ forunlinked and linked pairs of genes ? |
-Unlinked genes are on different chromosomes , always have independent assortment in meiosis -Linked genes are on the same chromosomes, majority of time, passed on together. Only passes independently due to crossing over events. |
|
|
What is the difference betweenrecombinant and parental chromatids and how do they arise? |
- Recombinant chromatid - cross over event-created a new chromatid now a combo of both parents -Parent chromatid- exact copy from mom/dad |
|
|
Howdo incomplete dominance and co dominance increase the number of phenotypes? |
- Incomplete dominance- 2 alleles are expressed together forming a 3rd phenotype EX) red and white flower ->off spring pink flower - Co-dominance- 2 alleles are expressed together forming 3rd phenotype Ex)blood type express both A&B evenly |
|
|
What is pleiotropy? |
One gene creates multiple phenotypes Ex. morfans syndrome, connective tissue disorder, multiple effects across body because all tissues have connective tissues |
|
|
Whydo males and females express recessive X-linked alleles differently? |
Men only have one X chromosones . Y does not mask any trait. Females have x chromosones and must have two copies to express it. |
|
|
Howare pedigrees helpful in determining a disorder’s mode of inheritance |
Can trace back the genes pAssed on to the next generation -Autosumal Dominat/recessive -sex linked |
|
|
What is a polygenic trait? |
Trait that depends on multiple genes . Ex. Skin/eye color and height |

