![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
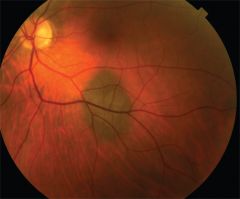
What is a nevus?
|
a congenital hamartoma
Atypical, benign-appearing melanocytes |
|
|
What are the BENIGN melanocytic lesions that occur in the CB and Choroid called?
|
Nevi
|
|
|
In what percentage of people are nevi found in the CB and choroid?
|
30%
|
|
|
What percentage of people have multiple nevi in the same eye?
|
7%
|
|
|
In what percentage of people are one or more nevi found BILATERALLY?
|
3 - 4%
|
|
|
What percentage of people with choroidal nevi, have iris freckles too?
|
55%
|
|
|
What percentage of people have iris freckles without choroidal nevi?
|
20%
|
|
|
Is there a sex predilection in patients with CB or choroidal nevi?
|
No, M=F
|
|
|
Are choroidal and CB nevi common in children?
|
NO! it is extremely low!
|
|
|
What happens to the incidence as a person ages?
|
The incidence increases progressively during the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th decades, and then levels off at approx 35% of people
|
|
|
Where do nevi occur in the CB and Choroid?
|
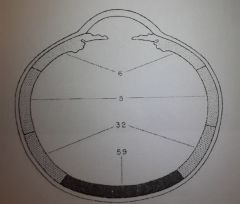
91% in the posterior 1/2
59% in the posterior 1/3 Almost equal incidence in the anterior 1/3 of the choroid and CB. 5% in anterior choroid 6% in the CB |
|
|
What is the range in size of a nevus of the choroid and CB?
|
Nevi: 0.5 - 11mm (0.33 - 7DD)
95% are 3mm (2DD) or less |
|
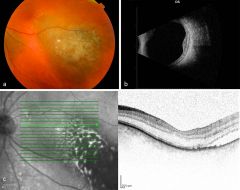
what thickness of the choroid does the nevus usually involve?
|
The FULL thickness of the choroid, excluding the choriocapillaris.
|
|
|
Describe the shape of a choroidal nevus
|
Flat, discoid lesions
67% > the thickness of the surrounding choroid |
|
|
Are choroidal and CB nevi relatively vascular or avascular?
|
AVASCULAR
|
|
|
Why is this important to know?
|
FA: decreased fluorescence.
a region of persistent choroidal hypofluorescence Useful in identifying amelanocytic nevi Melanomas are usually highly vascular |
|
|
What do the nevi cells look like?
|
Atypical benign-looking melanocytes
i.e. Nevus cells are plumper than normal melanocytes of the CB and choroid. |
|
|
How many different types of UVEAL melanocytes are there?
|
4
|
|
|
What are the 4 types of uveal melanocyte cells?
|

1) Plump polyhedral
2) Slender spindle 3) Plump fusiform & dendritic 4) Ballon cells |
|
|
Which is the most common type of the 4?
|
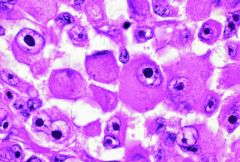
PLUMP POLYHEDRAL
|
|
|
Describe plump polyhedral melanocyte cells
|
Most common type
Maximally pigmented Majority of the cells in a "typical" nevus, are plump polyhedral melanocytes MELANOCYTOMA (magnocellular nevus): nevus commposed exclusively of plump polyhedral melanocytes |
|
|
What is a MELANOCYTOMA?
|
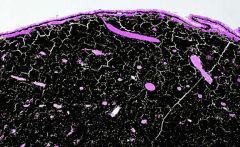
a nevus composed entirely of plump polyhedral melanocytes
|
|
|
Which is the second most common type of UVEAL melanocyte?
|
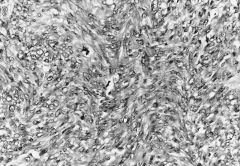
SLENDER SPINDLED
|
|
|
What are SLENDER SPINDLED melanocytes?
|
Nevus cells that contain little or NO pigment
|
|
|
What are PLUMP FUSIFORM and DENDRITIC melanocytes?
|
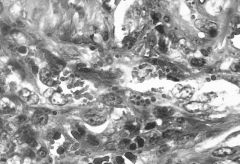
Less pigmented than PULM POLYHEDRAL
More pigmented than SLENDER SPINDLED "Intermediate" pigmentation |
|
|
What are BALLOON melanocytes?
|
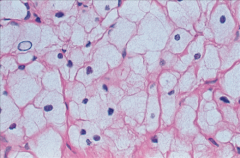
Large cells
Abundant foamy cytoplasm |
|
|
What is CONGENITAL OCULAR or OCULODERMAL MELANOCYTOSIS?
|
= A diffuse NEVUS of the uvea
Composed primarily of PLUMP POLYHEDRAL neus cells |
|
|
What effects do Choroidal & CB nevi have on adjacent tissue?
|
1) Nevi may NARROW the overlying choriocapilaris. May rarely obliterate it
2) Slight degeneration, proliferation or reactive deposition by the RPE, may occur. In 40%, this induces overlying DRUSEN formation 3) May cause outer neural retinal changes. Usually minimal 4) Rarely, CENTRAL SEROUS CHOROIDOPATHY and SUBRETINAL NEOVASC. may occur |
|
|
Are UVEAL NEVI a precursor to anything?
|
Precusor to most uveal MELANOMAS
|
|
|
Are there in increase or decreased number of nevi in an eye that develops uveal melanoma?
|
An INCREASE
|
|
|
What are predictive factors for the progression of a uveal nevus to a uveal melanoma?
|
1) SIZE: The greater the thickness of a choroidal nevus, the greater is the chance of it becoming a melanoma. Of nevi 2.5 mm in thickness, approximately 1% per month become melanomas
2) LOCATION: Nevi at the posterior portion of the eye more commonly become melanomas than those situated anteriorly 3) ORANGE PIGMENT: When choroidal nevi develop orange pigment on their surface, the chance of a melanoma developing greatly increases. 4) SEROUS FLUID: Serous fluid in the form of an overlying retinal detachment can be seen with nevi, but such nevi more likely become melanomas. 5) Hot spots on FA 6) SYMPTOMS (decreased vision or visual field defect). |

