![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the ends of neurons called? |
Terminal buttons (synaptic knobs) |
|
|
In which direction do the messages (signals) flow in a neuron? |
In the direction of dendrites (terminal buttons) |
|
|
How are the proteins moved around a neuron (through axon towards the synaptic cleft)? |
Synaptic vesicles with neurotransmitters (=> proteins) are carried by kinasine down the microtubules within axons |
|
|
What is the most common type of neurons in terms of polarity? |
Multipolar (eg. motor neuron) |
|
|
Where are bipolar neurons generally found? |
in sensory systems |
|
|
Where are the unipolar neurons generally found? |
in somatosensory systems (part of the sensory system. It is reponsible for giving response to changes at the surface/inside the body) |
|
|
How do neurons communicate to one another? |
via Action Potentials |
|
|
What is an Action Potential? |
the electrochemical signal that gets passed down the axon. It is the communication mechanism of neurons. |
|
|
How many mV is the resting potential of a neuron? |
-70 mV {millivolts} |
|
|
How is the resting potential set up? |
The difference in the concentration of positively/negatively charged ions outside/inside of a neuron dictates when the resting potential occurs. In resting potential the inside of a neuron is -vely charged, whereas the outside is +vely charged. |
|
|
What is the order in which reactions happen in action potential (neuron firing)? |
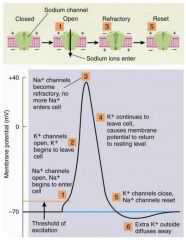
|
|
|
Does the action potential ever get regenerated while it travels down the axon? |
Yes, it does - in the Nodes of Ranvier [because otherwise it reduces in size] This is called Saltatory Conduction |
|
|
Are there any other types of cells in the CNS except for neurons? If yes, what are they? |
Yes, there are. Another major and important group is glial cells (Glia). |
|
|
What are the types of Glial cells? |
- Oligodendrocytes - Astrocytes - Microglia |
|
|
What are the functions of Oligodendrocytes? |
- provide support for neurons; - produce myelin. |
|
|
What type of cells in PNS has similar functions to Oligodendrocytes in CNS? |
Schwann cells |
|
|
What are the functions of Astrocytes? |
- support the blood-brain barrier; - provide neurons with nutriens; - repair damaged nervous tissue; - facilitate neurotransmittion. Overall: housekeeping, support, insulation |
|
|
What are the functions of Microglia? |
- inflammatory response to infection; - removal of dead tissue. |
|
|
What are the 2 approaches to measuring communication between neurons? |
- Electrical {Neurophysiology - measure flow of ions in the brain tissue} - Chemical {Microdialysis - measure levels of chemicals (eg. glucose, neurotransmitters) in the brain} |
|
|
What are the types of neurophysiological recording? |
- EEG (Electroencephalogram) - Multi-cell recording - Single-cell recording - Intracellular |
|
|
What can be studied with the use of EEG? |
- Sleep - Epilepsy (to pinpont the focus of seizure activity) - Cognitive processes |
|
|
Advantages of using EEG |
- High temporal resolution - Non-invasive (use with humans) |
|
|
Disadvantages of EEG |
- Low spatial resolution, - Recording only from cortex. |
|
|
What can multi-cell recording be used for? |
- Record signals from groups of neurons; - Record brain rhythms - local field potential (LFP) |
|
|
Advantages of multi-cell recording |
- OK spatial resolution (groups of neurons); - OK temporal resolution |
|
|
Disadvantage of multi-cell recording |
- only groups of neurons can be recorded; - Invasine |
|
|
Advantages of single-cell recording? |
- Very high spatial resolution (=> can be used to measure multiple single neurons); - High temporal resolution (=> can be used to measure action potentials) . |
|
|
Disadvantages of single cell recording |
- Doesn't give info of intracellular events (as it is extracellular); - Invasive |
|
|
What did Intracellular recording allow us to understand? |
how Action Potentials work |
|
|
Advantages of Intracellular recording |
- Very high spatial resolution (single neuron); - Allows to examine sub-cellular processes. |
|
|
Disadvantages of Intracellular recording |
- Only 1 cell at a time; - Invasive => allows to examine only animals under anaesthesia |
|
|
What is LFP (local field potential)? |
Brain rhythms; synchronous neuron firing that produces measurable waves of activity, & co-ordinates different brain areas. |
|
|
Example of how LFP works |
Memory (hippocampus) & attention (prefrontal cortex) coordinate by having coherent LFP when rats make a decision based on their memory (eg. as it happens at choice points of a maze) |
|
|
Is frequency or size more important in action potentials? |
Frequency; size is always the same. The more frequent, the stronger the signal. |
|
|
What are the 2 main types of post-synaptic receptors on dendrites? |
- Ionotropic (quick - "what colour are the traffic lights?"); - Metabotropic (slow - "keep you vigilant while driving"). |
|
|
What are the 2 main types of neurotransmitters? |
- Excitatory; - Inhibitory. |
|
|
What is the main function of excitatory neurotransmitters? |
- cause depolarisation (generate action potential by moving charge up from resting potential). - creates EPSP (excitatory post-synaptic potential), which increases the chances of post-synap. neuron firing. - eg. Glutamate |
|
|
What is the main function of inhibitory neurotransmitters? |
- cause hyperpolarisation (stop the generation of action potentials by making the membrane potential more -ve).
- create IPSP (inhibitory post-synaptic potential), which decreases the chance of post-synap. neuron firing. - eg. GABA (that treats depression) |
|
|
When does a neuron fire? |
when EPSP > IPSP |

