![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a substance capable of inducing an immune response, in most contexts synonymous with antigen?
|
Immunogen (antigen)
|
|
|
What is used to draw a distinction with substances capable of reacting only with antibody (antigens or haptens) or to denote a form of an antigen that induces an immune response as opposed to a tolerogen, a form that induces tolerance?
|
Immunogen (antigen)
|
|
|
What are any of the structurally related glycoproteins that are divided into five classes on the basis of structure and biologic activity?
|
Immunoglobulin (antibody)
|
|
|
What is a cell that displays an immunogen on its surface through the use of an MHC complex. Can be macrophages, dendritic cells and B cells?
|
Antigen Presenting Cell (APC)
|
|
|
What is a Chemical group against which immunoglobulin is formed. A site on the surface of an antigen molecule to which a single antibody molecule binds. Generally, an antigen has several or many different antigenic determinant and reacts with antibodies of many specificities?
|
Epitope (antigenic determinant)
|
|
|
What is a small molecule, not antigenic by itself, that can react with antibodies of appropriate specificity and elicit the formation of such antibodies when conjugated to a larger antigenic molecule, usually a protein, called in this context the carrier or schlepper. Antibody production involves activation of B lymphocytes by the hapten and helper T lymphocytes by the carrier?
|
Hapten
|
|
|
What is a Multi-specific antigen where More than on type of antigenic determinant is present?
|
Complex Immunogen
|
|
|
What has More than one antigenic determinant is present (all the same type)?
|
Multivalent Immunogen
|
|
|
These are very important in tissue transplants. Remember that human chromosomes have two strands, meaning that unless you're identical twins, you'll never have an exact match, even with siblings.
|
Major Histocompatibility Complex
|
|
|
What is another term for MHC?
|
HLA
|
|
|
What markers are on all nucleated human cells (every cell except erythrocytes). They give your tissue a "self" marker. For example, if you had an organ transplant, the marker for your new organ would be different than the markers on your native cells. This would illicit an immune response.
|
MHC Class I Markers
|
|
|
What markers can only hold endogenous antigens, meaning antigens that are made inside the cell. These antigens can be made solely from the human contents of the cell, or from a virus setting up its replication inside the cell.
|
MHC Class I Marker
|
|
|
These markers are only on immunocompetent (aka immunoresponsive) cells. Note: Lymphocytes have both Class 1 and class 2 MHCs on their surface.
|
MHC Class II Marker
|
|
|
What markers are made up of an alpha and beta chain. The peptide antigens attach right between the alpha and beta chains. There are two transmembrane sections, one on the alpha chain, one on the beta chain, that ties the marker inside the cell.
|
MHC Class II Markers
|
|
|
What markers are made up of an alpha chain and a beta chain. On the alpha chain is the "peptide binding groove," which is a region that varies depending on the antigen that can attach there. There is also a transmembrane section of the alpha chain that ties the marker into the cell.
|
MHC Class I
|
|
|
Which markers' role is to direct the CD4 lymphocyte, also known as the TH cell, to illicit an immune response and call other immunoresponsive cells into the area.
|
MHC Class II
|
|
|
What is A generic term for non-antibody proteins released by one cell population on contact with specific antigen, which act as intercellular mediators, as in the generation of an immune response?
|
Cytokines
|
|
|
What is An immunoglobulin heavy or light chain class or subclass characterized by antigenic determinants (isotypic markes) in the constant region. Every normal individual expresses all of the isotypes of its species.
|
Immunoglobulin Isotpes
|
|
|
What are monocytes that have left the blood stream, crossed the endothelium and enter tissues throughout the body. They reside in these locations for several months as macrophages?
|
Macrophage
|
|
|
What cells actively sample their environment by phagocytosis and serve as scavengers to remove cellular debris. Their ingested materials are enzymatically degraded?
|
Macrophages
|
|
|
What cells do this? when a TH-1 cell is activated, it sends out cytokines that call macrophages to the area. The macrophages will then ingest any foreign invaders. After ingestion, they will present an antigen of the foreign material on their surface, which can activate another immuno-cascade and call more immunoresponsive molecules to the area.
|
Macrophages
|
|
|
What are CD4 TH-1 lymphocytes?
|
1) Also called TDTH cells (Delayed Type Hypersensitivity)
|
|
|
1) These cells find an antigen in tissue the put out cytokine signals. This activates nearby cells, which are directed to attack
2) They recruit and regulate a variety of non-specific blood cells and macrophage in expression of delayed hypersensitivity reactions. 3) Cell-mediated immune response! |
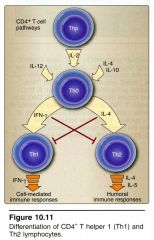
CD4 TH-1 lymphocyte
|
|
|
What cytokine would cause a Tho cell to differentiate into a Th2 cell?
|
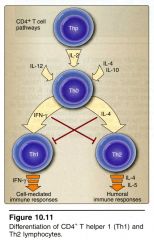
IL-4
|
|
|
1) Releases cytokines that attract both B cells and T cells.
2) Production of cytokines responsible for the proliferation and activation of B cells and their differentiation into plasma cells or memory B cells. 3) Humoral immune response! |
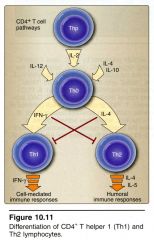
CD4 TH-2 lymphocyte
|
|
|
What are mature, active-antibody producing terminally differentiated B cells?
|
Plasma cells
|
|
|
What cells are held in reserve against future exposures to antigen and participate in the secondary adaptive immune response?
|
T or B memory cells
|
|
|
What cells are derived from T cells, but don't have either the CD4 or CD8 markers. They are NOT ANTIGEN SPECIFIC. They are drawn to the site and activated by Th-1 cells. They are cytolytic?
|
Natural Killer Cells
|
|
|
What antigens are made up of an alpha chain and a beta chain. On the alpha chian is the "peptide binding groove," which is a region that varies depending on the antigen that can attach there?
|
MHC Class I antigen
|
|
|
What antigen displays an immunogen from an endogenous source, meaning a source from within the cell. The immunogen can be native to the host cell, or can come from a virus replicating within the cell?
|
MHC Class I antigen
|
|
|
What antigen is found on all nucleated cells?
|
MHC Class I antigen
|
|
|
What antigen is made up of an alpha and a beta chain. The peptide antigens attach right between the alpha and beta chains?
|
MHC Class II antigen
|
|
|
What antigen displays an immunogen created from an exogenous source, meaning a source created outside the cell. This source can either be endocytosed, or, if we are talking about a B cell, it may have attached to a surface immunoglobulin and brought into the cell?
|
MHC Class II antigen
|
|
|
What type of antigen is found on APCs including dendritic, macrophage, and B cells
|
MHC Class II antigen
|
|
|
What type of antigen is recognized and bound by naturally occurring antibodies of the type IgM isotype?
|
ABO antigen
|
|
|
What type of antigens function in blood transfusions. Persons with type A blood develop antibodies against type B; persons with type B blood develop antibodies against type A; persons with type O blood develop antibodies against both type A and type B?
|
ABO antigen
|
|
|
What type of antigen is displayed on erythrocytes and some endothelial and epithelial cells?
|
ABO antigen
|
|
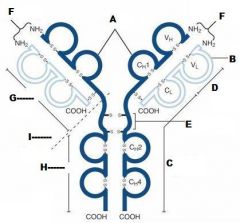
What is A?
|
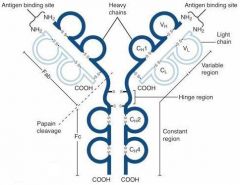
Heavy Chain
|
|
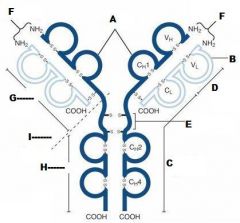
What is B?
|
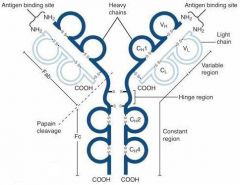
Light Chain
|
|
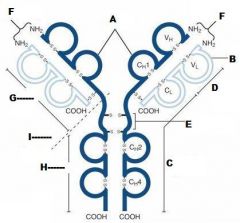
What is C?
|
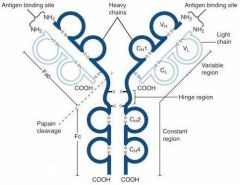
Constant region (Heavy chain along the entire length and light chain in the Fab portion)
|
|
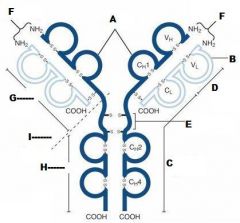
What is D?
|
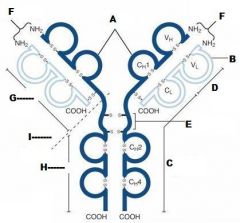
Variable Region
|
|
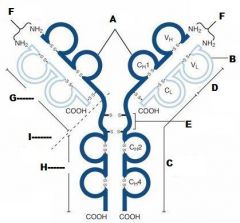
What is E?
|
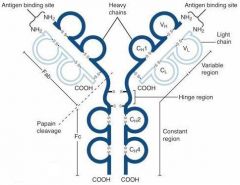
Hinge region
|
|
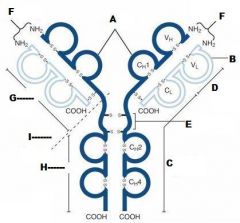
What is F?
|
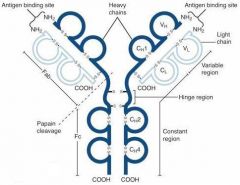
Antigen Binding Site
|
|
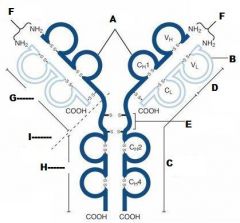
What is G?
|
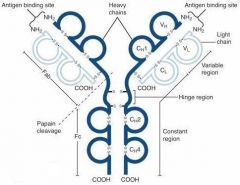
Fab Fragment
|
|
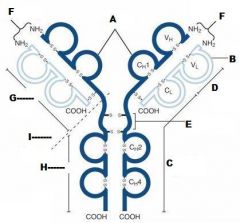
What is H?
|
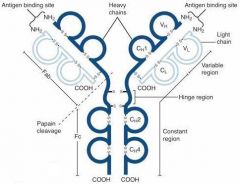
Fc Fragment
|
|
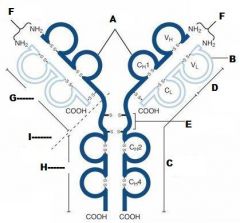
What is I?
|
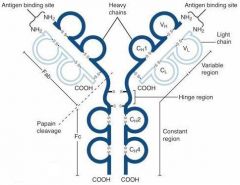
I is the vulnerable region when exposed to Papain, which creates 2Fab fragments and 1 Fc fragments
|
|
|
Where is the monomeric form of IgA found in the body?
|
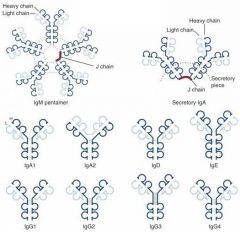
Serum
|
|
|
Where is the Dimer form of IgA found?
|
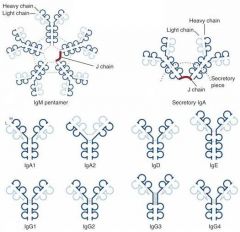
Mucosal surfaces, Saliva, Tears, Breast Milk and GI secretions
|
|
|
Are IgA immunoglobulins secreted, surface-bound, or both?
|
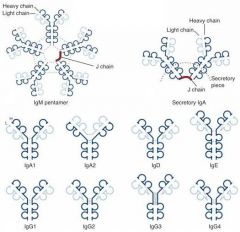
Secreted in monomer, dimer, and trimer forms
|
|
|
Which Immunoglobulin Dimer has a J chain, which is known as the secretory piece?
|
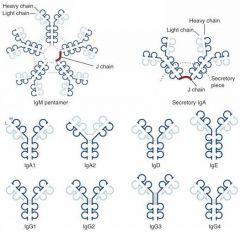
IgA
|
|
|
Which Immunoglobulins are capable of crossing the placenta?
|
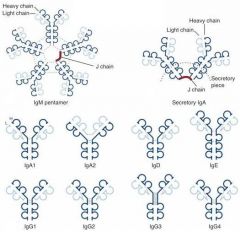
Only IgG
|
|
|
Which immunoglobulins can activate the complement system?
|
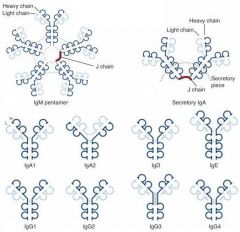
IgG & IgM(very efficient)
|
|
|
Which immunoglobulin provides:
1. Mucosal immunity 2. Neonate passive immunity 3. Transferred to mucosal cells where they are dimerized to be secreted into mucous |
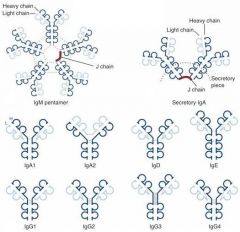
IgA
|
|
|
Are IgG immunoglobulins secreted, surface-bound, or both?
|
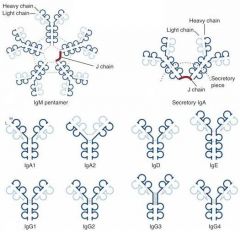
Both
Surface bound: Monomer Secreted: Monomer |
|
|
Which immunoglobulin makes up the greatest amount of antibodies in the serum?
|
IgG
|
|
|
What cell has the following surface markers?
1. CD4 2. β1 and β2 IL-12 Receptor 3. Releases IFNgamma |
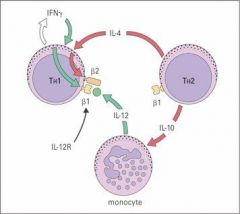
Th-1 Lymphocyte
|
|
|
Which cell has the following surface markers
1. CD4 2. β1 IL-12 Receptor 3. Release IL-4 and IL-5 |
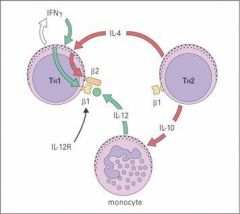
Th-2 Lymphocyte
|
|
|
What cell has a CD8 surface marker?
|
Tc Lymphocyte
|
|
|
What cell has IgD and/or IgM immunoglobulin on its surface?
|
B cell Lymphocyte
|
|
|
What cell has the following surface markers?
1. CD16 2. TCR gamma-beta (But NO CD8 or CD4) 3. Does not get processed in the thymus |
Natural Killer Cell
|
|
|
What is the process of an APC engulfing an exogenous complex (immunogen), processing it and displaying the antigenic determinants on its surface associated with the MHC class II marker?
|
1. Engulfment- macrophage engulfs the foreign material into a phagosome
2. Digestion- lysosome digests the contents of the phagosome 3. Peptides- during digestion the phagosome is reduced to peptides 4. MHC II receptors- MHC II receptors are created in the ER then transported to the golgi, where the remaining peptides from the digested phagosome are attached to the antigen binding site 5. Antigen displayed- The MHC II is released from the golgi and sent to the surface, where it becomes incorporated into the cell membrane and displays its antigen |

