![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Leishmaniasis takes three forms:
1. 2. 3. |
Leishmaniasis takes three forms:
1. cutaneous - restricted to skin 2. mucocutaneous - skin and mucosal surfaces 3. visceral- organs of reticulo-endothelial systems |
|
|
what are the 2 morphologic forms of leishmaniasis? Which is the infective form? |
Promastigotes (infective) in the vector (sand fly)
Amastigotes (in histiocytes of host) |
|

vector for what? |
Phlebotamus, Old World Leishmaniasis
Transmits: leishmania tropica, leishmania major
(butt is a little rounder than Lutzomyia of New World) |
|

vector for what? |
Lutzomyia, New World Leishmaniasis
Transmits: L mexicana, L braziliensis, L peruviana, L guyanesis, L panamensis
all names of places!!!!
(butt is a little pointier than Phlebotamus of Old World) |
|
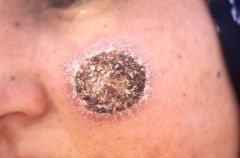
possible vectors? |
This is cutaneous Leishmaniasis
Vectors could be phlebotamus (old world) or lutzomyia (new world) |
|
|
Is disseminated cutaneous leishmaniaisis a Th1 or Th2 response? |
Th1 --> more effective in eradicating the organisms |
|
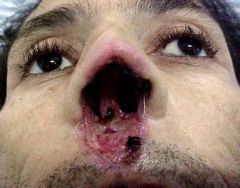
Pathogen? Clinical course? |
1st will get cutaneous ulcer, then will get mucosal lesions within 5-20 years
Old World: L aethiopica New World: L braziliensis |
|
|
Clinical symptoms of Kala-azar? |
Visceral leishmaniasis!
1st get cutaneous ulcer, then get visceral disease 1-36 months later
Macular hyperpigmentation in later stages (kala-azar = black fever)
Fever, wasting, cough, LAD, HSM, enteritis, oronasal/GI hemorrhage, PNA all can cause death in 2 years if not treated |
|
|
What is Marque Sign? |
amastigotes in histiocytes in Leishmaniasis |
|
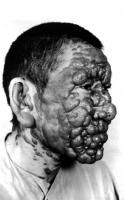
'but doc, I had visceral leishmaniasis YEARS ago, did it come back?' |
NOPE
post kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis
sequel to visceral leish that may arise several years after successful treatment of primary infection |
|
|
Treatment for:
cutaneous leish
mucocutaneous leish
visceral leish |
cutaneous- self resolving, but can use sodium stibogluconate antimony
mucocutaneous- pentavalent antimonials
visceral- pentavalent antimonials |
|
|
What are the major adverse side effects of pentavalent antimonials? Which are most commonly used? |
Megluminie antimoniate and sodium stibogluconate
used to treat mucocutaneous and visceral
cardiotoxicity (prolonged QT interval and ST-T wave changes), pancreatitis, hepatitis, thrombocytopenia
|
|
|
TOC for amebiasis? Skin findings with amebiasis? |
Entamoeba histolytica
less than 1% have cutaneous lesions (abscess, direct extension of rectal amebiasis to perianal/genital)
TOC: metronidazole |
|

Vector for? |
Reduvid bug
American trypanosomiasis (Chagas disease) |
|
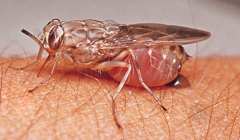
Vector for? |
Tse Tse fly
African trypanosomiasis (african sleeping sickness) |
|
|
Vector and cause of Chagas disease? Clinical course? |
Reduvid bug/ trypanosoma cruzi
Acute phase: lasts up to 2 months, fever, malaise, edema of face, romana sign, parinaud sign (romana plus periauricular LAD), macular eruptions
Intermediate phase: positive serology, asymptomatic
Chronic phase: myocarditis, megaesophagus, megacolon |
|
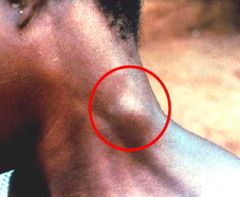
disease? |
Winterbottoms sign
posterior cervical LAD
seen with West African trypanosomiasis |
|
|
East vs West Trypanosomiasis, which more commonly gets cutaneous signs? |
East (rhodesiense) |
|
|
causative agents for african trypanosomiasis? |
East: trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense
West: trypanosoma brucei gambiense |
|
|
Skin symptoms associated with toxoplasmosis? Treatment? |
acquired- nodules, macular/papular/hemorrhagic eruptions
congenital- blueberry muffin
treat with sulfadiazine + pyrimethamine |
|
|
How does infection with the following Nematodes present?
1. strongyloides stercoralis
2. ancyclostoma caninum
3. gnathostoma dolorosi
4. anycyclostoma braziliense
5. dracunculus medinesis |
1. strongyloides stercoralis- larva currens (think of a racing current), moves 5-10cm/hr, disseminated thumbprint purpura near umbilicus with widespread petechiae
2. ancyclostoma caninum- rare cause of larva migrans
3. gnathostoma dolorosi- d/t eating raw fish
4. anycyclostoma braziliense- larva migrans (2cm/day)
5. dracunculus medinesis- from contaminated drinking water |
|
|
Cutaneous larva migrans is caused by what organism? Host? |
Larva of cat and dog hookworms --> ancyclostoma caninum and ancyclostoma braziliense
natural host is the dog and cat |
|
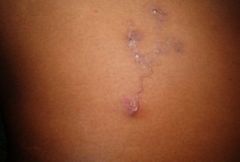
10 year old F presents after a vacation in mexico. Parents reported spending time sitting on the beach. MOC reports very slow expansion of the lesion. Most likely organism? Host? |
Cutaneous larval migrans-- anycylostoma braziliense (more common than canium)
remember, strongyloides stercoralis causes larva currens (5-10cm/hr)
cats and dogs are the host |
|
|
treatment for cutaneous larva migrans? |
albendazole, ivermectin |
|
|
Feared complication of Cutaneous Larva Migrans? |
Loeffler syndrome: patchy lung infiltrate |
|

Vector for? |
Black fly Simulium
Vector for onchocerca volvulus --> onchocerciasis |
|
|
Clinical presentation of onchocerciasis? Cause? |
Cutaneous changes: onchocercomas (nodules of worms) thick/wrinkled skin atrophy and pigment loss with perfollicular sparing on shins (leopard skin) chronic lymphatic obstruction (huge scrot) conjunctivitis keratitis |
|
|
Onchocerciasis treatment? |
oral ivermectin
adding doxycycline to treatment regimen kills the intracellular endosymbionts bacteria Wolbachia, which leads to nematode sterility and inhibits larval development |
|
|
Fiariasis is infection of the lymphatic system with tissue round worms by mosquito vectors... two pathogens? |
Wuchereria bancrofti
Brugia malayi |
|
|
3 MC species of schistosomiasis? Where do they infect? |
1. S. haematobium (urinary) 2. S. japonicum (GI) 3. S. mansoni (GI) |
|
|
Chronic infections with S. mansoni and S. japonicum can lead to... |
hepatic fibrosis, cirrhosis --> portal hypertension |
|
|
Chronic infection with S. haematobium can lead to... |
carcinoma of the bladder |
|
|
Intermediate host for schistosomiasis? |
snail |
|
|
Cysticercosis is d/t ingestion of the eggs of... 1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. taenia solium (pork) 2. taenia saginata (beef) 3. diphyllobothrium latum 4. hymenolepsis nana |

