![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is homeostasis? |
To regulation of conditions to maintain a stable environment |
|
|
Give 2 conditions that are controlled by homeostasis |
Blood glucose level Body temperature |
|
|
The body has control systems that regulate internal conditions. What components do all control systems include? |
Receptors, a coordination centre and effectors. |
|
|
Why is negative feedback important? |
Negative feedback helps to maintain a stable inyernal environment. It acts against a change in a conditiom, to return it back to normal levels. |
|
|
What are receptors? |
A group of specialised cells that detect a stimulus |
|
|
What are coordination centres? |
The corrdination centre recieves and processes information from receptors around the body |
|
|
3 examples of a coordination centre |
Brain Spinal cord Pancreas |
|
|
What are effectors? |
Effectors produce a specific response to a detected stimulus. |
|
|
Example of effectors |
A muscle contracting to move an arm |
|
|
What are muscles and glands examples of |
Effectors |
|
|
In humans, what does the central nervous system consist of? |
The brain and spinal cord |
|
|
Which type of neurome carries impulses from the CNS to effectors? |
Motor neurone |
|
|
Examples of receptors |
Eyes and tongue |
|
|
Examples of stimulus |
Light and sound |
|
|
Nervous coordination |
Electrical impulses transmitted by the nervous system |
|
|
Hormonal cordination |
Chemical messengers (hormones carried by the blood) |
|
|
What type of neurone carries impulses from the receptors to the CNS |
Sensory neurone |
|
|
Myelin sheath |
Insulates the Axon |
|
|
Axon |
Transmits nerve impulse |
|
|
Dendrites |
Makes lots of other connections with other neurones |
|
|
Why is the nervous system important in humans |
The nervous sytem means that humand can react to their surroundings and coordinate their behaviour |
|
|
How is the stimulus transmitted from receptors to the CNS? |
Sensory neurones carry the information from receptors to the CNS |
|
|
How does the CNS coordinate a humans response to something? |
The CNS decides what to do with the information it recieves. It then sends the information to the effectors along motor neurones. The muscles contract and the human reacts to the stimulus. |
|
|
What is reaction time? |
The time it takes to respond to a stimulus |
|
|
What is a synapse |
The small gap between where two neurons meet |
|
|
How are nerve signals transferred across a synapse? |
Chemicals diffuse across the synapse and set off a new electrical impulse in the next neurone |
|
|
What is a reflex arc? |
The passage of information in a reflex (from receptor to effector) |
|
|
Reflexes do not involve conscious parts of the brain. Why is this advantageous? |
It reduces the chance of an injury, as it means that reflexes can be rapid and automatic |
|
|
Alcohol is a depressant, which means it reduces the effectiveness of neurone signalling. Suggest what effect this would have on a person's reaction time |
Reaction time will be slower because the nerve signals take longer to transmit around the body, so the response will take longer. |
|
|
A womans hand gets burned when touching a kettle. A reflex causes her to immediately move her hand away from the kettle. What is the effector in this reflex action? |
The muscles in her hand |
|
|
Describe the pathway taken by this reflex from the kettle stimulus to the response |
1)The stimulus is detected by the pain receptors in the hand 2)These send impulses along sensory neurones to a relay neurone in the CNS. 3)The impulse is then transmitted between the relay neurone and moto neurone 4)Impulses travel along the motor neurone to the hand muscles (effector), which contract to kove her hand away from the kettle. |
|
|
How are hormones transported around the body? |
In the blood |
|
|
Do males have ovaries? |
No, they have testes instead |
|
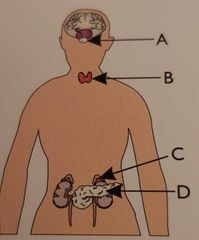
Which gland is the pancreas? |
Gland D |
|
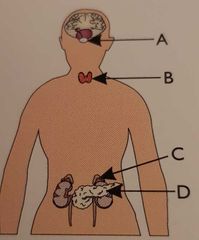
Which gland is the thyroid? |
Gland B |
|
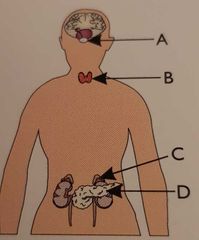
Which gland is the adrenile gland? |
Gland C |
|
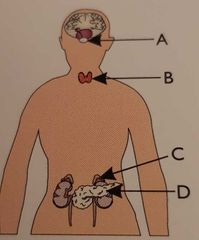
Which gland is the pituitary gland |
Gland A |
|
|
Why is the pituitary gland called the "master gland"? |
The hormones it releases acts on other glands, directing them to release hormones that bring out change. |
|
|
Jared burns his hand which leads to responses in both the endocrine system and the nervous system. Give two ways in which you would expect these responses to differ. |
1) The hormonal response in the endocrine system will be much slower than the nervous system response 2) The hormonal response will act in a more general way, whereas the nerves will act in a precise area |
|
|
Which gland monitors and controls blood glucose concentration? |
Pancreas |
|
|
In Type 2 diabetes, what happens to a persons insulin? |
The body cells no longer respond to insulin. |
|
|
Give 2 treatments for controlling type 2 diabetes |
Eating a carbohydrate-controlled diet and getting regular exersise |
|
|
What is type 1 diabetes and how is it treated? |
Type 1 diabetes is where the pancreas produces little or no insulin. It is treated with insulin therapy, where insulin is injected regularly throughout the day. Patients are also advised to exersise amd limit their carbohydrate intake |
|
|
A person without diabetes eats a carbohydrate meal. What happens to their blood glucose concentration? |
Insulin is secreted by the pancreas. This causes glucose to move from the blood into the cells of the liver and muscles, where it is stored as glycogen. |
|
|
What hormone increases that persons blood glucose levels |
Glucagon acts to increase glucose levels by converting glycogen into glucose, which is then released into their blood. |
|
|
Name the hormone that stimulates sperm production |
Testosterone |
|
|
What term is used to describe the release of an egg from an ovary? |
Ovulation |
|
|
Describe how hormones control the growth and release of an egg |
Follicle-stimulating hormones (FSH) causes an egg to mature in a follicle in one lf the ovaries. Luteinising hormone (LH) then stimulates the release of a matured egg at day 14. |
|
|
Describe how the lining of the uterus changes over the stages of the menstural cycle |
1) During stage 1 of the menstural cycle the uterus lining breaks down 2) During stage 2 the lining of the uterus builds up again into a thick layer of blood vessels 3) The lining of the uterus is then maintained during stages 3 and 4 4) If no embryo implants in the uterus wall by day 28, the uterus lining starts to break down, and a new cycle behins at stage 1 |
|
|
What is Oestrogen |
The hormone that causes the lining of the uterus to grow between days 4 and 14. It stimulates LH (which stimulates the release of an egg) and inhibits the release of FSH (which stops another egg from maturing during that month's cycle). |
|
|
One example of a non-hormonal method ofncontaception. |
Condom |
|
|
Which hormone does the contraception injection contain? |
Progesterone |
|
|
How does the contraceptive pill use hormones to reduce fertility? |
The pill contains oestrogen and progesterone. Oestrogen inhibits the production of FSH and so stops an egg from developing. Progesterone also inhibits egg maturation, therefore also inhibiting the release of an egg. |
|
|
What is "in vitro fertilisation"(IVF) |
When an egg is fertilised by sperm in a lab, and then transferred into a uterus |
|
|
One ethical reason why IVF is wrong |
It is unethical to destroy extra embryos that are not used |
|
|
At which point in the IVF process is someone given the hormones FSH and LH? Explain why these hormones are given. |
They are given before egg collection. They are given to stimulate several eggs to mature so that more than one egg can be collected |
|
|
One advantage of IVF |
It allows an infertile couple to have a child |
|
|
One disadvantage of IVF |
IVF has a low success rate |
|
|
Name the gland that produces adrenaline |
Adrenal glands |
|
|
What is the "basal metabolic rate" |
The rate at which chemical reactions happen in the body when the body is at rest. |
|
|
Owen has hypothyroidism, a disease which affects the activity of his thyroid. As a resuly he has a low basal metabolic rate. Suggest whether Owen has an overeactive or an undereactive thyroid. |
Owen has an undereactive thyroid. Not enough thryoxine is being released from the thyroid to stimulate his basal metabolic rate. |
|
|
If someone gets scared by something, explain their response |
1) the brain detects the fear and send nervous impulses to the adrenal glands which respond by secreting adrenaline.
2) this increases the heart rate to help increase the supply of oxygen and glucose to the brain and muscles to prepare for the "fight or flight" response. |
|
|
What is thyroxine |
Hormones prlduced and released by the thyroid gland |
|
|
How is the level of thyroxine in the blood controlled? |
Its levels are controlled by negative feedback. |

