![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an ecosystem |
A physical environment with a particular set of conditions, plus all the organisms that live in it |
|
|
What is a natural ecosystem |
They have high biodiversity, i.e many different species of plants and animals coexist in the same environment |
|
|
What is a artificial ecosystem |
Artificial ecosystems, e.g greenhouses, are designed and maintained for a particular purpose so they have a lower biodiversity |
|
|
What may be used in artificial ecosytems to prevent other animals and plants from growing alongside the crop |
Weedkillers Fertilisers Pesticides |
|
|
What are forestry plantations |
They are very carefully set up, controlled and maintained. They will have less biodiversity due to the fact they haven't been established for as long as natural woodland, which take years to form, and result from the relationships and interactions of the organisms that live there and their surroundings. Fewer species are introduced at the set up stage and not all species survive from the start |
|
|
Fish farms |
They will show less biodiversity due to the shorter time they have existed compare to lakes. Plus in the absence of many predators some fish species will thrive while others will not. Also there are fewer diseases which may result in too many of certain species reducing others |
|
|
What is a habitat |
The part of the physical environment where an animal or plant lived. An organism will have adapted to it's habitat, so it may be restricted to living there. It may only eat the food there |
|
|
What is a community |
The total number of individuals of all the different populations of plants and animals that live together in a habitat at any one time |
|
|
What is a population |
The total number of individuals of the Same species that live in a certain area |
|
|
What is a pooter |

A container used to collect insects easily,without harming them |
|
|
What is a sweepnet used for |

Collecting insects in long grass or moderately dense woodland where there are lots of shrubs |
|
|
What is a pitfall trap |
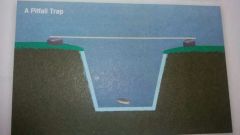
A container set into the ground to catch small insects e.g beetles |
|
|
What is a quadrat |

A square frame that has sides usually 0.5m long |
|
|
What are quadrats used for |
To count a smaller, representative part of a population. |
|
|
How should you use a quadrat |
You should throw them randomly onto the ground then count and record the number of each species within the quadrat. |
|
|
Estimating the population a a species in a given area |

|
|
|
Steps of the capture-recapture method |
- A TRAP IS USED TO CATCH A SAMPLE OF INDIVIDUALS E.G NICE - THE SAMPLE IS COUNTED AND RECORDED AND EACH INDIVIDUAL IS MARKED WITH A NUMBER TAG/ BAND OR DOT OF PAINT - THE INDIVIDUALS ARE THEN RELEASED UNHARMED BACK INTO THE ENVIRONMENT AND GIVEN TIME TO REDISTRIBUTE THEMSELVES AMONGST THE UNMARKED POPULATION - ANOTHER SAMPLE OF INDIVIDUALS IS CAPTURED, SOME OF WHICH ARE ALREADY MARKED AND SOME ARE UNMARKED - THE UNMARKED ANIMALS ARE COUNTED AND RECORDED. THEN MARKED AND RELEASED |
|
|
Formula for estimating the total population size in the habitat |
No. In 1st sample ×no. In 2nd sample ÷ the no. In 2nd sample which were previously marked |
|
|
What is a transect line used for |
To map the distribution of organisms. It is used for studies of how species change across a boundary between habitats e.g a rocky shoreline |
|
|
How do you do a transect line |
- a line like a tape measure is laid out - quadrats are distributed in regular intervals on the line, and the species in the quadrats are counted |
|
|
What do kite diagrams show |
Zonation |
|
|
What is zonation |
The gradual change in the distribution of species across a habitat |
|
|
What is a key used for |
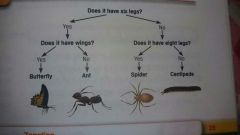
Correctly identifying species in a sample |
|
|
What is photosynthesis |
When green plants make their own food (glucose and starch) using sunlight |
|
|
What does photosynthesis produce |
Glucose for biomass and energy. Oxygen is released as a by product. |
|
|
Equation for photosynthesis |
Carbon dioxide + water ---》glucose + oxygen 6CO2 + 6H20 --》C6 H12 O6 + 6O2 |
|
|
Glucose and starch can be converted into: |
- energy during respiration -Proteins for growth and repair - starch, fats or oils that can be stored in seeds - cellulose which is needed for plant call walls |
|
|
Transprtation and storage of glucose |
Glucose is soluble. It can be transported around the plant as soluble sugar, but it must be converted into starch,which is insoluble, I'm order to be stored |
|
|
Photosynthesis can be increased by increasing: |
- the temperature using heaters in a greenhouse - the light intensity using lamps in a greenhouse - the carbon dioxide concentration using chemicals or as a by product of using gas heaters in a greenhouse |
|
|
Why do plants respire |
To break down glucose to release energy. They respire all the time e.g day and night |
|
|
Where does photosynthesis occur |
Mainly in the leaves of plants |
|
|
How are leaves specially adapted for efficiency |
-Contain pigmet chlorophyll which absorbs light in millions of chloroplasts - is broad and flat to provide a huge surface area to absord sunlight -Has a network of vascular bundles for support and to transport water to the cells and remove the products of photosynthesis e.g glucose - has a thin structure so the carbon dioxide and oxygen only have a short distance to travel to and from the cells - has stomata( tiny pores) on the underside of the leaf to allow exchange of gases |

