![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the advantages of being multi- over uni- cellular
|
Organism is larger
Cell differentiation Organisms can be more complexed |
|
|
What do multicellular organisms need to have organisms for
|
Communication between cells → nervous system circulatory system
Supplying the cells with nutrients → digestive system Controlling exchanges with the environment → respiratory system, excretory system |
|
|
What type of cells are body cells
|
Diploid
|
|
|
Why do chromosomes need to be copied
|
So that new cells can be produced for:
Growth Repair to damaged tissue Replacement of worn out cells Asexual reproduction (which involves only one parent) |
|
|
When is mitosis used
|
cell division
|
|
|
Explain the process of mitosis
|
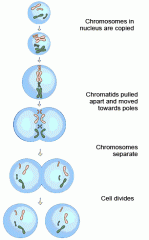
1. Chromosomes in the nucleus are copied
2. Chromatids pulled apart and moved towards the poles 3. Chromosomes separate 4. Cell divides |
|
|
What does human reproduction involve
|
Two parent
Sexual intercourse Offspring that are unique |
|
|
What type of cells are gametes
|
Haploid
|
|
|
What are the adaptations of a sperm cell
|
Tail - to move them towards the egg
Increased amount of mitochondria Acrosome - releases enzymes to digest the egg membrane |
|
|
How are gametes produced
|
Meiosis
|
|
|
What is a haploid
|
Contains only one just one of the chromosomes from each pair and half of the genetic material of a body cell
|
|
|
Why does fertilization lead to genetic variation
|
2 Gametes combine to form a diploid zygote
Genes on chromosomes combine to control the characteristics of the zygote |
|
|
Explain the process of DNA replication
|
The DNA 'unzips' to form single strands
Free nucleotides lock on to bases - complementary base pairing New double strands |
|
|
Explain the process of meiosis
|
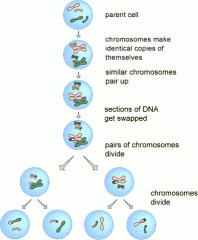
Chromosomes make a identical copies of themselves, whilst they're in the parent cell
Similar chromosomes pair up Sections of DNA get swapped Pairs of chromosomes divide - into diploid cells They then split - creating haploid cells |
|
|
What must happen before mitosis can occur
|
DNA repication
|

