![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name 5 AC waveforms. Which is the most common? |
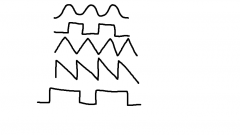
1) Sine Wave (Most common) 2) Square Wave 3) Triangle 4) Sawtooth 5) Rectangular |
|
|
What is the purpose of Electricity? |
To do work |
|
|
What is the primary function of DC electricity? |
To power the circuit |
|
|
What is one of the most important uses of AC electricity? |
To take the form of the information we process. AC adapts the information we want to send wirelessly across a long distance to the medium that will carry it. (a.k.a. the atmosphere for radio waves)
|
|
|
What are 3 forms that AC signals can take? |
1) Voice 2) Digital data 3) Analog signals |
|
|
What are the 3 requirements of a communication system? |
1) Transmitter (Ex: Mickey's mouth) 2) Medium (Ex: air, the atmosphere) 3) Receiver (Ex: my ears, assuming I am still awake...) |
|
|
Describe the steps that occur when a DC powered radio sends a signal to another one. |
1) DC powers radio 2) Mic converts sound waves into AC current 3) Radio waves are transmitted 4) Another DC powered radio receives the signal 5) AC speaker converts AC signal back into sound waves |
|
|
Describe Direct Current |
1) Current only flows in one direction
2) Current and Voltage can change in magnitude, but not direction 3) Current flow is caused by a difference in potential (+ and -) 4) DC is capable of performing work |
|
|
What causes the difference of potential that drives DC electricity? |
Electrostatic forces, that is, the forces of attraction and repulsion between + and - charges. |
|
|
________ is required to perform work. The ________ provide the ________ that allows electricity to perform work. |
MASS, ELECTRONS, MASS |
|
|
How many valence electrons does an insulator have? |
>4 electrons |
|
|
How many e-'s does a semi-conductor have? |
exactly 4 e-'s |
|
|
How many e-'s does a conductor have? |
<4 e-'s |
|
|
What are the 3 requirements of a circuit? |
1) Source of current flow 2) Conductor to carry current 3) At least one Load to use current |
|
|
What is a Capacitor? |
A device used to store electrical energy in an Electro-static field. Composed of 2 conductors separated by an insulator |
|
|
What is an Inductor? |
A coil or device used to induce current in a conductor |
|
|
Which rule applies to Electron Flow Theory, the Left Hand Rule for coils, or the RIght Hand Rule for coils? |
Left Hand Rule for coils; If fingers of left hand curl in direction of current flow in the coil, then the thumb indicates the North Pole of the magnetic field being generated |
|
|
What is Magnetism? |
The ability to attract materials containing Iron, and to influence e-'s |
|
|
What are the two types of Magnets? |
Permanent, Electromagnet |
|
|
What 7 things determine the strength of an electromagnet? |
1) Wire AWG 2) # of loops in coil 3) Size of loops in coil 4) Loop spacing 5) # of layers of loops 6) Core type 7) Amount of current flow |
|
|
Name the two types of Electrostatic Force |
1) Attraction (+ and -) 2) Repulsion (+ and+ or - and -) |
|
|
Define Voltage simply. |
A difference in potential between 2 unequal charges. Also called "Electromotive Force" |
|
|
What are the 4 characteristics of Electricity? What are their symbols? What are their units? |
1) Current (I), amps 2) Voltage (E), volts 3) Resistance (R), ohms 4) Power (P), Watts |
|
|
Define "Ampere" |
1 Coulomb of charge through a point in 1 second |
|
|
What is a "Coulomb?" |
6.28 Billion Billion electrons |
|
|
What is a "Volt?" |
Electrical pressure (EMF) required to push 1 Amp of current through 1 Ohm of resistance |
|
|
What is an "Ohm" |
The amount of resistance that limits current flow to 1 Amp under 1 Volt of pressure |
|
|
What is a "Watt" (and Who's on second?) |
The amount of power consumed when 1 Amp of current flows through 1 Ohm of resistance under 1 Volt of pressure |
|
|
What causes resistance? What does it produce? |
Friction, Heat |
|
|
Resistance _________ 'I', __________ 'V', and _________ 'P'. |
Opposes, Drops, Consumes |
|
|
Define "Power" |
A measure of the rate at which energy is used. It often takes the form of heat (whatever that means...) |
|
|
Name 3 effects that heat has on electrical components |
1) Changes their values 2) Changes their resistance 3) Causes them to fail |
|
|
What are the 3 failure modes? VERY briefly describe each one |
1) Catastrophic - "BOOM," the thing failed.
2) Latent - Should have taken better care of it... (shortened working life) 3) Intermittent - It's a very on-again, off-again kind of relationship. |
|
|
Give the equations for Ohm's Laws |
E = I x R P = I x E |
|
|
What determines the type of circuit that a circuit is, or chooses to be if it wasn't born that way? |
The number of different paths for current |
|
|
What determines the resistance of a conductor? |
1) AWG (cross-sectional area) 2) Length 3) Material (Al or Cu on aircraft) 4) Temperature (T and R are directly proportional) |
|
|
Name 4 benefits of the Single Wire Method used in aircraft |
1) Cost savings 2) Weight savings 3) Space savings 4) Less electromagnetic/radio frequency interference |
|
|
What special equation can be used for Parallel circuits if the resistance in ALL Branches is the SAME? |

|
|
|
What special equation can be used for Parallel circuits if there are ONLY 2 Branches? |
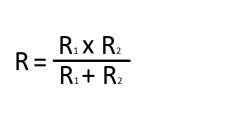
|
|
|
Why is AC current used more and more in aircraft? (4 reasons) |
1) It is easier to produce in large quantities 2) AC values are easier to change (current, voltage) 3) Requires smaller components 4) Savings in Weight, Space, and Cost |
|
|
What 3 things are required in order to produce AC using Magnetism? |
1) Motion 2) Conductor 3) Magnetic Field |
|
|
Define "Induction" |
The wireless transfer of energy |
|
|
When using the term "AC," it can be assumed that the ___________ __________ is being referred to. |
Effective Value |
|
|
Average Value = ? |
Average Value = 0.637 x Peak Value |
|
|
Which value of AC is considered to be the Most Important value? |
Effective Value |
|
|
What is another name for the Effective Value? |
Root-Mean-Squared value |
|
|
Describe the Effective Value |
1) It can be compared to DC by the amount of work it can perform 2) EV = 0.707 x Peak Value (70.7% of PV) 3) EV is the value that is MEASURED by multimeter or other equipment |
|
|
AC Peak = ? AC Peak - Peak = ? |
AC peak = 1/2 of Peak - Peak value or = 1.41 x RMS AC Peak - Peak = 2x Peak value |
|
|
Define "Frequency" for AC |
# of cycles of AC per second. Measured in Hertz (Hz) |
|
|
What is a "Hertz?" |
1 Hertz (Hz) = 1 AC cycle in one second |
|
|
What is the most common Frequency in Aircraft AC systems? |
400 Hz |
|
|
Define "Period" |
Time required for one cycle of AC to occur (in seconds, mSec, uSec, etc.) |
|
|
What is "True Power?" |
Power value that takes into account Phase Shift, and is the actual amount of Power available for use. |
|
|
What is "Apparent Power?" |
AP = Effective 'E' x Effective 'I' Does NOT take into account Phase Shift IS expressed in VOLT-AMPS (VA) instead of watts |
|
|
What is the "Power Factor?" |
1) The amount of 'I' that is IN PHASE with the 'E' 2) Ratio between True Power and Apparent Power 3) When 'E' and 'I' are in phase, PF = 1.0 4) PF = cos(phase angle) when 'I' and 'E' are NOT in phase 5) When PF = 1.0, True Power = Apparent Power |
|
|
What is "Impedence?" |
The total opposition to the flow of current. (Resistance + Reactance) Symbol = Z |
|
|
What is "Reactance?" |
The opposition to the flow of current from Inductance or Capacitance. Total reactance is the sum of these two. (Symbol for reactance = X) |
|
|
Give the equation for Ohm's Law for AC |

|
|
|
Give the equation for Inductive Reactance |

|
|
|
Give the equation for Capacitive Reactance |
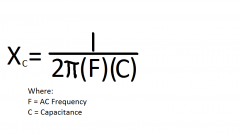
|
|
|
Give the equation for Total Reactance |
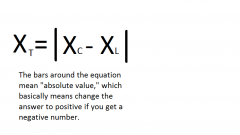
|
|
|
Give the equation for Impedence |

|
|
|
Give the equation for Apparent Power |
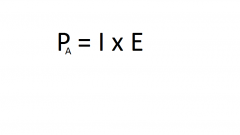
|
|
|
Give the equation for True Power |
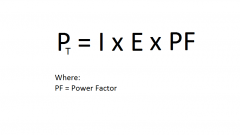
|
|
|
Give the equation for Power Factor |

|

