![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
149 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Birds belong to what taxonomic class?
|
Class Aves
|
|
|
Name 5 orders of birds commonly used in research.
|
Galliformes, Anseriformes, Columbiformes, Passeriformes, Psittaciformes
|
|
|
Which order includes chickens, turkeys, and quail?
|
Order Galliformes
|
|
|
Which order includes pigeons and doves?
|
Order Columbiformes
|
|
|
What is the genus & species of the domestic chicken?
|
Gallus domesticus
|
|
|
What breed/strain of chicken is a model of vitiligo?
|
Smyth Chicken
|
|
|
What breed/strain of chicken is a model of scleroderma?
|
White Leghorn
|
|
|
What breed/strain of chicken is a model of Hashimotos thyroiditis?
|
Obese strain (OS)
|
|
|
What breed/strain of chicken is a model of hereditary muscular dystrophy?
|
New Hampshire
|
|
|
What is the genus and species of the Japanese quail?
|
Coturnix cotunix japonica
|
|
|
What is the genus and species of the turkey?
|
Meleagris gallopavo
|
|
|
What disease in turkeys is a model for congestive cardiomyopathy in humans?
|
Round Heart Disease of turkeys
|
|
|
What is the genus and species of the duck?
|
Anas platyrynchos
|
|
|
What is the Guide recommendation for floor area for the pigeon?
|
0.8 square feet
|
|
|
What is the Guide recommendation for floor are for the following sized chickens(in sq.ft)?
a. < .25 kg _____________ b. Up to .5 kg _____________ c. Up to 1.5 kg ____________ d. Up to 3.0 kg ______________ e. > 3.0 kg _________________ |
a. .25
b. .50 c. 1.00 d. 2.00 e. >3.00 |
|
|
What is the Guide recommended temperature range for farm animals and poultry?
_______________ degrees Celsuis; ______________ degrees Fahrenheit |
16-27; 61-81
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most appropriate incubation period (in days) for chicken and pigeon eggs, respectively?
a. 21 and 12-15 b. 28 and 12-15 c. 21-28 and 27-28 d. 21 and 17 e. 28 and 18 |
D
|
|
|
What avian cell is larger than any other single cell in any animal?
|
The primary oocyte
|
|
|
In most female birds, what side of the reproductive tract is functional?
|
The left side
|
|
|
What part of the female reproductive tract of birds is often referred to as the uterus?
|
The shell gland
|
|
|
What is the etiology agent of Fowl Cholera?
|
Pasteurella multocida
|
|
|
What is the etiological agent of Necrotic Enteritis?
|
Clostridium perfringens
|
|
|
What is the common name for Botulism( Clostridium botulinum) in birds?
|
Limberneck (also Western Duck Sickness)
|
|
|
What is the etiologic agent of Red Skin Disease?
|
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
|
|
|
What avian species is primarily affected by Red Skin Disease?
|
Turkeys
|
|
|
What species of Salmonella is most commonly associated with parathyroid infection?
|
S. typhimurium
|
|
|
What is the etiologic agent of Pullorum Disease?
|
Salmonella pullorum
|
|
|
In very extremely elementary, don’t think too hard, incredibly simple terms, describe the mortality associated with Pullorum Disease in young chicks and poults?
|
It is very high
|
|
|
What is the etiologic agent of Fowl Typhoid?
|
Salmonella gallinarum
|
|
|
What is the etiologic agent of Avian Mycoplasmosis, Chronic Respiratory Disease (CRD) in chickens, PPLO Infection, and Infectious Sinusitis of Turkeys?
|
Mycoplasma gallisepticum
|
|
|
What is the etiologic agent of Infectious Synovitis?
|
Mycoplasma synoviae
|
|
|
“Musky Chick Disease” refers to what condition?
|
Omphalitis (Navel Ill)
|
|
|
What is the etiologic agent of Infectious Coryza?
|
Haemophilus paragallinarum
|
|
|
Ornithiosis refers to infection with what organism?
|
Chlamydophila psittaci
|
|
|
Name two stains that can be used to diagnose Ornithosis?
|
Maciavello and Giemsa
|
|
|
Name the forms of Fowl Pox?
|
Cutaneous and Wet (Diphtheritic)
|
|
|
What avian disease can be diagnosed by demonstration of Bollinger bodies?
|
Fowl Pox
|
|
|
Infectious Laryngotracheitis is caused by a virus in the family _______, and subfamily _______.
|
Herpesviridae; Alphaherpesvirinae
|
|
|
The presence of intranuclear inclusion bodies in tracheal epithelium is pathognomic for what disease?
|
Infectious Laryngotracheitis
|
|
|
Newcastle Disease is a member of the viral family _____________________.
|
Paramyxoviridae
|
|
|
What are the three forms of Newcastle Disease, and which is the most severe?
_________________, _________________________, ______________________. |
lentogenic, mesogenis, and velogenic; velogenic is most severe
|
|
|
Fowl plague, also termed _____________ ___________, is an Orthomyxovirus.
|
Avian Influenza
|
|
|
What viral family causes Infectious Bronchitis?
|
Coronoviridae
|
|
|
Avian Encephalomyelitis (Epidemic tremor) is caused by a member of what viral family?
|
Picornaviridae
|
|
|
Viral Arthritis and Tenosynovitis are caused by what family of virus?
|
Reoviridae
|
|
|
What type of herpes virus causes Marek’s Disease?
|
Alphaherpesvirus
|
|
|
What is the primary differential for Marek’s Disease?
|
Lymphoid Leukosis
|
|
|
What viral family does EEE belong to?
|
Togaviridae
|
|
|
What viral family includes the etiologic agent of Lymphoid Leukosis?
|
Retroviridae
|
|
|
Infectious Bursal Disease (Gumboro Disease) is caused by a member of the family __________?
|
Birnaviridae
|
|
|
What is the primary target of Infectious Bursal Disease?
|
The cloacal bursa
|
|
|
Infectious Anemia of Poultry ( Chick anemia agent) is caused by a virus in the family ___________, a single stranded, non-enveloped DNA virus.
|
Circoviridae
|
|
|
What parasite contains the causative agent of Blackhead(Infectious Enterhepatitis)?
|
Heterakis gallinarum
|
|
|
What is the causative agent of Blackhead? What type of organism is this agent?
|
Histomonas meleagridis, protozoan
|
|
|
What is the causative agent of Turkey malaria and how is it transmitted to susceptible turkeys, chickens and other birds?
|
Leukocytozoon smithi
|
|
|
What is the genus and species of the Gapeworm?
|
Syngamus trachea
|
|
|
You have found a chicken with roundworms infestation. What is the likely genus and species? You have found a pigeon with the same condition, What is the likely genus and species?
|
Ascaridia galli; Ascaridia columbae
|
|
|
“Hairworm and “Cropworm” infestation refer to infestation of what parasite?
|
Capillaria
|
|
|
The most important external parasite of caged layers and breeding chickens is ______________________ (genus and species), also known as _______________________(common name).
|
Ornithonysus sylviarum; Northern Fowl Mite
|
|
|
What is the genus and species of the scaly leg mite?
|
Knemidokoptes mutans
|
|
|
Where on the body does the scaly leg mite primary live?
|
unfeathered skin, often on the shanks and feet
|
|
|
What etiologic agent causes brooder pneumonia?
|
Aspergillus fumigatus
|
|
|
What condition causes “Crazy Check Disease”?
|
Vitamin E deficiency
|
|
|
What condition(s) is/are the main cause(s) of Perosis(slipped tendon)?
|
Mainly due to deficiency of manganese or choline
|
|
|
What type of crystals are involved in articular gout?
|
uric acid crystals
|
|
|
Pigeon genus and species?
|
Columba livia
|
|
|
What are the three most common orders of avians used in research?
|
Galliformes, Anseriformes and Columbiformes are phylums/class/order/genus of avians?
|
|
|
Birds have ________ bones.
|
pneumatic
|
|
|
What is the organ of mastication in the bird?
|
gizzard
|
|
|
Birds have a dilatation in the midesophagus called a _____.
|
crop
|
|
|
Only the left/right ovary and oviduct is functional in the hen.
|
left
|
|
|
Coligranuloma (________ Disease) is caused by what organism? Differential diagnosis?
|
Hjarre's disease: E. coli Diff diag ---- TB
|
|
|
What org (same genus, different species) causes gangrenous dermatitis, necrotic enteritis, ulcerative enteritis (Quail Disease) and Limberneck?
|
Clostridium ---C. septicum, C.perfringens, C. colinum, C.botulinum in that order
|
|
|
What organism causes infectious Coryza? What are the staining characteristics of the organism?
|
Hemophilus paragallinarum, gram negative, bipolar rod
|
|
|
The bird most commonly affected by Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae is the ________. Clinical signs?
|
turkey; clinical signs -----depression, diarrhea, lameness, snood of male turkey is swollen
|
|
|
Match organism with disease:
a. fowl cholera a. S. gallinarum b. fowl typhoid b. S. pullorum c. paratyphoid c. Pasteurella multocida d. pullorum disease d. S. typhimurium, et al |
a. fowl cholera - P. multocida
b. fowl typhoid - S. gallinarum c. paratyphoid - S. typhimurium, et al d. pullorum disease - S. pullorum |
|
|
Avian TB is primarily respiratory or gastrointestinal?
|
Gastrointestinal - Emaciation, diarrhea, lameness pale combs, wattles, nodules in intestines, liver & spleen
|
|
|
What is CRD? PPLO? Causative agent?
|
Chronic Resp Disease; Pleuro Pneumonia Like Org; Mycoplasma gallisepticum
|
|
|
What is the route of transmission for Mycoplasma meleagridis?
|
EGG
|
|
|
What is the cause of ornithosis in poultry? The organism forms ICIB or INIB's in what organs?
|
Chlamydia psittaci; ICIB in air sacs, spleen, and/or liver
|
|
|
What type of inclusions are pathognomonic for "Inclusion Body Hepatitis"?
|
Cowdry Type A intranuclear inclusions in hepatic cells - Adenovirus
|
|
|
Adenovirus strain CELO causes high mortality in quail. What does CELO stand for?
|
Chick Embryo Lethal Orphan
|
|
|
What is the causative agent of "Marble Spleen Disease" in pheasants?
|
Adenovirus - INIB in the spleen are pathognomonic
|
|
|
What causes infectious bronchitis? Effected organ system?
|
coronavirus; respiratory system
|
|
|
What is ILT? Cause? Effected System?
|
infectious laryngotracheitis; herpesvirus - Respiratory System
|
|
|
You have high mortality in young chicks with resp and CNS signs and the laying hens are laying white instead of the normally brown eggs? What is the Suspected Disease?
|
Newcastle Disease
|
|
|
What is the causative agent of Newcastle Disease?
|
paramyxovirus
|
|
|
What are the strains of Newcastle virus?
|
lentogenic, mesogenic, velogenic --- velogenic most pathogenic
|
|
|
What are the two forms of Fowl pox? Pathognomonic lesion?
|
Cutaneous Pox and Wet Pox; Eosinophilic ICIB (Bollinger bodies with elementary bodies - Borrel bodies) in cutaneous and oral lesions.
|
|
|
Fowl plague is caused by what viral agent?
|
Influenza virus - orthomyxovirus
|
|
|
Causative of Marek's Disease? Differential Diagnosis?
|
Herpesvirus; ; diff - lymphoid leukosis
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a clinical sign of Marek's Disease? a. paralysis of wings & legs b. gray eye w/irregular pupil c. swollen feather follicles d. visceral tumors e. all of the above are clinical signs
|
e. all of the above are clinical signs
|
|
|
How is Marek's disease transmitted?
|
lateral via dander
|
|
|
Cause of Lymphoid Leukosis?
|
retrovirus
|
|
|
Marek's disease or Lymphoid Leukosis occurs in birds less than 16 weeks?
|
Marek's disease
|
|
|
Infectious Bursal Disease or _____________ is caused by what type of virus?
|
Gumboro Disease; family - Birnaviridae (RNA)
|
|
|
Chick anemia virus or infectious anemia of poultry is caused by a DNA/RNA virus of the _________ family?
|
DNA virus - Circoviridae
|
|
|
What genus of coccidia affect birds? Differential diagnosis?
|
Eimeria. Diff Diag:---- Salmonella & Histomoniasis, ulcerative and necrotic enteritis (Clostridium)
|
|
|
Which Eimeria species causes "Bloody Coccidiosis"? a. E. acervulina b. E. necatrix c. E. maxima d. E. brunetti e. E. tenella
|
e. E. tenella
|
|
|
What is the causative agent of Blackhead? How is it transmitted?
|
Histomoniasis meleagridis a protozoan flagellate in cecal lumen. 1. Fecal-oral; 2. ova of cecal worm Heterakis gallinarum; 3. earthworms with infected Heterakis larvae
|
|
|
What is the oral protozoa of pigeons?
|
Trichomonas gallinae
|
|
|
What is the roundworm infecting chickens?
|
Ascaris galli
|
|
|
What are hairworms in chickens?
|
Capillaria obsignata
|
|
|
What nematode causes severe respiratory disease in game birds?
|
gapeworm --- Syngamus trachea
|
|
|
What fungus causes brooder pneumonia? Clinical signs?
|
Aspergillosis (Asp fumigatus); resp signs, CNS sometimes; blindness if org in anterior chamber of eye.
|
|
|
Causative agent of crop mycosis?
|
Candida albicans
|
|
|
Diets made with this grain_______ can be deficient in Vitamin _____. Histo includes squamous metaplasia.
|
stored corn, Vit A
|
|
|
What Vitamin Deficiency causes Crazy Chick Disease or encephalomalacia?
|
Vit E Def
|
|
|
Vitamin E Deficiency is observed in feeds high in ______________ fats.
|
polyunsaturated or rancid fats
|
|
|
Biotin deficiency is due to the addition of ________ to the diet.
|
Egg white - contains avidin - makes sense since we see strepavidin or avidin/biotin in so many diagnositc tests.
|
|
|
Hereditary Muscular Dystrophy is seen in what two poultry breeds?
|
22 - New Hampshire chickens, autosomal recessive, Atrophy, phagocytosis and fatty degeneration of the pectoralis muscle 337 - White Pekin ducks (Anas platyrhynchus) show difficulty in walking within two days.
|
|
|
What is the poultry cardiomyopathy model?
|
49 - S - Congestive Cardiomyopathy (CCM) - Round Heart Disease (RHD) of Turkeys (Broad-Breasted Turkeys - BBT) - 50% incidence in inbred flock of turkeys with broad breasts
112 - Alpha1-Antitrypsin Deficiency - Round Heart Disease of Turkeys - similar to congestive cardiopathy in man, heart enlarged, dilated right or both ventricles, wall of the ventricles is thinner than normal, mortality is 15 - 20% in poults 2 - 10 weeks, |
|
|
Spontaneous, hereditary autoimmune thyroiditis (SAT) similiar to Hashimoto Thyroiditis occurs in what breed of chicken?
|
85 - of Obese Strain (OS) Chickens - Obese Strain (OS) chickens, B-cell mediated. Autosomal polygenetic dominant trait. Associated with hypothyroidism.
|
|
|
Amyloidosis in the White Pekin Duck is seen most frequently in what two locations?
|
174 - Amyloidosis in the spleen and adrenals, stain with thioflavin-S
|
|
|
What is the syndrome analogous to tibial syndrome in military personnel that occurs in poultry.
|
224 - March Gangrene - Deep pectoral myopathy, Oregon disease, Green muscle disease in broilers. 40% of turkeys and 19% of chicken broilers exposed to stress.
|
|
|
T/F Avian osteopetrosis is the result of defective osteoclasis and is a metaphyseal sclerosis
|
False - 246 - Skeletal Hyperostoses - Viral Induction of Avian Osteopetrosis - chicken, Gallus domesticus, Avian osteopetrosis is the result of excessive osteoblast proliferation and is mid diaphyseal
|
|
|
Birds are defective in what clotting factor?
|
Avians and reptiles do not have factor XII Fas 263 - Human Dz: Hageman Trait - Animal Model: Factor XII Deficiency in Domestic Cats - Factor XII occurs in the plasma of all mammals except the Cetacea family(dolphins, porpoises, killer whales).
|
|
|
Atherosclerosis is induced White Leghorn Chickens with what agent?
|
338 - Atherosclerosis Induced by Marek's Disease Herpesvirus Infection in White Leghorn Chickens
|
|
|
What is the avian model for Vitiligo?
|
347 - Vitiligo - Smyth Chicken, vit/vit mouse, Sinclair Minature Pig, and grey horse, Human disease: discrete areas of hypopigmentation, both in the skin and ocular that results from a progressive loss of melanocytes
|
|
|
White Leghorn Chicken with a progressive connective tissue disease characterized by fibrosis of the skin and often internal organs are a model of what human disease?
|
323 - Progressive Systemic Scleroderma - Scleroderma in Chickens - White Leghorn Chicken, Progressive Systemic Scleroderma (PSS)
|
|
|
The abnormal curvature, either laterally or anterio-posteriorly of the vertebral column is called ________.
|
333 - Scoliosis - animal model: Scoliosis in Chickens
|
|
|
____________ in man is a myopathic condition in which the sternocleidomastoid muscle shows evidence of myositis myodegeneration, fibrosis, and to some degree regeneration of muscle.
|
314 - Torticollis - animal model: Torticollis in White Pekin Ducks
|
|
|
T/F Avian osteomyelitis experimentally induced by Staphylococcus is similar to human osteomyelitis.
|
True 313 - Acute Haemotogenous Staphylococcal Osteomyelitis in Chickens
|
|
|
Organ of mastication in the bird?
|
Gizzard
|
|
|
Birds do/don’t have a diaphragm and they do/don’t have vocal cords.
|
NO diaphragm, and NO vocal cords (do have larynx)
|
|
|
Avian TB is primarily respiratory or gastrointestinal, Clinical Signs?
|
Gastrointestinal - Emaciation, diarrhea, lameness pale combs, wattles, nodules in intestines, liver & spleen
|
|
|
Birds posses T cells for cell mediated immunity, which are made in the Thymus and they also posses B cells for antibody mediated immunity however these are produced and mature in the ______________.
|
Bursa of Fabricius
|
|
|
Why are IP injections not recommended in birds?
|
Presence of air sacs throughout body cavity
|
|
|
What are conditionally acceptable methods of euthanasia in birds?
|
Maceration, cervical dislocation, decapitation, N2, Argon, thoracic decompression. Reference- 2007 AVMA Euthanasia Report
|
|
|
What are acceptable methods of euthanasia in birds?
|
Barbiturates, inhalants, CO2, CO, gunshot. Reference- 2007 AVMA Euthanasia
|
|
|
Maceration is listed as a conditionally acceptable method of euthanasia in what type (age) of birds?
|
Pipped eggs, poults, day old chicks. Reference- 2007 AVMA Euthanasia Repo
|
|
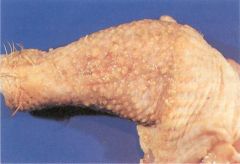
__________is a herpesvirus induced neoplastic disease of chickens characterized by infiltration of various nerve trunk and organs with pleomorphic lymphoid cells. It can cause transient flaccid paralysis of the neck and limbs (11 wk pullet) and you may see skin lymphomas (legs).
|
Marek’s Disease
|
|
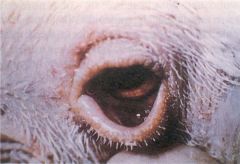
___________disease infects a variety of avian species causing a disease of considerable agricultural and economic significance. One may see nervous symptoms in 5 weeks old broiler (torticollis) or diphtheriod inflammation of the Peyer’s patches (intestinal lymphoid tissue) that later turns ulcerative.
|
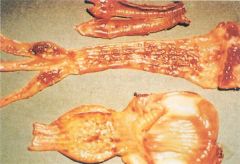
Newcastle
|
|
|
T or F- Birds have only air sacs and no lungs?
|
F- birds have both air sacs and lungs
|
|
|
T or F- Male birds have an os penis?
|
False- not a “true penis” or os penis. Actually males have phallic bodies of the cloaca that
swell during mating and they discharge semen onto protruded oviduct |
|
|
T or F- fertilization of the egg occurs in the magnus?
|
F- Fertilization occurs in the infundibulum; albumin added to egg in magnus
|
|
|
On a bird, what purpose does the brood patch serve?
|
Area on a bird's abdomen when feathers are lost it becomes Engorged blood vessels (breeding season). When patch is next to the eggs, it transfers warmth of the parent (If male assists in incubation they too can develop a brood patch) p 862 Clinical Avian Medicine.
|
|
|
What avian nematode is also termed “gapeworm or redworm”?
|
Syngamus trachea
|
|
|
In terms of polyclonal antibody production in chickens, an immunized hen’s egg has more or less IgY (progenitor of IgG) Ab than that of immunized rabbit serum?
|
Yolk from an immunized hen has 4X- 10X IgY AB than serum from a immunized rabbit. Advantages include: Ab persists in hen for about 1 month; IgM (egg white) IgY/G (egg yolk) with same specificity; Storage of eggs up to several months refrigerated; Using few animals and little manipulation. ILAR journal Volume 46, Number 3 2005- Refinement of Polyclonal Antibody Production by Combining Oral Immunization of Chickens with Harvest of Antibodies from the Egg Yolk
|
|
|
Feather pecking and cannibalism in poultry and other captive birds are examples of common/uncommon and persistent behavioral abnormalities that have a single/ multifactorial causes.
|
Feather pecking and cannibalism in poultry and other captive birds are examples of common and persistent behavioral abnormalities that have multifactoral causes.
|
|
|
T or F- Feather pecking is the pecking and tearing of the skin and underlying tissues of another bird?
|
false- Feather pecking is the pecking and pulling at the feathers of another bird, cannabilism = is the pecking and tearing of the skin and underlying tissues of another bird. BB pg. 1253.
|
|
|
T or F- In terms of occurrence of feather pecking and cannibalism in captive birds and poultry, the presence of litter material for foraging, dustbathing, and exploring has been shown to have little impact on the incidence.
|
FALSE- In terms of occurrence of feather pecking and cannibalism in captive birds and poultry, the presence of litter material for foraging, dustbathing, and exploring has been shown to have PATICULAR IMPORTANCE on the incidence
|
|
|
Which of the following has not been shown to influence the incidence of feather pecking and cannibalism in captive birds and poultry?
a. light intensity b. seasonal weather c. housing system d. group size e. strain of animal |
B. BB pg. 1253
|
|
|
Name some laboratory animal species that harbor natural Chlamydial infections:
|
Birds, mice, GPs, hamsters, rabbits, ruminants, swine, cats, ferrets, muskrats, and frogs
|
|
|
Of the list above, what host species with what infection have proven to be the most frequent source of virulent human infection?
|
Birds, particularly psittacines, with Chlamydophila psittaci BB pg. 1077
|
|
|
Chlamydial infections are spread to humans from infectious material present in?
a. exudates b. secretions c. dessicated fecal material d. aerosol e. all of the above |
E. BB pg. 1077
|
|
|
________ infection is an important feature of epizootology of the Chlamyadiophila psittaci infection in birds. This term is defined by stress causing a reactive shedding of organisms and clinical signs.
|
Latent. BB pg. 1077
|
|
|
Name the three most common sites for blood collection in avian species:
|
Brachial v. of the wing, jugular v, and heart. BB pg. 1012
|
|
|
Which jugular v. R or L, is usually larger in birds?
|
Right is usually largest in birds. BB pg. 1012
|

