![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Peripheral nervous system is divided into which two groups |
somatic and autonomic |
|
|
Somatic |
sensory neurons: senses motor neurons: voluntary muscle contractions |
|
|
autonomic nervous system |
sensory neurons: monitor internal environment (chemo/mechanoreceptors) motor neurons: involuntary regulation of visceral activities |
|
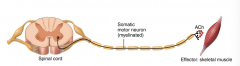
which nervous system |
somatic |
|
|
autonomic nervous system is divided in two |
Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic nervous system |
|
|
Sympathetic |
"fight or flight", increases alertness and metabolic activity |
|
|
Parasympathetic |
"rest and digest", conserves energy and nutrients |
|
|
Where do sympathetic preganglionic neurons leave from |
the thoracolumbar area of the spinal cord |
|
|
where do parasympathetic preganglionic neurons leave from |
leave from the craniosacral areas of the spinal cord |
|
|
Sympathetic pre-ganglionic neurons must travel where before reaching the effector cell? |
sympathetic trunk ganglion |
|
|
sympathetic responses |
pupils dilate, increase heart rate and contraction, dilation of airways, blood vessels constrict to: kidneys and GI tract, blood vessels dilate to: skeletal muscles, heart, liver, adipose tissue, glycogenolysis: liver releases glucose |
|
|
parasympathetic response |
decreased heart rate, decrease in airway diameter, constriction of pupils, increased salivation, lacrimation (tears), urination, digestion, defecation |
|
|
what do cholinergic neurons release |
acetylcholine |
|
|
two types of receptors (sympathetic) at the preganglionic neuron |
nicotinic and muscarinic |
|
|
Ach is degraded by which enzyme? |
acetylcholinerase |
|
|
effect of nicotine binding to nicotinic receptors in the PNS |
excessive release of NE and EPI cause increase in HR and BP |
|
|
effect of nicotine binding to nicotinic receptors in the CNS |
stimulates dopaminergic (pleasure) addiction begins due to down regulation of nicotinic receptors |
|
|
effect of muscarine binding to the muscarinic receptors in the PNS |
MAGIC SHROOMS, blurred vision, excessive salvation, increased sweating, bradycardia, cramping, diarrhea |
|
|
what is an example of a muscarinic antagonist and what is it used for
|
Atropine, used for pupil dilation, IBS as it relaxes the hyper mobile bowel |
|
|
cholinergic receptors |
nicotinic and muscarinic, integral proteins in the postsynaptic membrane activated by the neurotransmitter acetylcholinerase |
|
|
locations of nicotinic and its effects |
Located: chromaffin cells of adrenal medulla: episode and nonepi secretion, sarcolemma of skeletal muscle fibers: excitation and contraction, plasma membrane of postganglionic sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons: excitation impulses in postganglionic neurons. |
|
|
locations of muscarinic and effects |
sweat glands-> increased sweating innervated by the parasympathetic neurons: sometimes excitations, sometimes inhibition skeletal muscle blood vessels (cholinergic sympathetic postganglionic neurons): inhibition-relaxation-vasodilation |
|
|
what do adrenergic neurons release? |
norepinephrine and epinephrine |
|
|
chromaffin cell in adrenal medulla release what % of what |
80% epinephrine, 20% Norepinephrine |
|
|
2 types of adrenergic receptors |
Alpha and Beta |
|
|
Types of alpha receptors |
a1: excitation a2: inhibition |
|
|
Two types of Beta receptors |
B1: excitation B2: inhibition |
|
|
Noepinephrine stimulates which adrenergic receptor stronger |
Alpha |
|
|
Epinephrine stimulate which adrenergic receptor stronger |
both equally |
|
|
Alpha 1 adrenergic (excitation) location + action |
smooth muscle fibers (vasoconstriction) eye (dilation) sphincter muscles: close sweat glands: increased sweating |
|
|
Alpha 2 adrenergic (inhibitory) location + action |
pancreas (inhibits digestive enzymes)` |
|
|
Beta 1 adrenergic (excitation) location + action |
cardiac muscle (increased force + rate of contraction) kidney and pituitary (hormone secretion to save water) adipose tissue (breakdown of triglycerides and FA release) |
|
|
Beta 2 adrenergic (inhibitory) location + action |
smooth muscle in airways (relaxation) smooth muscle in blood of heart/adipose/skeletal muscle (relaxation) radial muscle of eye (dilates pupil) liver cells (glycogenolysis) |
|
|
agonist |
mimics the effects of a neurotransmitter |
|
|
example of an agonist |
phenylephrine (A1 agonist), constricts blood vessels in nasal mucosa = reducing mucous production |
|
|
examples of high blood pressure meds |
propranolol: blocks B1 and B2 adrenergic receptors, B1 reduces HR and force of contraction |
|
|
undesired effects of blood pressure meds |
blocks B2 which results in reduced glycogen breakdown (low blood sugar), bronchoconstriction, example of a better med is metoprolol which selectively blocks B1 |
|
|
Autonomic tone |
balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic activity, regulated by hypothalamus, structure which receive only sympathetic innervation: sweat, arrector pili muscles, kidneys, spleen, most blood vessels, adrenal meduallae |

