![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the GP?
|
extension of the Eustachian or auditory tube that connects the middle ear to the pharynx
|
|
|
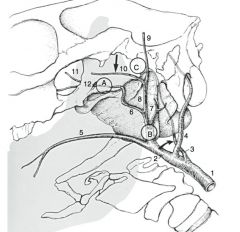
What is the medial border of the GP?
|
paired pouches are separated by a median septum of mucous membrane, which is ventral to the longus capitus and the rectus capitus ventralis muscles
|
|
|
The rostral border of the GP:
|
basisphenoid bone
|
|
|
The ventral border of the GP:
|
pharynx, retropharyngeal LN, and the esophagus
|
|
|
The caudal border of the GP:
|
atlantooccipital joint
|
|
|
The lateral border of the GP:
|
digastricus muscles and the parotid and mandibular salivary glands
|
|
|
The dorsal border of the GP:
|
petrous part of the temporal bone, tympanic bulla, and auditory meatus
|
|
|
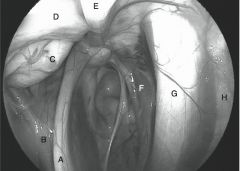
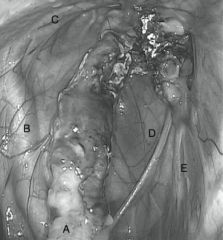
What structures are on the caudal wall of the GP?
|
internal carotid artery, the cranial cervical ganglion, the cervical sympathetic trunk, the vagus nerve, the glossopharyngeal nerve, the hypogossal nerve, and the accessory spinal nerve
|
|
|
What structures are under the mucosa of the ventral floor of the medial compartment?
|
cranial laryngeal nerve and the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve
|
|
|
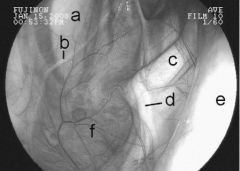
What structures are located in the lateral wall of the lateral compartment?
|
external carotid artery, its branches, the caudal auricular artery, and the superficial temporal artery
|
|
|
What structures are on the dorsal aspect of the lateral compartment?
|
maxillary artery, CN7 (facial) is located in the caudal dorsal aspect, mandibular nerve, a branch of the trigeminal nerve, travels rostrally
|
|
|
What structure can also be affected by GP diseases that affect the facial nerve?
|
vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) does not enter the GP, but is closely related to the facial nerve
|
|
|
Cellular composition of The mucous membrane of the GP:
|
pseudostratisfied ciliated epithelium which have goblet cells
|
|
|
What muscles open the pharyngeal orifice?
|
TVP, LVP, palatopharyngeus, and pterygopharyngeus muscles open the pharyngeal orifice to the GP
|
|
|
What is involved with opening/ expanding the auditory tube?
|
increased inspiratory pressure as well as the stylopharyngeus and pterygopharyngeus muscles
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|

