![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
X ray spectroscopy, like optical spectroscopy is based on _________, absorption,_______ , fluorescence, and diffraction electromagnetic radiation |
emission scattering |
|
|
What is the range of elements that can be analyzed? |
Atomic number above sodium |
|
|
What are the two types? |
X-ray fluorescence Spectroscopy (XFS) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) |
|
|
Principle of XFS |
X-ray beam causes e- to eject. When electrons fall in the empty spot, they emit fluorescence. |
|
|
Types of analysis that can be performed |
Qualitative Quantitative Non-destructive |
|
|
In XFS: Elements are identified by ________ __________ Concentrations are identified by _________ |
characteristic radiation intensity and comparison with a standard |
|
|
What is the principle of XRD? |
X-rays are diffracted by the planes of a crystal |
|
|
How are elements and concentrations determined in XRD ? |
Positions and intensities of diffracted X-Rays Can tell crystal structure, solid composition, particle size, disorder, etc |
|
|
What is the theory of X-ray fluorescence? Fluoresced rays are separated using an analyzer crystal mounted on an angle measuring device called a __________. The intensity is measured by a __________. The separation of the emitted x-rays depends on ________. |
goniometer scintillation counter Bragg's Law |
|
|
What is the Bragg's Law eg? |
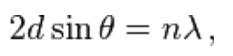
where n is a positive integer and λ is the wavelength of incident wave. |
|
|
Name 5 advantages for X-ray fluorescence |
1. Little sample preparation 2. Simple spectra (only K and L shells involved) 3. Non-destructive 4. Sample relationship between sensitivity and atomic number 5. No deviation from linearity 6. Speed |
|
|
Name 5 disadvantages for X-ray fluorescence |
1. Can't analyze elements lower than sodium 2. Matrix interference 3. Not as sensitive as emission 4. High initial cost 5. Sample Homogeneity is critical |
|
|
Name five interferences in x-ray quantitative analysis |
1. Grain Size 2. Thickness of sample 3. Nature of Surface 4. Matrix interference 5. Elemental enhancement effects |
|
|
XDR: From Bragg's law we get ___ values, which are located in index's so can do a ______ analysis |
d qualitative |
|
|
X ray powder diffraction is unique, it is the only analytical method capable of providing _______ and _______ information about a compound present in a solid sample. |
qualitative, quantitative |
|
|
Advantages of XRD |
1. Works with crystalline material (metals & minerals) 2. Small sample is required 3. Identifies compounds present 4. non-destructive |
|
|
Disadvantages of XRD |
1. Only capable of identifying substances in the powder diffraction file 2. Substances present in low concentrations may not show up. |

