![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Isotopes
|
Atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons.
|
|
|
Atomic Number
Mass Number |
Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
Number of particles (protons and neutrons) in the nucleus. |
|
|
An Ion
|
Positively or negatively charges atom or (covalently bonded) group of atoms (a molecular ion.
|
|
|
Relative Isotopic Mass
|
The mass of an atom of an isotope compared with one-twelth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
|
|
|
Relative atomic mass (Ar)
|
Weight mean mass of an atom of an element compared with one-twelth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
|
|
|
Relative molecular mass (Mr)
|
Weighted mean mass of a moloeculoar compared with one-twelth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
|
|
|
Relative formular mass
|
Weight mean mass of a formular unit compared with one-twelth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
|
|
|
Amount of substance
|
the quantity whoes unti is the mole. Chemists use 'amount of substance' as a means of counting atoms.
|
|
|
Avogadro constant (Na)
|
Number of atoms per mole of carbon-12 isotope. (6.02 x 10^23 mol-1)
|
|
|
A Mole
|
The amount of any substance containing as many particles as thre as carbon atoms in exactly 12g of the carbon-12 isotope.
|
|
|
Molar Mass
|
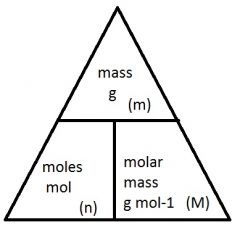
Mass per mole of a substance. The unit of molar mass are g mol -1.
|
|
|
Empirical formula
|
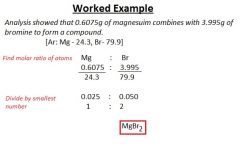
Simplest whole-number ratio of aroms of each element present in a compound.
|
|
|
A molecule
|
Small group of atoms held together by covalent bonds.
|
|
|
Molecular Formula
|

Actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule.
|
|
|
Molar Volume
|
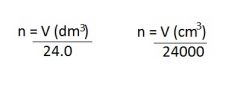
The volume per mole of gas. The units of molar volume are dm^3 mol-1. At room temperature and presure, the molar volume is 24.0 dm^3 mol-1.
|
|
|
Concentration
|
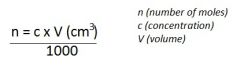
Amount of solute, in mol, dissolved per 1 dm^3 (1000cm^3) of solution.
|
|
|
Standard Solution
|
A solution of known concentration. Standard solutions are normally used in titrations to determine unknown information abouth another substance.
|
|
|
Species
|
Any type of particle that takes part in a chemical reaction.
|
|
|
Stoichiometry
|
Molar relationship betwen the relative quantities of substances taking part in a reaction.
|
|
|
Acid
|
A species that is a prton donor.
|
|
|
A Base
|
A species that is a proton acceptor.
|
|
|
Alkali
|
Type of base that dissolves in water to form hydroxide ions.
|
|
|
A Salt
|
A chemical compound formed from an acid when an H+ ion from the acid has been replaced by a metal ion or another postive ion.
|
|
|
A Cation
|
Positively charged ion.
|
|
|
An Anion
|
Negatively charge ion.
|
|
|
General Equations
|

|
|
|
Hydrated
|
Refers to crystalline compound containing water molecules.
|
|
|
Anhydrous
|
Refers to a substance that contains no water molecules.
|
|
|
Water of crystallisation
|
Refers to the water molecules that form an essential part of the crystalline structure of a compund.
|
|
|
Titrations
|

Special type of volumetric analysis, in which you react a solution of an acid with a solution of a base.
|
|
|
Oxidation Number
|
Measure of the number of electrons that an atom uses to bond with atoms of another element.
|
|
|
Oxidation
Reduction |
Loss of electrons or increase in oxidation number.
Gain of electrons or decrease in oxidation number. |
|
|
Redox reaction
|
Reaction in which npth reduction and oxidation take place.
|
|
|
Reducing agent
Oxidising agent |
Reagent that reduces (add electrons to) another species.
Reagent that oxidises (takes electrons from) another species. |
|
|
First ionisation energy
|
The energy required to remove one electron from each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ions.
|
|
|
Electron Shielding
|
Repulsion between electrons in different inner shells. Shielding reduces the net attractive force from the positive nucleus on the outer-shell electrons.
|
|
|
Successive ionisation energies
|
Measure of the energy required to remove each electron in turn.
|
|
|
Second ionisation energy
|
Energy required to remove one electron from each ion in one mole of gaseous 1+ ions to form one mole of gaseous 2+ ions.
|
|
|
A shell
|
Group of atomic orbitals with the same principal quantum number, n. Also known as main energy level.
|
|
|
Principal Quantum number, n
|
The number representing the relative overall energy of each orbital, which increases with distance from the nucleus. The sets of orbitals with the same n-value are referred to as electron shells.
|
|
|
Atomic orbital.
|
A region that can hold up to two electrons, with opposite spins.
|
|
|
A sub-shell
|
Group of the same type of atomic orbitals (s, p, f or f) within a shell.
|

