![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
King from Ife; african (kingship was important) 11th century
-super realistic, scaring -Europeans claimed greeks made because africans were inferior -coral beads = power -horns = divinity -naturalistic |
|

|
running(dancing) woman; 5000bce prehistoric (african)
-horns- divinity -dots maybe seeds(fertility) or tatoo's -shows movement -simplified and abstract, repetition -shows hierarchic scale |
|
|
Cycladic culter
|
2500bce; known for marble; very abstract simple figures
|
|

|
Figure; Cycladic; 2500bce
-Geometric- abstract and simplified -burial goods -reproductive(hand on tummy and pubic triangle and breasts -Fertility |
|

|
Haprist; cycladic
-simple -funeral or music ritual -uses negative space (harp) |
|

|
Possible fake cycladic harp
Museums keep fakes because: -they don't want to admit they have a fake |
|
|
Minoan culture
|
2000-1400bce "golden age'
-favor assymmetric natural looking -nature based religeon -enjoyed luxery and comfort enjoyed life -based in crete -depicts nature, nature in motion, energy, pleasure joy -will infuence religeon |
|

|
girl gathering cracus; minoan from thera
-more alive, asymmetric, pure, flowing lines, delicate, pleasure Subject- possible ritual girl entering womanhood |
|

|
spring fresco; minoan; From Theralandscape
-preserved volcanic eruption -nature in motion -showing natural world (lillies, wind, stem, birds, springtime) renewl, rebirth |
|
|
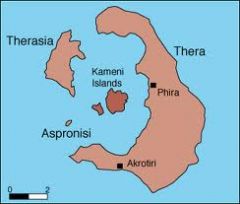
Thera:
-The center is an active volcano. -In 1628 BCE the volcano erupted. -The eruption was dated using the layer of resulting dirt in the ice cores. -The city may have been evacuated. -The eruption did not destroy the Minoans. |
|
|
agean map
|
|

|
octopus vase; minoan; 1450bce
-asymmetric -filling entire space on vase showing movement |
|

|
bull leaping fresco; minoan; 1430bce (RESTORED-decent job)
-prob a ritual (jumped over the bull) -bull drugged and killed -sweeping lines movement -restored decent job |
|

|
knossos stairwell, crete; minoan; 1500bce
-columns restored by sir arthur evans (bad job); original wood column he recast them in concrete and painted red; tapered colums -well lightwells constructed to allow light and air in |
|
|
mycencaeans
|
-The Minoans are eventually conquered by the the Mycenaeans.
-The Mycenaeans are based on mainland Greece. -They borrow and transform Minoan culture. -They were a warrior aristocracy. The elite were warriors. The -Mycenaeans valued good warriors. -Mycenaean warriors are he basis for Homer's writing. They are important to the Greeks |
|

|
Lion gate; mycenaean; 1300bce
-columns borrowed from minoan but mycen's columns are wider (showing strength) -created for defense(narrow entrance strategic); meant to intimidate -lions symbolize power and kings -uses post and lintel above the door is lighter helping str. |
|

|
Burial mask; 1550bce- Mycenaean- Gold
-influenced by Egyptians -abstract -from a body - not concerned with beauty; badly done - |
|

|
warrior vase; mycenaean; 1200bce
-warriors going to battle, repetitive, static -women waving good bye -depicts readiness to go to battle |
|

|
octopus vase; mycenaeans;
-you can tell mycen beause its symmetric, lack of energy; didn't care about art -less delicate The Mycenaeans eventually fall to pirates and raiders. This leads to a dark age which will last 300 years. There will be no authority nor any economic stability. People will lose the ability to read and write. Stories will only be passed orally until Homer. The heroes of these stories will be the foundation for the Greeks. - |
|
|
Ancient Greeks
|
-Humanism; Believed in humans
-believed they were superior -respected nude male form(not female) |
|
|
Archaic Period
|
6th century
-The Greeks settled during this period. -They borrow from other cultures. -They colonized Egypt and Anatolia (Turkey) Krisos. A Kouros (Male youth) statue. -Borrowed from the Egyptians. Shares the same pose, arms, and closed composition. -Different: Greeks do not care if the statue breaks. Statues to serve both the living and the dead. -Created in an open way. -Commemorative. -Depicts ideal naturalism, more open and more natural than Egyptian statues. -Difference in material. -Nude. -Greeks had respect for the nude male form. The believed that the body was worth looking at. The Olympics were performed in the nude. |
|

|
koiuros; archaic greek;
-Borrowed from Egypt(Ka Statue)- same pose, arms, closed comp; Differences- more ideal(muscles);the smile -Krisos displays the "Archaic Smile." -Used to suggest life. -Greek statues are created to be walked around. They are life size. -Statues were placed at city entrances. Cemeteries on both sides. The statue would have been commemorative for the dead, but also for the living, the family. -The Greeks believed that accomplishments were important. the Greeks move quickly into naturalism |
|

|
Calf bearer; archaic; 6th century (good sheppard)
-experimenting with w/new poses -damaged by persians -Depicts a sacrifice being given to Athena. -Was used as fill when the temple was reconstructed. -The arms and the calf's legs create an "X." -It is possible to date Greek pieces by the degree of naturalism that they display. --The calf bearer is older than Krisos. -It is proof of experimentation. -It serves as the source for Christian depiction of the Good Shepard.Kore figure. |
|

|
kore; archaic; 510bce
-different from male male figures(wearing cloths) -was colored (encaustic-painting with wax) -Was buried under the Acropolis. -experiment new poses -arms going forward breaking free of formal |
|
|
Encaustic
|
painting with wax
|
|

|
back figured painting; by exekias(was signed says exekias painted me) Closed comp
-Painted on vase then scrapped off -depicts ajaxleft and achilliesright(cousins and rivals) -playing a games(shows competition between them) -ajax a little bigger -Exekias is the best artist of this type of work -closed comp -excepted homosexuality; women were inferior -achillies died in war and ajax didn't get his stuff so he flipped out; realized he was wrong and killed himself |
|
|
Classical period
|
The Classical Period, 5th Century BCE.
-Period of great things.**Confidence from victory over the Persians** -It is a product of the war between the Greeks and the Persians, the Greco-Persian War. -The Greeks started to colonize Anatolia. -The Persians took the Greeks' land, the Greeks rebelled. -In 490 the Persians sailed to Marathon. -The outnumbered Greeks defeat the Persians. -Phidipides runs 26 miles to deliver news of the Persians' defeat. He dies after arriving. He is considered a hero. He dies a hero. -As a result the 26-mile race is called the Marathon. -The Persians attack again in 480 BCE. The invade with 250,000 men by land and sea. The Persians come through Thermopylae -They destroy all temples. This is why statues such as the calf bearer are used as rubble. -The Persians get into the mainland. -Athenians lure them into a bay. -The Persian ships were overfilled. the Persians were not a seafaring culture, they could not swim. -The Greeks knew the tides. -The Athenians lead the attack. -As a result of defeating the Persians, the Greeks became confident. This manifests itself in the optimism and confidence shown in their work. -City states band together and form a protection league, gather money. The money is given to Athens. -The Athenians rebuild with the protection league's money. -The Parthenon is built with this money. Its use will eventually lead to civil war |
|

|
dying warrior; classical;
-depicts trojan war recorded by homer -shows as hero -Perfect body. -He is dying well, his body is not contorted. -He is dying in control. He is not showing pain. -Shows perfect body and mind. -Trying to pull himself up. Line in upward motion. -Shown physically perfect. -Mistake: The torso is too twisted. Belly button is out of place. |
|

|
Apollo*sun god,music,logic,reason*(Laipths & Centaurs)
**Classic** -Party;drink too much start fighting;grabbing of breasts -Visible display of Greeks over persians -Apollo extends his arm to stop the fighting*reason* -face is calm and in control; Ideal naturalism(also with woman being grabbed) |
|

|
Warrior; Classic greek 5th century;
-Blends naturalism and idealism. -The warrior is muscular, in his prime. He has potential. -He has a commanding presence; Shows that he has the ability to succeed. -His face is cool, calm, collected. -He is masculine. -Lifelike. -He shows a Weight Shift--Invented by the Greeks. Highly influential pose. Placement of the weight on one foot. A change from equal weight placed on both. Breaks symmetry. -Turns spine into a line. More relaxed. -Working leg and working arm are on opposite sides. -He would be holding a spear. -He is mathematical in proportions. The Greeks believed that beauty is rational. -Back has sense of movement. -He looks like he can speak. -Eyes were inlaid for increased naturalism |
|

|
Discus Thrower by Myron; Classic
-This is a Roman copy. The Romans add supports that the original would not have had. -The Romans made fairly accurate copies. -The figure is in a back swing. -Depicts the potential to win. -Potential energy. -Continuous sweep of the arm. -He is perfect. -He has a calm face. He shows no sense of strain. -He is in complete control. -Greek pieces are meant to be walked around. |
|
|
Bronze and metals during classical
|
Melted down
|
|

|
Parthenon; Classical; for athena: Goddess
-Built on Acropolis- settlement and elevated area -damaged by acid rain **Repatriation see flashcard** -steps are pedistal -symmetric building -doric column-manly; strong shaft(bigger at bottom tapers)short capital -corner columns are bigger by 2" -OPTICAL REFINEMENTS(making center of a line stronger for drooping) -Fluting-notches or grooves in columns making shadows -For greeks beauty was rational and mathimatical -Inside was Athena w/ nike(god of victory) |
|

|
Parthenon frieze; british have
-A frieze is a continuous band of sculpture. -The carvings on the Parthenon commemorate celebrations for Athena. -The people are bringing gifts. -The closer the horsemen get to the East end, the riders get more excited and the horses get more energized. -This is significant because it marks the first time that people are put on a level with the gods. -People placed on a temple. -On literally the same level as the gods Gods and Goddesses. Apollo (Center) is totally composed. Eternally youthful. In control of feelings and emotions |
|
|
Late Classical
|
4th century; war of greek city states penopnnesian war 27yrs
-Plague kills a third of the population -shift in feelings no confidence more insecurities; like Gods less -Dionysus becomes more important |
|
|
The four periods
|
Time Line
6th Century BCE: Archaic Period 5th Century BCE: Classical Period. 4th Century BCE: Late Classical Period 323-31 BCE: Hellenistic Period The Archaic period displays fair amounts of naturalism. The Classical period is the peak. The Late Classical period was the result of a war. The war with the Persians in the 5th Century had resulted in the Greeks being sure of their institutions. Between 431-404 Greece became engulfed in civil war. The war was a result of the Athenians' use of protection league money and their own elevated self-image. The Spartans were the first to attack the Athenians.. The fighting created a power vacuum and the Greeks had no way to fend off outside attackers. A plague spread through Athens and wiped out 1/3 of the population of Athens. This resulted in the Greeks being disillusioned with no confidence in the city states and their religion. This manifests itself in the art becoming more personal, more immediate, and less restrained. |
|
|
Repatriation
|
Return to the country of origin
On going issue of the world |
|
|
Late Classical
|
-Change is result of war
-Brings Gods down earth -Style-longer, smaller head, more feminine |
|

|
Hermes and Dionysus; by praxiteles; late classical
-Dionysus- God of wine;partying;emotion -Hermes-messenger for Gods -Shows Hermes teasing a baby dionysus with grapes -Open Comp -Relaxed and less manly (feminine) |
|

|
Aphrodite; Late classical; was on Nitos island off coast of turkey **shows godess in nude**
-Restoration- several pieces added(head,arms,leg,nose)-Gods get dirty like common people, they are like us people came from all over to see it (nudity) -Taking cloths off to bathe -50 copies meaning it was popular |
|

|
Theater at epidauros; late classical; 387 ft; use of geometry
-Theaters were associated with Dionysus -built into landscape -Great acustics |
|

|
Horned alexander the great
-devine |
|
|
Hellenistic Period
|
Starts with the death of Alexander
-Opposite of classical period---Way more emotion -Grand scale and Stage craft(theatrical) -This is where the Hellenistic world comes in. It accelerates skepticism. -Culture is based in cities. -Imported peoples feel alienated -The cities are rich and cosmopolitan. -The works are large scale. |
|

|
Altar of Zeus at Pergamon**Hellenistic**
-The frieze is 400' long and 7' high(open comp spills out into viewers space) -First time you pain and suffering meant to touch your emotions -There is an altar inside. -Hellenistic: Theatrical. -It is a special environment like a stage. -There are huge emotions. -It is in the Berlin Museum. It may someday have to be repatriated. |
|

|
Nike- Godess of Victory**Hellenistic**
-Commemorating a Victory in sea battle -contrast light and dark -shirt transparent -It is naturalistic. -Very theatrical -There is convincing movement. The wings are acting as break. |
|

|
Sleeping eros**hellenistic**(cupid as child-son of aphrodite)
-real; good study -It is a naturalistic depiction of a child. -There is a sense of gravity, his flab pulls. -He is behaving like a child. -It is a realistic depiction. -The subject of sleep is common in the Hellenistic Period (represents dreaming or letting go/releasing). This is never seen in the Classical Periods. |
|

|
Seated boxer**Hellenistic**
-Difference: He has been beaten/tired/sad looking/strikes emotion -About 4' high. Can be looked down on. -He is older, no longer a victor, not in his prime.(opposite of the warrior in classic period, in his prime standing tall) -No control. -He has scars. -His nose is nicked and broken. -He is breathing through his mouth. -He is dazed, out-of-it. -There is no capacity to win. -There is a sense of sorrow. -This is emotive. |
|

|
Dying gaul**Hellenistic period**Naturalistic
-A dying soldier. -There is pain. -The viewer can feel his suffering. -He is physically shown. -His legs do not work. -His veins are bulging. -His head is down. -His attitude depicts him accepting death. -He is a loser. -This piece is reminiscent of the Dying Lioness but the opposite of the dying warrior in classical period |
|

|
Sleeping saytr*hellenistic** Satyr-goat and human(loved sex and drinking)
-Depicts sleep; Dreams allow people to let go of reason; Allow for a irrational side. -Sleeping off a hangover. -He is having bad dreams. -His muscles show tension. -It is beautifully carved. -There is good anatomy. -It is a sensual image. -There is restoration. -Bernini discovered and restored the statue. -He restored the right leg, knee, and foot. -He spread the right leg more. -Baroque is a sensual style. the change may not have been intentional. -It will not be repaired because Bernini is too famous. -The Satyr has a perfect body. -Treatment has shifted. Hellenistic period is important because Alexander spreads Greek art. |

