![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Bi-conical Urns |
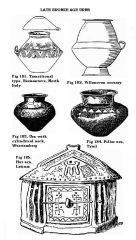
Villanovan urns in which cremated ashes were stored. Made using a slow-turning potter's wheel and stored in large stone containers. |
|
|
Corinthian Pottery |

Distinctive shape with parallel friezes containing floral and fauna motifs. Popular import of the Etruscans during the late 7th and early 6th c. B.C. |
|
|
Bucchero |

Native Etruscan potter that imitates metal-ware. Divided into heavy and light. Appears throughout the Mediterranean, indicating Etruscan exportation. |
|
|
Cerveteri |
Etruscan town which contains the "Necropoli della Banditaccia." |
|
|
Necropoli della Banditaccia |
Tomb complex of the Etruscan city of Cerveteri. Early tombs consist of dromoi leading to the tomb, while later tombs imitated the house of the deceased. The appearance of "tomb streets" indicates a crisis of the Etruscan aristocracy. |
|
|
tumulus |
Large, circular burial mound |
|
|
δρομος (dromos) |
Long, linear passage leading to an Etruscan tomb. |
|
|
Tarquinia |
Settlement which contains more painted tombs than any other Etruscan city. |
|
|
Pyrgi |
Etruscan harbor city in which there are the remains of two temples (Temple A, B). |
|
|
Temple A (Etruscan) |
Etruscan temple at Pyrgi. Decorated with scenes from the Theban cycle. |
|
|
Temple B (Etruscan) |

Etruscan temple at Pyrgi. Decorated with scenes of the Labors of Hercules. |
|
|
Sarcophagus of the Spouses |
Terracotta figures form the late 6th c. BC (found in Cerveteri) of a bride and groom. Created in the archaic style, there is a clear emphasis on the upper body and the figures seem to penetrate the space around them. An important step in the artistic quest for naturalism. |
|
|
The Apollo of Veii |
Sculpted by Vulca in the 6th c. B.C. and located on the acroterion - flanked by sculptures of Hercules and Minerva. |
|
|
Cista Ficoroni |
Jewel casket of made in the 4th c. B.C. Found in Palestrina but crafted in Rome. Indicates the existence of a Roman elite who appreciated Greek culture. |
|
|
Temple of Capitoline Jupiter (Rome) |
Located on the Capitoline Hill and inaugurated in the 509 B.C., this temple became the model for all Capitolii in all Roman provinces. When first erected, it was the largest temple in Italy, and displays the ambition of Rome to be taken seriously as an Italic power. During the Republican and Imperial Age, it became the destination of the triumphal procession. |
|
|
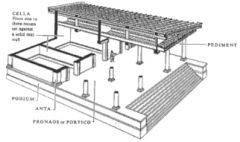
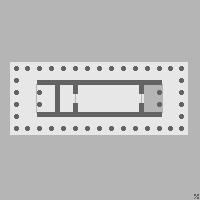
Etrusco-Italic Temple |
CHARACTERISTICS: -square shape -cellae are in rear of podium -προναος -no columns in rear -emphasis of facade -native building materials (tufa, travertine, etc.) |
|
|
προναος (pronaos) |
The inner area of the portico of a Greek or Roman temple, situated between the portico's colonnade or walls and the entrance to the cella, or shrine. |
|
|
Temple of Hercules (Forum Boarium) |
Est. 100 B.C. This temple is the earliest preservedlp marble temple in Rome. |
|
|
Temple of Portunus |
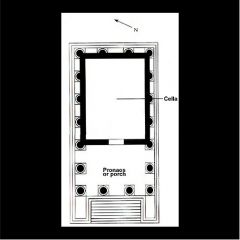
1st c. B.C. This temple provides a good example of electicism, or the hybridization of Greek and Italic styles. |
|
|
Temple of Apollo (Field of Mars) |
Originally built in the 4th c. B.C. and renovated by Augustus, this was the first temple to a foreign god in Rome. |
|
|
plinth |
the lower square slab at the base of a column. |
|
|
Temple of Jupiter (Porticus Octavia) |
Temple from the 2nd c. B.C. This temple was the first marble temple in Rome. |
|
|
Temple A (Largo Argentina) |
Built in the 3rd c. B.C. An eclectic temple; Temple A is constructed of local building material with a lower podium and cella in the rear. |
|
|
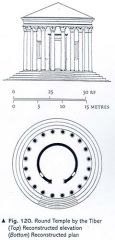
Temple B (Largo Argentina) |
Est. 100 B.C. Temple B is circular but subjected by an attached vestibule staircase. It is the same floor plan as the Pantheon |
|
|
Temple C (Largo Argentina) |
The oldest of the Largo Argentina temples (4th c. B.C.), it has a very conservative style: a raised podium, and emphasis on the facade and a large width. |
|
|
Temple D (Largo Argentina) |
The largest of the four, it dates to the 2nd c. B.C. with Late Republican restorations. |
|
|
Theater of Pompey |

Built in the 60s B.C. The first permanent theater in Rome. It also incorporated a temple to Venus Victrix to celebrate Pompey's conquests in the East and his privileged relationship with the gods. |
|
|
Temple of Jupiter Anxur |
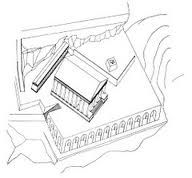
Built in the late 2nd/early 1st c. B.C. This temple was built on a pre-existing sanctuary and is composed of an artificial terrace built on an arch complex. It is a good example of "functional aesthetics." |
|
|
opus reticulatum |
Consists of diamond-shaped bricks of tuff, referred to as cubilia, placed around a core of opus caementicium. |
|
|
opus mixtum |
Opus reticulatum mixed with brickwork |
|
|
red porphyry |
A purple colored marble hailing from Egypt. It is used in statues to represent Imperial power. |
|
|
pavinazetto |

A marble used to portray enemies of Rome. Used in the "Barbaro Inginocchiato" in the A.M.N. |
|
|
Cnidian Aphrodite |
Also referred to as the "Prudish Venus," it was sculpted by Praxiteles in the 4th c. B.C. It is a paradigm of the Hellenistic ideal of the female figure. |
|
|
Hercules Farnese |
Following Lysippus' recalculation of the ratios of sculpture, this statue is an excellent representation of the Hellenistic ideal male. |
|
|
Polykleitos |
Wrote the τον κανον, which was a work on the mathematical application of the ideal image |
|
|
Doryphoros ("The Spear Bearer") |

Sculpted in the 5th c. B.C. by Polykleitos, this statue is a paradigm of the Classical ideal male. |
|
|
Villa of the Papyri |
Located in Pompeii, this house contains the most complete collection of statues found in a Roman Villa as well as hundreds of carbonized scrolls of the philosopher of Philodemes. |
|
|
1st Style Wall Painting |

Relief of an imitation of a wall made out of painted blocks (3rd c. B.C.) Appears in the Basilica of Pompeii, House of the Faun. |
|
|
2nd Style Wall Painting |

Wall is dominated by architectural framework. Early phase includes heavy architecture; mature phase becomes more decorative and fantastical. |
|
|
3rd Style Wall Painting |

A purely linear and ornamental system. Indicates a search for extreme refinement. |
|
|
4th Style Wall Painting |

A continuation of 3rd style with a return to the fantasy of the mature 2nd style. |
|
|
Alexander Mosaic |
Originally located in the House of the Faun, it portrays the conflict between Alexander the Great and the Persian King Darius. It is a copy of a Hellenistic painting. |
|
|
Temple of Apollo (Pompeii) |
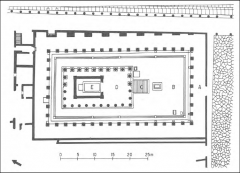
Built in the 6th c. B.C. and monumentalized in the Samnite Period. Included a column with a sundial. |
|
|
Imperial Portraiture |

The official imperial portrait was approved by the emperor. Imperial portraiture can be understood as how an emperor wanted to present himself. It is loaded with ideological messages. |
|
|
Breccia Verde |

Green colored marble hailing from Egpyt |
|
|
Dainads |

The 50 daughters of Danaus who killed their Egyptian husbands on the wedding night. Became a symbol of Roman superiority over Egypt and the East. Found in the house of the Papyri and the Temple of Apollo on the Palatine Hill. |
|
|
Basilica (Pompeii) |
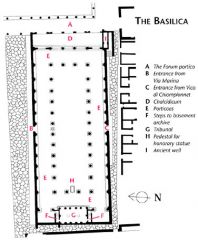
Dating from the late 2nd c. B.C., the construction of the basilica is demonstrative of the Pompeian elite attempting to Romanize their public spaces. This is our earliest preserved basilica and includes 2 floors with a gallery, mixed architectural orders, walls with engaged columns and 1st style wall painting. |
|
|
Eumachia Building |
This building was dedicated in the 1st c. A.D. by a public priestess of Pompeii - Eumachia. While its exact purpose is unknown, it has been designated as a building of the Fuller's Guild. The building is dedicated to Concordia and the Pietas of Augustus and is a clear evocation of imperial propagation. |
|
|
Iseum (Temple of Isis) |
The first phase of this temple dates from the 2nd c. B.C. Its enclosed layout demonstrates its function as a meeting place for an initiate cult. Its surrounding porticus was decorated in the 4th style. It was the first building that was restored after the earthquake of 62 A.D. |
|
|
Holconius Rufus |
Member of Pompeian elite who restored and updated the theater. He received a reserved seat in the theater for this public service. A statue base with his name also exists at the intersection of the 2 main streets of Pompeii near the Stabian baths. |
|
|
Stabian Baths |
Dating from the 4th c. B.C., these baths contains 4th style paintings on stucco, which Vetruvius states is the most appropriate decorative material for a bath complex. |
|
|
atrium |
The focal point of the Roman house. It functioned as a vehicle to access all parts of the house. It contained an impluvium and was mostly on a vertical axis with the tabularium and peristyle. |
|
|
impluvium |
A cistern in the center of the atrium that collected rainwater. Also had a strong decorative element. |
|
|
tabularium |
A room in a Roman house in which a patron would receive clients and conduct daily business. |
|
|
peristyle |
A colonnaded courtyard used to entertainment and leisure. Often, peristyles would be surrounded by multi-purpose rooms used for entertainment and dining. Demonstrative of the Roman elite trying to emulate Greek culture. |
|
|
Necropolis |
Located outside of the city walls, the tombs created an inventory of important citizens that could be viewed by those entering and exiting the city. |
|
|
Heraion at the mouth of the Sele |

Founded at the beginning of the 6th c. B.C. Notable are its Doric metope, which depict the myths of Sisyphus and Aias in the archaic style. |
|
|
Temple of Athena (Paestum) |
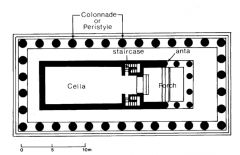
Dating from 510 BC, this temple is the earliest example of the use of 2 architectural orders. |
|
|
Temple of Zeus and Hera (Paestum) |
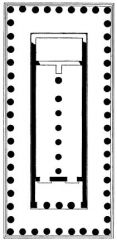
Dated 550 BC. The columns that divide the space of the interior indicate that 2 deities were worshiped here. |
|
|
Temple of Apollo (Paestum) |
Constructed in 450 BC. A good example of optical correction. The temple appears to be in perfect balance and exudes naturalism and aesthetic satisfaction. |
|
|
Temple of Fortuna Primigenia (Palestrina) |
Built in the late 2nd c. BC. Includes a series of artificial terraces leading to the θολος. It is the first example of a covered concrete ceiling. It is a theater/temple complex, which Pompey used as a model for his own theater. |
|
|
Temple of Juno (Gabii) |
Dated 200 BC, this temple is yet another example of the Roman style of mastery of the landscape (terrace). |
|
|
Temple of Hercules Victor (Tivoli) |
Built around 50 BC, this temple includes a latge, artificial platform, a 3 armed porticus, and a theater. Became a model of the Muniquan theater complex in Spain. |
|
|
The temple of Augustus and Livia (Vienne) |
1st c. AD. Example of the "Classical Roman Temple." Also indicates a rapid spread of imperial cult in the early 1st c. throughout the provinces. |
|
|
Temple of Jupiter Heliopolitanus (Baalbek) |
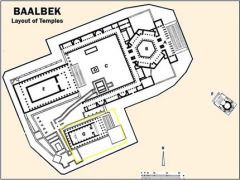
Built in the 1st c. AD. Notable for its immense size and its ornate decoration. This style of decoration is often referred to as "Roman Baroque" and is the result of horror vacui (the fear of empty space) |
|
|
Sanctuary of Aphrodite (Baalbek) |
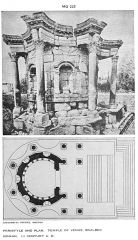
3rd c. AD. Rhythmical architecture; the sanctuary is composed of alternating convex and concave lines. |
|
|
Temple to Bel (Palmyra) |
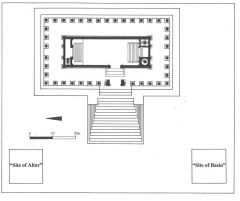
Constructed in the 1st c. AD, this temple combines local elements (additional axis, cella within a cella, off-center staircase) with traditional Greco-Roman elements and demonstrates how local gods and cults were often absorbed into Roman religion. |

