![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Who was Hippocrates? |
A Greek physician who is also known as the father of modern Medicine, born in Kos in 460BC |
|
|
|
What were the three things he developed? |
Hippocratic Oath, Theory of the four humours, clinical observation |
|
|
|
What is the h————- o——? |
Idea doctors should put the patient’s best interest first, not doing anything for the purpose of selfishness or for solely gaining wealth |
|
|
|
What is the T——- of the F—- H———? |
The idea unbalanced fluids in the body caused illness |
|
|
|
What is the idea of C——— O———? |
The idea doctors and physicians should listen to/observe/test patients, to ensure an accurate diagnosis and consultation to the patients needs |
|
|
|
Who was Claudius Galen? |
He was a Roman doctor and gladiator surgeon who developed the works of Hippocrates |
|
|
|
How did he develop the theory of four humours? |
The theory of opposites - where the opposite method should be used to combat too much of one humour in the body |
|
|
|
How was too much blood combatted using this theory? |
Bleeding |
|
|
|
How was too much yellow bile combated using this theory? |
Purging using laxatives and purgatives - to either **** or vomit the humour out |
|
|
|
What were the two conditions described for each humour in the body? |
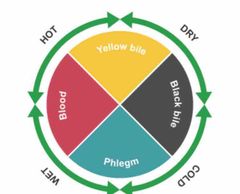
|
- Temperature; moisture |
|
|
How was excess phlegm treated? |
Through A hot treatment such as a pepper |
|
|
|
Why did the Church agree with the ideas of Galen? |
His ideas fit into the church’s on human anatomy |
|
|
|
What ideas are still taught today and why? |
Very influential and important - Hippocratic Oath and Clinical Observation |
|
|
|
How were their ideas influential through monks? |
Their ideas were noted down by monks, through what they noted down, and passed down for thousands of years |
|
|
|
What was the significance of their ideas being taught? |
Their ideas were passed down to medical students for thousands of years |
|
|
|
What were the four believed causes of disease in Medieval Britain? |
Four Humours, Astrology, Miasma theory, God |
|
|
|
Which two causes were natural? |
Miasma theory and Four humours |
|
|
|
Which two causes were supernatural? |
Astrology and God |
|
|
|
What is the difference between a natural and supernatural cause? |
Natural - Happened in control of humans or societal conditions at the time Supernatural - Happened as a result of factors out of control of humans at the time |
|
|
|
What are u————- h———-? |
When the fluids black bile, yellow bile, blood and phlegm were out of balance, causing illness. Taught by Greek and Roman physicians |
|
|
|
How did a————- cause illness? |
When illness was linked to the movements of planets and stars in the solar system |
|
|
|
How did G— cause disease? |
People believed, as what was taught by the church, illness was sent as a punishment from God for sins, and this encapsulated diseases such as the Black Death |
|
|
|
What is m———? |
The idea infected or evil spirits in air caused disease, and this included bad smells and filthy air, believed to be sent through bad/devilish/ evil spirits in the air |
|
|
|
What is a z———- C——-? |
A chart that used the positions of astrological bodies such as the sun, moon and stars, to tell a doctor what part of the body to treat and when |
|
|
|
What ways were disease diagnosed? |
Zodiac Charts, urine charts (Uroscopy) |
|
|
|
What ways were diseases treated? |
Herbal remedies, Bleeding |
|
|
|
How was disease Prevented?What |
Cleaning the streets |
|
|
|
What were H———- R————? |
Natural concoctions and medicinal treatments produced through a combination of natural ingredients, such as herbs, minerals and animal parts |
|
|
|
What ways were diseases treated? |
Herbal remedies, Bleeding |
|
|
|
How was disease Prevented?What |
Cleaning the streets |
|
|
|
What were H———- R————? |
Natural concoctions and medicinal treatments produced through a combination of natural ingredients, such as herbs, minerals and animal parts |
|
|
|
Who administered these remedies? |
Women, mainly the patient’s wife, mother or close relative, and most women knew many be heart |
|
|
|
What were herbals? |
Books where remedies were passed down and written in herbals, with pictures of ingredients and explanations of how potions should be mixed, but also the exact quantities of needed ingredients |
|
|
|
What was the role of wise women? |
Local women in villages who could read and write, and had even more knowledge from previous generations, who assisted women in villages when they needed help |
|
|
|
Why were prayers said during the collection of herbs and ingredients? |
To increase the hypothetical chance of effectiveness and curing ability |
|
|
|
When did Edward III order the Lord Mayor to clean the streets of London? |
1349 - During the Black Death |
|
|
|
Why did he order this? |
He believed it was factoring into ill health and disease at the time |
|
|
|
What theory does filfh in the streets link to? |
Miasma |
|
|
|
What is b————? |
The process of blood being removed from a patient, either from skin being cut or leeches sucking blood from arms |
|
|
|
How much were patients bled each time, and how much blood was released? |
Blood was let 7-12 times yearly in monasteries, with up to 3-4 pints produced each time- almost reaching unconsciousness |
|
|
|
What is u———-? |
The method of using a urine sample to see which humours needed to be treated at a certain point, to check the four humours were balanced |
|
|
|
How were charts used for this? |
Urine charts were used to tell a doctor how to treat the patient based on the colour, smell and thickness of the sample, and sometimes the taste |
|
|
|
What is a physician? |
A university trained doctor, who was also the highest status and best-paid. Taught in the ways of Galen |
|
|
|
What were their treatments based on? |
The four humours |
|

