![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Where did crude oil come from? |
• Found in rocks. • Formed over millions of years from remains of plankton (sea creatures) which were buried in the mud. • Crude oil is a finite resource. |
|
|
|
What is crude oil? |

• Mixture of hydrocarbons
(Methane has single covalent bonds |
|
|
|
What are hydrocarbons? |
Hydrocarbons are molecules made of hydrogen and carbon molecules only |
|
|
|
Examples of alkanes |

General formula: Cn H(²n+²) Methane CH⁴ Ethane C²H⁶ Propane C³H⁸ Butane C⁴H¹⁰ Pentane C⁵H¹¹ |
|
|
|
Structure of Alkanes |
• saturated hydrocarbons (carbons are fully bonded to hydrogens) • single (covalent) bonds • only contain hydrogens and carbons |
general formula is Cn H(²n+²) |
|
|
Q: Propane is an alkane with 3 carbon atoms. Draw the structure of propane. |

|
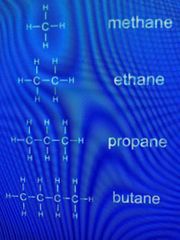
MEMORISE THESE!!! |
|
|
Boiling point of hydrocarbons |
Short chain = lower boiling point Long chain = higher boiling point |
Boiling point: the temperature at which the liquid boils or the gas condenses |
|
|
Volatility of hydrocarbons |
Short chain = higher volatility Long chain = lower volatility |
Volatility: the tendency to turn into a gas |
|
|
Viscosity of hydrocarbons |
Short chain = low viscosity = very runny Long chain = high viscosity = thick |
Viscosity: how easily it flows |
|
|
Flammability of hydrocarbons |
Short chain = higher flammability Long chain = lower flammability |
Flammability: how easily it burns |
|
|
What is cracking? |
When a large alkane is broken down to produce smaller molecules. |
Crackalacka |
|
|
Products of cracking (and what they are used for) |
Shorter chain alkane > used for fuels eg. in cars. Alkene |
|
|
|
Conditions for cracking |
In catalytic cracking we use heat and a catalyst. The catalyst speeds up the reaction. In steam cracking, we use heat and steam. |
|
|
|
Alkenes |
• Have double carbon bonds. • Can be used to make polymers and other chemicals. • Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. |
|
|
|
Testing for Alkenes |
• Use bromine water which is orange. • Bromine water turns colourless. |
|
|
|
Q: Cracking equation: Work out the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in the second product molecule. C²⁵H⁵² ---> C²⁰H⁴² + C...H... |
C²⁵H⁵² ---> C²⁰H⁴² + C⁵H¹⁰ |
The number of carbon and hydrogen atoms on the right hand side must be the same as the left hand side. |
|
|
Testing for alkanes |
• Use bromine water which is orange. • Bromine water stays orange. |
|
|
|
Combustion of hydrocarbons |
• Hydrocarbon fuels release energy when combusted. • During combustion the carbon and hydrogen atoms in the fuel react with oxygen. The carbon and hydrogen are oxidised. |
|
|
|
Complete combustion |
• If the oxygen is unlimited, this reaction produces carbon dioxide and water. • H oxidises = H²O • C oxidises = CO²
Equation is: Hydrocarbon + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water
|
Plenty of oxygen!! |
|
|
Incomplete combustion |
• If there is not enough oxygen, • carbon is released as soot. Equation is: Hydrocarbon + oxygen --> carbon monoxide + carbon + water |
|
|
|
Fractional distillation of crude oil |
• First, crude oil is heated to a very high temperature which • causes crude oil to boil. • All hydrocarbons evaporate and turn into a gas. • Crude oil vapour is now fed into the fractional distillation column. • Column hotter on bottom and cooler at the top. • Hydrocarbon vapour rises up. • Hydrocarbons condense when they reach their boiling point. • Liquid fractions are then removed and • Remainers continue rising until they condense. |
Very long chain hydrocarbons have very high boiling points. These are removed at the bottom of the column. |
|
|
Uses of alcohols |
• Fuels • Solvents • Alcoholic drinks |
|
|
|
What are Alcohols? |

• A homologous series. •Same functional group -OH |
|
|
|
Making ethanol between steam and ethene |

C²H⁴(g) + H²O(l) <=> C²H⁵OH(aq) • Steam • 300°C - 400°C • 70 atm • Catalyst (H³PO⁴) |
Advantage: high yield of ethanol Disadvantage: high temp so uses a lot of energy |
|
|
Making ethanol using fermentation |

C⁶H¹²O⁶(aq) --> 2C²H⁵OH(aq) + 2CO²(g) • Sugar solution mixed with yeast. • 37°C • Neutral pH •Yeast • Must take place in anaerobic conditions (without oxygen) |
CO² also produced Advantages: low temp, less energy. From plants, renewable. |

