![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is Cognitive Psychology? |
Studio what goes on inside the head, how people learn, and how experience/knowledge/context interact with the learning situation. |
|
|
|
Where does knowledge come from? |
Rationism? Empiricism? A combination of the two? |
|
|
|
Nature |
You're born with everything that makes you YOU. |
|
|
|
Nurture |
The environment in which you're raised is what forms you. |
|
|
|
Memory Model |
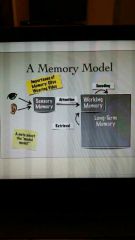
|
|
|
|
The role of attention... |
More practice 》More automaticity 》Less attention |
|
|
|
Attentional Capacity |
We have resource limited tasks (turning down music when driving in rain) and data limited tasks (poor source to work with). |
|
|
|
Automaticity |
Automatic process (riding a bike, swimming, & reading) |
|
|
|
Working memory |
Processes meaning and has a limited capacity (space or time) |
|
|
|
Chunking |
Putting information into meaningful chunks instead or randomized nonsense. |
|
|
|
Depth of processing |
The connections we make when memorizing matter more than the time spent. |
|
|
|
Baddeley's Model |
Visuospatial Sketchpad 《》Central Executive 《》Phonological loop |
|
|
|
Phonological Loop |
Hearing and the length of the word |
|
|
|
Visuospatial Sketchpad |
Visual and Spacial Memory |
|
|
|
Cognitive Load Theory |
Different tasks place different demands on the learner |
|
|
|
Declaritive Memory |
Factual knowledge (2+2=4) |
|
|
|
Semantic Memory |
Memory of general concepts and principles (lemons are yellow) |
|
|
|
Episodic Memory |
Autobiographical experience (birthdays) |
|
|
|
Explicit Memory |
Conscious recall or recognition of previous events |
|
|
|
Implicit Memory |
Unintentional, nonconscious retention that influences our actions |
|
|
|
Three sources of cognitive demands |
Learner, content, & environment. |
|
|
|
Prototypes |
Smallest unit of meaning |
|
|
|
Exemplars |
Storage of all past examples to 'check' membership |
|
|
|
Propositions |
How we organize memorized information. |
|
|
|
Schemas in Declaritive Memory |
Mental filing cabinets used to organize knowledge. (Swimming: free style, breast stroke, butterfly...) |
|
|
|
Productions |
The script we follow throughout our lives. |
Conceptualizing procedural memory |
|
|
Dual-code hypothesis |
Information can be stored in both visual and auditory systems. |
|
|
|
Memory models in LTM |
Network model (Web of connections) ACT theory Conectionalist models |
|
|
|
Maintenance |
Keeping information active in short term memory |
Encoding |
|
|
Elaborative rehearsal |
Rehearsing in order to remember information |
Encoding |
|
|
Imagery |
Putting a picture with something you're trying to remember. |
Elaborative rehearsal |
|
|
Mnemonic Techniques |
Creating elaborate connections for material in order to remember it. Pairing or new information to old information. |
Encoding |
|
|
Peg Method |
Hanging new information on previously pegged ideas. *one is bun. |
Mnemonic Techniques |
|
|
Method of Loci |
Using a familiar location to "place" new information visually |
Mnemonic Techniques |
|
|
Link Method |
Putting an image with a word in order to remember it |
Mnemonic Techniques (story, first letter, keyword ) |
|
|
Schemas |
Using existing stuff to understand new stuff |
|
|
|
Guided Questioning |
Connecting information throughout a text or an example. |
|
|
|
Levels of Processing |
Deeper processing of something the better |
|
|
|
Metacognition |
Thinking about thinking |
|
|
|
Knowledge of Cognition |
Knowing your cognitive abilities |
|
|
|
Regulation of Cognition |
Recognizing strategies that best work for you and when something isn't working. |
|

