![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Principle of complementarity of structure and function |
All specific functions are performed by specific structures in the form of a structure relates to its function |
|
|
Anatomy |
The study of internal and external body structures and their physical relationships among other body parts |
|
|
Physiology |
The study of how living organisms perform their vital functions |
|
|
Human anatomy |
The study of the structure of the human body |
|
|
Gross anatomy / macroscopic anatomy |
Involves examining fairly large structures. Gross anatomy (from the Latin term grossus meaning "thick" or "massive") can be conducted without using a microscope and can involve the study of anatomy by dissecting a cadaver |
|
|
Human physiology |
The study of the functions or workings of the human body |
|
|
Major levels of organization of the human body from the simplest to the most complex |
Chemical Cellular Tissue Organ Organ system Organism |
|
|
Atoms |
The smallest stable units of matter |
|
|
Cells |
The smallest living units in the body |
|
|
Tissue |
A group of cells working together to perform one or more specific functions |
|
|
Organs |
Made of two or more tissues working together to perform specific functions |
|
|
Organ system |
A group of organs interacting to perform a particular function |
|
|
Organism |
An individual life form |
|
|
Surface Anatomy |
Involves locating structure on or near the body surface |
|
|
Supine |
A person lying down while facing up |
|
|
Prone |
A person lying down while face down |
|
|
Superior |
Above or at a higher level toward the head |
|
|
Lateral |
Away from the midline |
|
|
Mediastinum |
A mass of tissue separating the right and left pleural cavities |
|
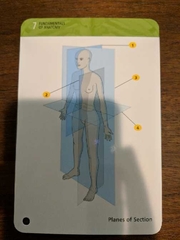
|

|
|
|
Pericardial cavity |
A small chamber that surrounds the heart |
|
|
Pleural cavities |
A cavity within the thoracic cavity holding the lungs separated by a tissue called the mediastinum |
|
|
Thoracic cavity |
contains the lungs and heart associates organs of the respiratory cardiovascular and lymphatic systems the inferior portion of the esophagus in the thymus |
|
|
Autoregulation |
A process that occurs when a cell, tissue, organ, or organ system adjusts in response to some environmental. |
|
|
Extrinsic regulation |
The process that results from the activities of the nervous system or endocrine system.these organ systems detect and environmental change and send an electric electrical signal or chemical messenger to control or just the activities of another or many other systems simultaneously. |
|
|
Homeostasis |
stable internal environment. |
|
|
Homeostatic regulation |
The adjustment of physiological systems to preserve homeostasis. |
|
|
Hypothalamus |

Thermoregulatory center in brain. |
|
|
Negative feedback |
A way of counteracting a change. Opposes variation from normal. |
|
|
Positive feedback |
Initial stimulus produces a response that amplifies or enhances the original change in conditions rather than opposing it. |
|
|
State of equilibrium |
Exist when opposing processes or forces are in balance. |
|
|
Dynamic equilibrium |
When physiological systems continually adapt and adjust to changing conditions. |
|
|
Abdominal cavity major organs |
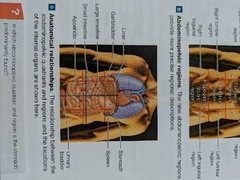
Liver, gallbladder, large intestine, small intestine, appendix, stomach, spleen, urinary bladder. |
|
|
Thoracic cavity major organs |
Lungs, heart, associated organs of the respiratory, cardiovascular, lymphatic systems, inferior portions of the esophagus, and thymus |

