![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Neurotransmitters |
Includes Serotonin, Dopamine, Acetylcholine, Norepinephrine, GABA, Substance P, and Endorphins. |
|
|
|
What is a Neurotransmitter? |
A neurotransmitter is a chemical messenger that carries signals between neurons and other cells in the body. Usually a neurotransmitter is released from the axon terminal after an action potential has reached the synapse. The neurotransmitter crosses the synaptic gap to reach the receptor site of the other cell or neuron. Then the neurotransmitter goes through a reuptake where the neurotransmitter attaches to the receptor site and is reabsorbed by the neuron. |
Synapse |
|
|
Nerve |
In the Peripheral nervous system a bundle of axons is called a nerve. In the Central Nervous system a bundle of axons is called a tract. Nerves can be either spinal or cranial. |
|
|
|
Axon |
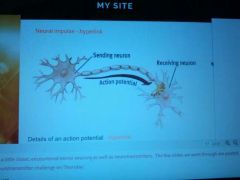
Long threadlike part of a nerve cell along which impulses are conducted from the cell body to other cells. |
|
|
|
Cerebrum |
Responsible for control of voluntary movements and coordinate mental actions. |
|
|
|
Medulla |
Controls heartbeat and breathing. |
|
|
|
Pons |
'Bridge' Coordinates movement Involved in sleep, arousal, and facial expression. |
|
|
|
Reticular Formation |
Responsible for mood, arousal and sleep. The neurons here are the source of most serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain. |
|
|
|
White Matter |
Myelin on the nerve fibers (axons) makes it white. Fatty insulators speed communication, one of the type of glial cells. |
|
|
|
Grey Matter |
Part of brain controlled by nerve cell bodies and the majority of true dendrites. Grey because neuronal nuclei and somas and dendrites don't have fatty myelin. Does the real processing. |
|
|
|
Areas of Cerebral Cortex |
Sensory- Processes incoming info from sensory systems (vision, smell, etc) Motor- Helps you move to the best of your abilities.
Association- Helps build bridges beteen sensation and action, language, and abstract thought. |
SAM |
|
|
Cerebral Cortex Lobes |
Frontal Lobe- Speaking, muscle movements, judgements and planning. Temporal Lobe- Auditory areas. Parietal Lobe- Sensory Cortex, receives info regarding touch and body position. Occipital Lobe- Visual area, receives info from eyes. |
|
|
|
Fissures |

Lateral Fissure (Sulcus) and Central Fissure (Sulcus) |
|
|
|
Somatosensory Cortex |
Tissue stimulation can cause a person to report feeling touched or to feel as if they have moved a limb when they haven't. |
|
|
|
Audito |

Auditory Cortex and Visual Cortex |
|
|
|
Broca's area |
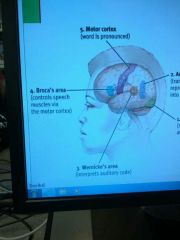
Controls speech muscles via the motor cortex |
|
|
|
Angular Gyrus |

Transforms Visual representations into an auditory code. |
|
|
|
Visual Cortex |

Receives written words as Visual stimulation. |
|
|
|
Wernicke's Area |

Interprets auditory code. |
|
|
|
Acetylcholine (ACh) |
Enables muscle action, learning, and memory. As ACh-producing neurons deteriorate, it marks Alzheimer's disease. |
|
|
|
Dopamine |
Influences movement, learning, attention and emotion. Excess dopamine receptor activity linked to schizophrenia; starved of dopamine the brain produces the tremors and decreased mobility of Parkinson's disease. Excess dopamine receptor activity linked to schizophrenia; starved of dopamine the brain produces the tremors and decreased mobility of Parkinson's disease. |
|
|
|
Norepinephrine |
Helps control alertness and arousal. Undersupply can depress mood. |
|
|
|
Serotonin |
Affects mood, hunger, sleep and arousal. Undersupply linked to depression. |
|
|
|
GABA (Gamma aminobutyric acid) |
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter. Undersupply linked to seizures, tremors and insomnia. |
|
|
|
Glutamate |
Major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory. Oversupply can overstimulate brain, leading to migraines or seizures. |
|
|
|
Cognition |
All mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering and communicating |
|

