![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
105 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. Which is NOT a major function of the blood?
|
e. Production of oxygen
|
|
|
2. The normal average temperature of blood is around
|
b. 100.4F
|
|
|
3. The normal pH range for blood is
|
e. 7.35-7.45
|
|
|
4. Which of the following is not a component of blood?
|
c. Carbon dioxide
|
|
|
5. The hematocrit is composed of
|
c. RBC
|
|
|
6. How much of blood plasma is water (approximately)?
|
b. 91%
|
|
|
7. Which of the following plasma proteins plays a role in disease resistance?
|
b. Globulins
|
|
|
8. Which of the following plasma proteins plays a role in blood clotting?
|
c. Fibrinogens
|
|
|
9. A hemocrit measures
|
a. A. Percentage of RBC in packed blood
|
|
|
10. The process by which formed elements of the blood develop is called:
|
b. Hemopoiesis
|
|
|
11. A megakaryoblast will develop into
|
c. C. Platelet
|
|
|
12. During hemopoiesis, some of the myeloid stem cells differentiate into
|
a. Progenitor cells
|
|
|
13. This hormone stimulates proliferation of red blood cells in red bone marrow
|
a. EPO
|
|
|
14. How many hemoglobin molecules are in each RBC?
|
c. 280 million
|
|
|
15. Ferritin is used to
|
b. Store iron
|
|
|
16. A red blood cell’s function is
|
d. Gas transport
|
|
|
17. A red blood cell without a nucleus is called a
|
e. Reticulocyte
|
|
|
18. Which of the following is a phagocyte?
|
a. Monocytes
|
|
|
19. Which of the following reduces blood loss?
|
b. Platelet
|
|
|
20. Which of the following promotes inflammation?
|
d. Basophil
|
|
|
21. Which of the following destroys antigen-antibody complexes?
|
a. Eosinophil
|
|
|
22. Which of the following provides immune responses?
|
a. Eosinophil
|
|
|
23. Which of the following is not an agranular leukocyte?
|
d. Basophil
|
|
|
24. The process of a white blood cell squeezing between cells to exit the blood vessel is called
|
a. Emigration
|
|
|
25. Which of the following do mast cells not release?
|
c. Nitric oxide
|
|
|
26. This hormone causes the development of megakaryoblasts.
|
b. Thrombopoietin
|
|
|
27. Which methods provide hemostasis?
|
platelet plug formation, vascular spasm, clotting
|
|
|
28. Once this is formed, the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways are identical.
|
b. Prothrombinase
|
|
|
29. Which of the following clotting factors has the most to do with strengthening and stabilizing a blood clot?
|
d. Factor XIII
|
|
|
30. Considering Rh blood types, which of the below situations would result in maternal antibodies attacking the fetus?
|
d. Mom is Rh positive and fetus is Rh positive.
|
|
|
31. Which of the following opposes the action of thromboxane A2?
|
e. Prostacyclin
|
|
|
32. Which of the following is an anticoagulant?
|
a. Heparin
|
|
|
31. Which of the following opposes the action of thromboxane A2?
|
e. Prostacyclin
|
|
|
32. Which of the following is an anticoagulant?
|
a. Heparin
|
|
|
31. Which of the following opposes the action of thromboxane A2?
|
e. Prostacyclin
|
|
|
32. Which of the following is an anticoagulant?
|
a. Heparin
|
|
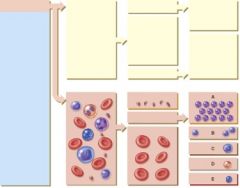
33. Which of the following cells will develop into macrophages?
|
c. C
|
|
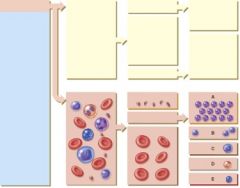
34. Which of the following cells will increase the number of nuclear lobes as they age?
|
a. A
|
|
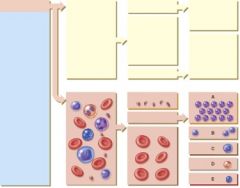
35. Which of the following cells is normally classified as small or large?
|
b. B
|
|
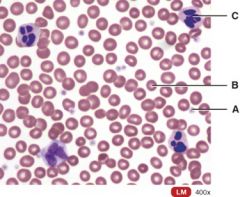
36. Which one is a WBC?
|
c. C
|
|
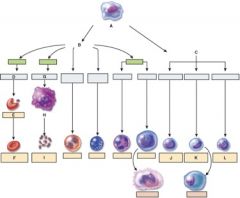
37. Which one is the pluripotent stem cell?
|
a. A
|
|
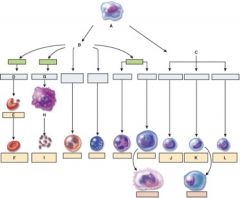
38. Which cell is the myeloid stem cell?
|
b. B
|
|
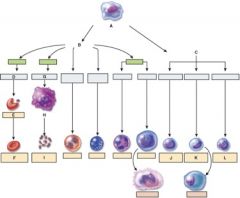
39. Which cell is the reticulocyte?
|
c. E
|
|
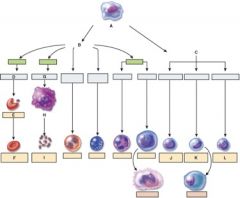
40. Which cell is the T lymphocyte?
|
b. J
|
|
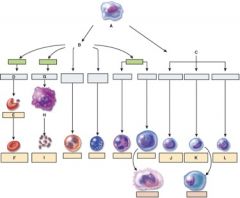
41. Which cell is the natural killer cell?
|
e. L
|
|
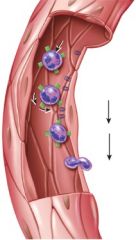
42. What is this figure demonstrating?
|
c. Emigration
|
|
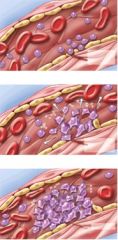
43. What does this figure represent?
|
d. Clot formation
|
|
|
44. What antibodies does a person with type O blood have in their plasma?
|
c. A and B
|
|
|
45. What antigens does a person have on their RBC if their plasma has antibody A?
|
b. B
|
|
|
1. This is the mass of tissue from the sternum to the vertebral column between the lungs.
|
d) Mediastinum
|
|
|
2. This is the layer that protects the heart.
|
a) Epicardium
|
|
|
3. To which side of the body is the apex pointed?
|
b) To the left
|
|
|
4. Which of the following consists of inelastic dense irregular connective tissue?
|
c) Fibrous pericardium
|
|
|
5. This is used to reduce the friction between membranes of the heart.
|
d) Pericardial (serous) fluid
|
|
|
6. This consists of mesothelium and connective tissue.
|
a) Epicardium
|
|
|
7. Which layer consists of cardiac muscle tissue?
|
c) Myocardium
|
|
|
8. This is used to increase the capacity of the atrium.
|
e) Auricle.
|
|
|
9. This marks the boundary between the ventricles.
|
e) Anterior and posterior intercentricular sulcus
|
|
|
10. These extend into the auricle.
|
a) Pectinate muscles
|
|
|
11. Through which structure does blood pass from the right atrium to the right ventricle?
|
c) Tricuspid valve
|
|
|
12. What types of tissue comprise the valves of the heart?
|
b) Dense irregular connective tissue
|
|
|
13. From the left ventricle, where does blood pass?
|
d) Aortic semilunar valve
|
|
|
14. In a fetus, this structure temporarily shunts blood from the pulmonary trunk into the aorta.
|
e) Ductus arteriosus
|
|
|
16. As each ventricle contracts where does blood move?
|
a) Into an artery
|
|
|
17. As each atrium contracts where does blood move?
|
d) Through an atrioventricular valve
|
|
|
18. Which of the below valves prevents blood from flowing back from the lungs?
|
c) Pulmonary valve
|
|
|
20. In this disorder the aortic valve is narrowed.
|
d) Aortic stenosis
|
|
|
22. This heart structure carries deoxygenated blood.
|
c) Right atrium and ventricle
|
|
|
23. This vessel distributes oxygenated blood to the myocardium.
|
a) Coronary artery
|
|
|
24. Cardiac muscle fibers electrically connect to neighboring fibers by
|
c) Gap junctions
|
|
|
25. Which of the following contains the largest amount of mitochondria?
|
c) Cardiac muscle
|
|
|
27. This is a network of specialized cardiac muscle fibers that provide a path for each cycle of cardiac excitation to progress through the heart.
|
d) Conduction system
|
|
|
28. This is a the correct sequence of structures that allows the normal sequence of excitation to progress through the heart.
|
d) SA node, AV node, Bundle of His, Purkinje fibers
|
|
|
29. By comparison, cardiac muscle cells have _____________contraction plateau time than skeletal muscle cells.
|
b) a longer
|
|
|
30. This is the volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle into the aorta each minute.
|
a) Cardiac output
|
|
|
31. This term refers to the period of time during a cardiac cycle when contraction occurs and blood pressure rises.
|
b) systole
|
|
|
32. Which of these periods represents greatest cardiac output?
|
d) ventricular systole
|
|
|
33. The second heart sound represents which of the below events?
|
d) Semilunar valves closing
|
|
|
34. This part of the heart can initiate a contraction and can set a constant heart rate of about 100 beats per minute.
|
d) Sinoatrial node
|
|
|
35. Stimulation of this nerve reduces heart rate.
|
d) Vagus nerve
|
|
|
36. Which of the below reduces heart rate.
|
c) Increased potassium levels
|
|
|
37. This part of the brain regulates heart rate.
|
c) Medulla oblongata
|
|
|
38. This electrical event represents repolarization of the ventricle.
|
b) Twave
|
|
|
39. Which of the below factors would increase Stroke volume?
|
c) increased preload, decreased afterload, increased contractility
|
|
|
40. This electrical event triggers contraction of the atria.
|
d) P wave
|
|
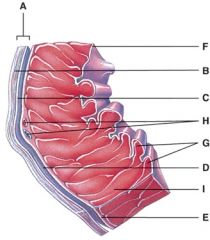
41. This portion of the heart wall is responsible for the pumping action.
|
e) I
|
|
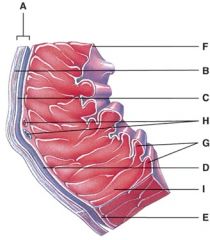
42. This is comprised of a thin layer of endothelium overlying a thin layer of connective tissue.
|
d) F
|
|
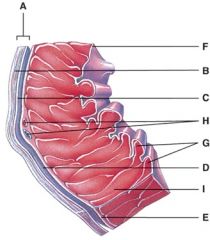
43. Which layer of the pericardium consists of dense irregular connective tissue?
|
b) B
|
|
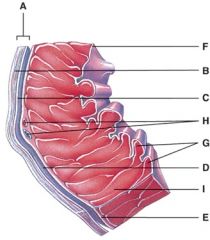
44. In the diagram, where is the trabeculae carnae?
|
d) G
|
|
45. In the diagram, where is the coronary sulcus?
|
b) E
|
|
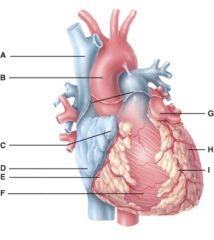
46. In the diagram, where is the left auricle of left atrium?
|
c) G
|
|
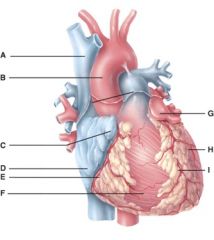
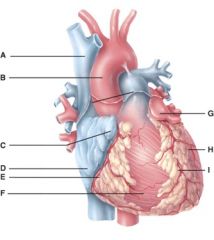
47. In the diagram, where is the ascending aorta?
|
b) B
|
|
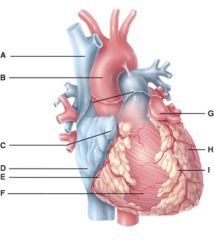
48. In the diagram, these contain coronary blood vessels and a variable amount of fat.
|
d) E and I
|
|
49. In the diagram, where does the blood pass from the right atrium into the right ventricle?
|
b) B
|
|
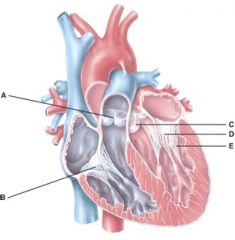
50. In the diagram, where are the semilunar valves?
|
e) None of the above
|
|
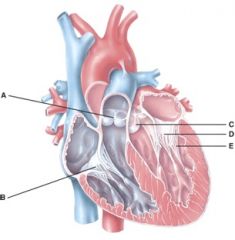
51. In the diagram, where is the atrioventricular valve?
|
d) B and D
|
|
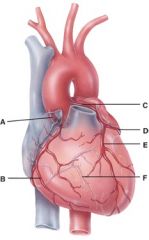
52. In the diagram, this supplies the walls of the left ventricle with oxygenated blood.
|
e) F
|
|
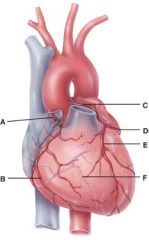
53. In the diagram, all of the following carry oxygenated blood.
|
d) E
|
|
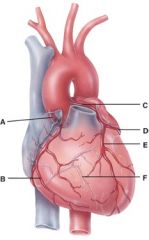
54. In the diagram, where is the marginal branch?
|
b) B
|
|
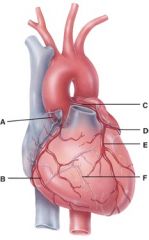
55. In the diagram, where is the posterior interventricular branch?
|
d) F
|
|
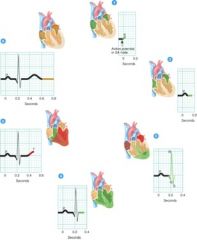
58. Where in the figure does depolarization events occur?
|
b) 1 and 3
|
|
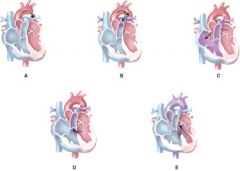
59. Which of the follow represents coarctation of the aorta?
|
a) A
|
|
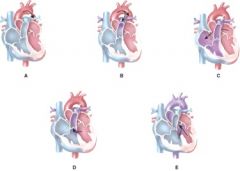
60. Which of the following represents an atrial septal defect?
|
c) C
|
|
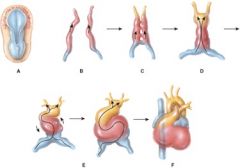
61. Which of the following represents the formation of the primitive heart tube?
|
c) C
|
|
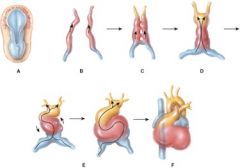
62. Which of the following represents formation of the endocardial tubes?
|
b) B
|

