![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What charges are involved in the electric force
|
Electrons, negative, are free to move about from atom to atom in a conductor. Protons are bound in place to the nucleus.
|
|
|
Charging by induction
|
A neutral object becomes charged when a charged object approaches it.
|
|
|
The Fundmaental unit of charge.
|
The electron.
1.6 x 10^-19 Coulombs |
|
|
Electrostatic force between two charged objects.
Coulombs law |
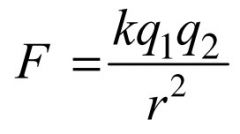
|
|
|
The Electric Field
|
A region of space where a small test charge feels an electrostatic force.
Units: Newton/Coulomb Its direction is the direction of the force on a positive test charge. |
|
|
Electric Field from a single change.
|
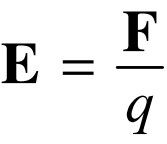
|
|
|
Superposition of the electric field.
|
recall that since the electric field is a vector, it must be summed with vector arithemetic.
|
|
|
Electric Potential Energy
|
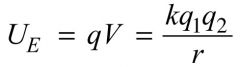
The energy stored in an arrangement of electric changes. It is equal to the work need to bring charges from a distance of infinity to their arrangement.
|
|
|
Electric Potential or Potential Difference or Voltage
|
The energy per unit change between two places in space or in a circuit.
V=Ed |
|
|
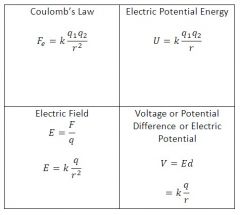
Electrostatics Formula square
|
|

