![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
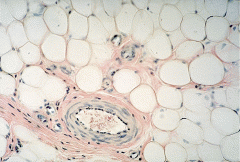
- nucleus
- cytoplasm - plasma membrane p 134 |
Adipose Tissue
|
|
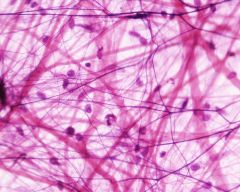
- fibroblast
|
Areolar Connective Tissue
|
|
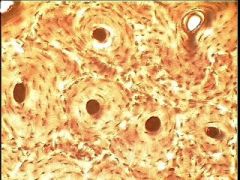
- osteocyte
- canaliculi - lacuna - lamellae |
Osseous (bone) Tissue
|
|
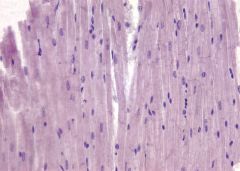
- striations
- nucleus |
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
|
|
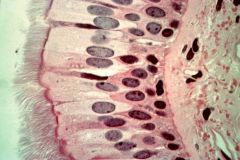
- cilia
- goblet cells - lumen - basement membrane - connective tissue |
Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
|
|
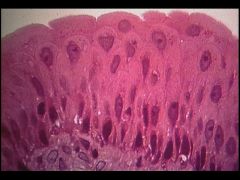
-lumen of jejenum
- nucleus - basement membrane - microvilli or cilia - goblet cell |
Simple Columnar Epithelium
|
|
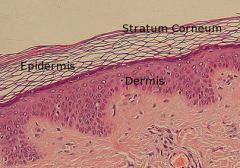
- stratum corneum
- stratum basale |
Epidermis
|
|
- lacuna
- chondrocyte - nucleus - collagen fibers (blue) |
Fibrocartilage
(blue) |
|
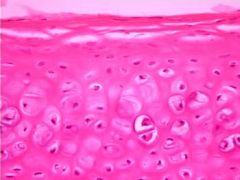
- lacuna
- nucleus |
Hyaline Cartilage
|
|
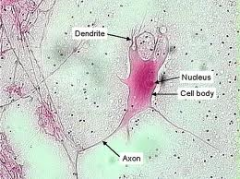
- dendrite
- axon - nucleus |
Nervous Tissue
|
|
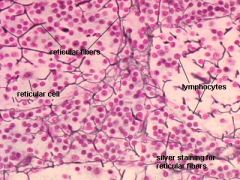
- reticular fiber
- nucleus |
Reticular Connective Tissue
|
|
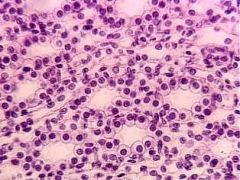
- plasma membrane
- nucleus - connective tissue - lumen - basement membrane |
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
|
|
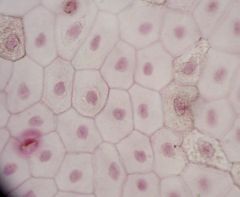
- plasma membrane
- cytoplasm - nucleus |
Simple Squamous Epithelium
|
|
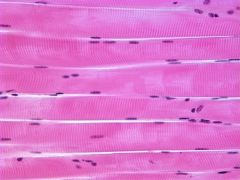
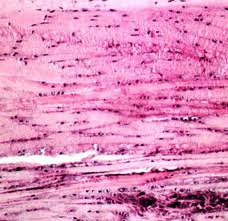
- nucleus
- striations |
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
|
|
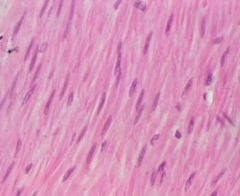
- nucleus
- muscle fiber |
Smooth Muscle Tissue
|
|
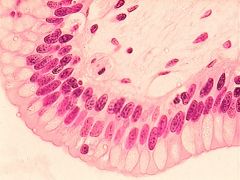
- nucleus
- apical surface - basement membrane - connective tissue |
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
|
|
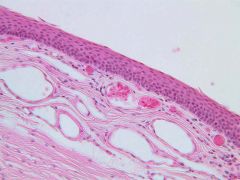
- nucleus
- lumen - basement membrane |
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
(buccal smear) |
|
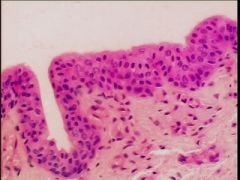
- lumen
- apical surface - nucleus - connective tissue |
Transitional Epithelium
|
|

- nucleus of fibroblast
- collagen fiber |
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Collagenous fiber |
|
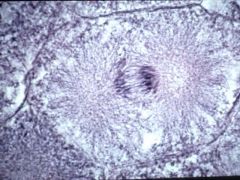
What stage of mitosis is this?
|
Mitosis: Anaphase
Separation of sister chromatids (ie chromosomes) Move toward the poles |
|
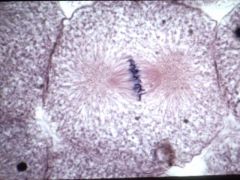
What stage of mitosis is this?
|
Mitosis: Metaphase
Chromosomes align along the metaphase plate Centrioles reach plate - aster rays - spindle fibers - centrioles |
|
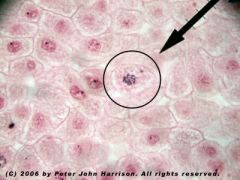
What stage of mitosis is this?
|
Mitosis: Prophase
Nuclear membrane disappears Chromatin condenses |
|
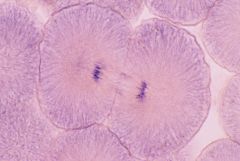
What stage of mitosis is this?
|
Mitosis: Telophase
cytokinesis occurs cleavage furrows nuclear membrane forms chromosome uncondenses (disappears) |
|
|
Name the four tissue types.
|
1. Epithelial
2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous |
|
|
Epithelial tissue: arrangement.
Name the four cell shapes and describe them. |
1. Squamous: broad, flat cell
2. Cuboidal: square or round 3. Columnar: tall, thin 4. Transitional: looks like stratified cuboidal cells; found mast commonly in urinary tract |
|
|
Name the three arrangements of epithelial tissues and describe each.
|
1. Simple: a single layer of cells
2. Stratified: 2 or more layers of cells 3. Pseudostratified: all cells touch the bottom, but not all cells reach the surface |
|
|
Cili is for ____ and microvilli is for ______.
|
movement, absorption
|
|
|
Name the three types of fibers.
|
1. Collagen fibers - tough, non stretchy
2. Elastin fibers - can be stretched 1/2 times their original shape without damage 3. Reticular fibers - more rigid |
|
|
What part of this is a type and what is subtype:
Simple Squamous Epithelium |
Subtype: Simple squamous
Type: epithelium |
|
|
What type of tissue is fibrocartilage?
|
Connective
ie Fibrocartilage connective tissue |

