![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What do the ovaries produce? |
2nd oocytes and hormones |
|
|
What do the uterine tubes transport? |
fertilized ova |
|
|
What does the vulva consist of? |
Vagina and external genitalia |
|
|
Where does fetal development occur? |
uterus |
|
|
The ovary |
pair of organs in upper pelvic region -tunica albuginia -cortex -medulla -germinal epithelium |
|
|
Tunica Albuginia |
capsule of dense connective tissue |
|
|
Cortex of Ovary |
region just deep to tunica, contains follicles |
|
|
Medulla of Ovary |
deeper region composed of connective tissue, blood vessels & lymphatics
|
|
|
Germinal Epithelium |
simple epithelial covering over the ovary
|
|
|
Reproductive Ligaments |
-Broad ligament suspends uterus from side wall of pelvis
-Mesovarium attaches ovaries to broad ligament -Ovarian ligament anchors ovary to uterus -Suspensory ligament covers blood vessels to ovaries -Round ligament attaches ovaries to inguinal canal |
|
|
Stages of Follicular Development |
primordial
primary secondary graafian ovulation |
|
|
Corpus Luteum |
ovulation wound
fills in with hormone secreting cells |
|
|
Corpus Albicans |
white scar left after corpus luteum is not needed
|
|
|
Histology of Graafian Follicle |
Zona pellucida -- clear area between oocyte & granulosa cells
Corona radiata is granulosa cells attached to zona pellucida--still attached to oocyte at ovulation Antrum formed by granulosa cells secreting fluid By this time, the oocyte has reached the metaphase of meiosis II stage and stopped developing -- first polar body has been discarded |
|
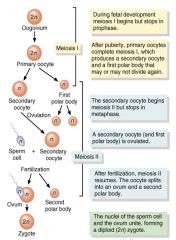
|
oogenesis |
|
|
Uterine Tube |
aka Fallopian tube -narrow 4 inch tube that extends from ovary to uterus infundibulum: open, funnel shaped portion near the ovary (fimbriae are moving, finger like processes) ampulla: central region of the tube isthmus: narrowest portion, joins uterus |
|
|
Histology of uterine tube |
mucosa = ciliated columnar epithelium with secretory cells provide nutrients & cilia move along ovum
muscularis = circular & longitudinal smooth muscleperistalsis helps move ovum down to the uterus serosa = outer serous membrane |

