![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
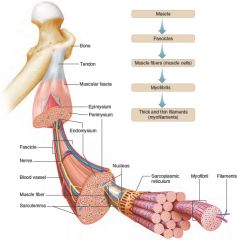
A skeletal muscle is composed of a variety of tissues, including layers of connective tissue. Fascia covers the surface of the muscle, epimysium lies beneath the fascia, and perimysium extends into the structure of the muscle where it separates muscle cells into fascicles. Endomysium separates individual muscle fibers. |
|
|
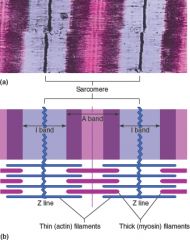
A sarcomere is a functional unit of muscle contraction. (a) Micrograph (16,000×). (b) The spatial relationship of thin and thick filaments in a sarcomere makes contraction possible. |
|

|
Anterior view of superficial skeletal muscles
|
|

|
Posterior view of superficial skeletal muscles.
|
|
|
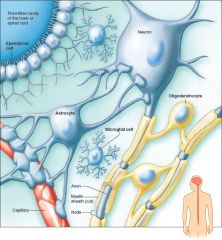
Types of neuroglia in the central nervous system include the microglial cell, oligodendrocyte, astrocyte, and ependymal cell. (Ependymal cells have cilia into early childhood. In adults, cilia remain only on ependymal cells in the ventricles of the brain.)
|
|
|
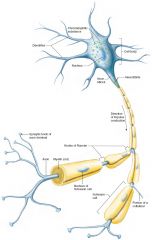
A common neuron
|
|
|
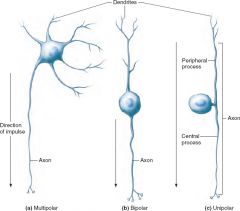
Structural types of neurons include(a) the multipolar neuron, (b) the bipolar neuron, and (c) the unipolar neuron.
|
|
|
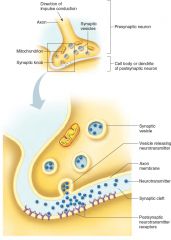
Action across a synapse. When an impulse reaches the synaptic knob at the end of an axon, synaptic vesicles release a neurotransmitter that diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to specific receptors on the membrane of the postsynaptic cell.
|
|

|
A withdrawal reflex involves a sensory neuron, an interneuron, and a motor neuron.
|
|

|
Meninges. (a) Membranes called meninges enclose the brain and spinal cord. (b) The meninges include three layers: dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater.
|
|
|
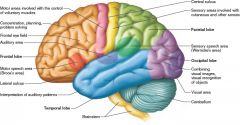
Some sensory, association, and motor areas of the left cerebral cortex.
|
|

|
Ventricles in the brain. (a) Anterior view of the ventricles within the cerebral hemispheres and brainstem. (b) Lateral view.
|
|

|
Most sympathetic fibers are adrenergic and secrete norepinephrine at the ends of the postganglionic fiber; parasympathetic fibers are cholinergic and secrete acetylcholine at the ends of the postganglionic fibers. Two arrangements of parasympathetic postganglionic fibers are seen in both the cranial and sacral portions. Similarly, sympathetic paravertebral and collateral ganglia are seen in both the thoracic and lumbar portions of the nervous system. (Note: This representation does not show dendrites.)
|
|

|
Major parts of the ear. The outer ear includes the auricle, external acoustic meatus, and eardrum. The middle ear includes the auditory ossicles (malleus, incus, and stapes) and the oval window. The inner ear includes the semicircular canals and the cochlea.
|
|

|
Transverse section of the right eye (superior view).
|
|
|
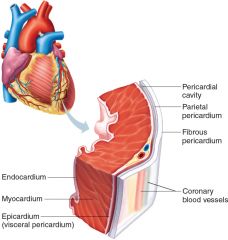
The heart wall has three layers: an endocardium, a myocardium, and an epicardium.
|
|
|
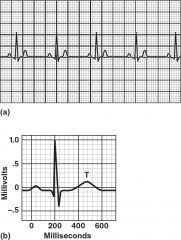
An electrocardiogram records electrical changes in the myocardium during a cardiac cycle. (a) A normal ECG. (b) In an ECG pattern, the P wave results from a depolarization of the atria, the QRS complex results from a depolarization of the ventricles, and the T wave results from a repolarization of the ventricles.
|

