![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Tissue |
A group of cells with common embryonic original Specialized activities |
|
|
|
Extra cellular matrix |
Complex, Nonliving material between cells in a tissue Some tissues have a large amount while some have hardly any
Different kinds of components= different characteristics |
|
|
|
Histology |
Study of tissues |
|
|
|
4 types of tissues are: |
Epithelial Connective Muscular Nervous |
|
|
|
Epithelial tissue |
Cover body surfaces and lines hollow organs, body cavities, ducts and forms glands |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Protects, supports and binds tissues Stores energy as fat, provides immunity |
|
|
|
Muscular tissue |
Generates the physical force needed to make body structures move and generate body heat |
|
|
|
Nervous tissue |
Detects changes in body and responds and responds by generating nerve impulses |
|
|
|
Components of extra cellular matrix |
A. Water B. Proteins 1. Structural proteins a.collagen: strong, flexible fiber b.elastin: elastic fibers 2. Glycoproteins: proteins with carbohydrates a.fibronectin and laminin- help connect components to cells C. Proteoglycans 1. Mostly carbohydrates attached to a protein backbone 2. Different functions a. Shock absorber b.thickens fluid c. Reduces blood clotting |
|
|
|
Two types of epithelial tissue |
1.Membranous (covering or lining) 2. Glandular: secretory units of endocrine and exocrine glands |
|
|
|
Functions of epithelial tissue |
A. protection B. Sensory functions C. Secretion D. Absorption E. Excretion |
|
|
|
Generalization of epithelial tissue |
Avascular- no blood vessels Basement membrane close junctions Capable of reproduction Limited amount of matrix |
5 properties |
|
|
Simple squamous epithelium |
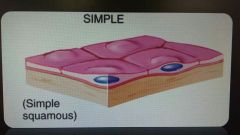
Found at sites for filtration and diffusion |
|
|
|
Simple cuboidal epithelium |
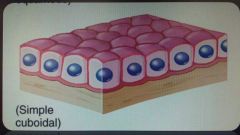
Cuboidal shaped cells -found in thyroid gland and kidneys -functions in secretion and absorption |
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelium |
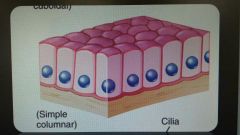
Column shaped cells Nonciliated and ciliated In stomach lining and lines airways |
|
|
|
Stratified epithelium |
Two of more layers of cells |
|
|
|
Stratified squamous epithelium |
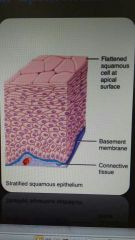
Several layers of cells that are flat in the apical layer New cells are pushed up toward the apical layer |
|
|
|
Stratified cuboidal epithelium |
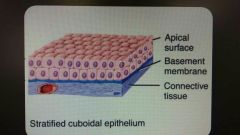
Fairly rare type of epithelium Apical layers are cuboidal Functions in protection & some secretion/absorption Found in ducts of apocrine sweat glands |
|
|
|
Pseudostratified |
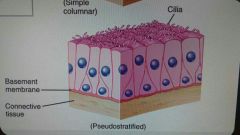
Lines some airways and most of the upper respiratory tract |
|
|
|
Transitional epithelium |
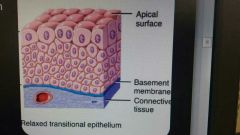
Found only in the urinary system Variable appearance Ideal for hollow structure subjected to expansion ex. Bladder |
|
|
|
Glandular epithelium Endocrine glands |
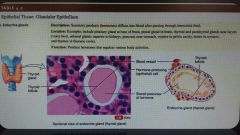
Secrete hormones, diffuse directly into the bloodstream Function in maintaining homeostasis |
|
|
|
Glandular epithelium Exocrine glands |
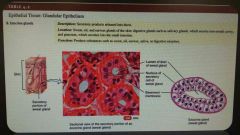
Secrete products into ducts that empty onto the surface of epithelium Mucus,sweat, oil, earwax, saliva and digestive enzymes |
|
|
|
Types of exocrine glands |
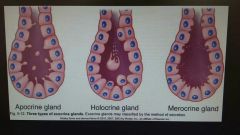
Apocrine Holocrine Merocrine |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Numerous functions |
|
|
|
Four main types of connective tissue |
Fibrous Bone Cartilage Blood |
|
|
|
Fibrous connective tissue: areolar |
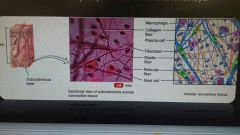
Most widely distributed in the body Contains several types of cells and all three fibers Combined with adipose, makes the subcutaneous layer |
|
|
|
Fibrous connective tissue: adipose |
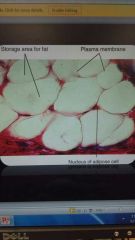
Fat |
|
|
|
Fibrous connective tissue: reticular |
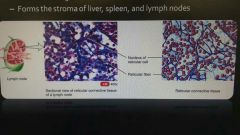
Fine interlacing reticular fibers and cells Forms the stroma of liver, spleen, and lymph nodes |
|
|
|
Fibrous connective tissue: dense regular |
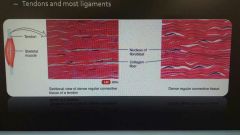
Bundles of collagen fibers are regularly arranged in parallel patterns for strength Tendons and most ligaments |
|
|
|
Fibrous connective tissue: dense irregular |
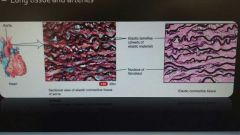
Contain branching elastic fibers Strong and can recoil to original shape after stretching Lung tissue and arteries |
|
|
|
Bone tissue |
Bones are organs composed of several different connective tissue: Bone tissue(osseous) Periosteum Endosteum |
|
|
|
Hyaline cartilage |
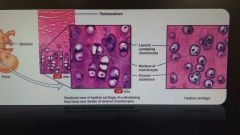
Most abundant cartilage in the body Provide flexibility and support |
|
|
|
Fibrocartilage |
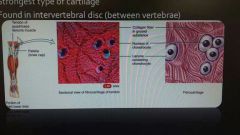
Chondrocytes are scattered amound bundles of collagen fibers within the extracellular matrix Lack a perchondrium Strongest type of cartilage Found in intervertebral disc (between vertebrae) |
|
|
|
Elastic cartilage |

Chrondrocytes are located within a thread-like network of elastic fibers Provides strength and elasticity |
|
|
|
Liquid connective tissue |
Blood tissue -connective tissue with liquid extracellular matrix called blood plasma Lymph |
|
|
|
Muscular tissue |
Consists of elongated cells called muscle fibers or myocytes -cells use ATP to generate force -several functions of muscle tissue Classified into three types: skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscular tissue |
|
|
|
Three types of muscular tissue |
Skeletal Cardiac Smooth muscular tissue |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle tissue |
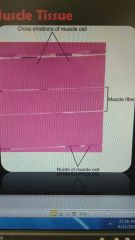
Attached to bones of skeleton Has striations Voluntary movement Vary in length (up to 40 cm) and are roughly cylindrical in shape |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle tissue |
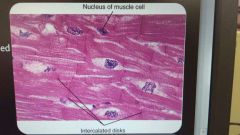
Has striations Involuntary movement Intercalated disc, unique to cardiac muscle tissue |
|
|
|
Smooth muscle tissue |

Walls of hollow internal structures -blood vessels, airways of lungs, stomach, and intestines Non striated Usually involuntary |
|
|
|
Nervous tissue |
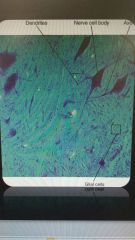
Consists of two principle types of cells -neurons or nerve cells -neuroglia |
|

