![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Articulations |
Joints are also called |
|
|
Articulations |
Are points where bones meet |
|
|
300 joints |
The body contains over |
|
|
Hyoid bone in the neck |
Only bone without a joint is |
|
|
Joints are |
Completely immovable Limited movement Considerable movement |
|
|
Joint structures |
Allow the body to walk run dance throw a ball Type on computer |
|
|
Joint classified according to |
How movable they are : fixed, semi-movable, freely movable |
|
|
Fixed joints (fibrous joints ) are |
Bound by fibers |
|
|
Cartilaginous joints |
Semi-movable joints are joined by cartilage and are called |
|
|
Synovial joints |
Freely movable joints contain a fluid-filled joint capsule and are called |
|
|
Fibrous joints (synarthroses) |
When collagen fibers from one bone penetrate the adjacent bone , anchoring the bones in place |
|
|
Fibrous joints |
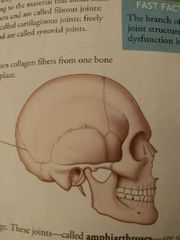
Adult skull's suture joints ____
-once growth is complete , the bones of skull knit together securely
-offering protection to the brain |
|
|
Classification of joints |
1. Fibrous joints 2. Cartilaginous joints |
|
|
Cartilaginous joints ( amphiarthroses) |
Two bones are joined by cartilage -slightly movable |
|
|
Symphysis |
Two pubic portions of the os coxae are joined by pad of cartilage called - forming the joints known as the symphysis pubis |
|
|
Intervertebral discs |
Fibrocartilaginous pads reside between each vertebrae, making the vertebrae of spine cartaginous joints |
|
|
Fibrocartilaginous pads |
Absorb shock and allow for limited movement |
|
|
Arthrology |
Branch of science that studies joint structure ,function , and dysfunction is called |
|
|
Classification of joints |
-fibrous -cartilaginous Synovial |
|
|
Synovial joints (diarthroses) |
Are freely movable - most numerous and versatile of all the body's joints |
|
|
Every synovial joint contains this structures: |
Joint capsule Synovial membrane Joint cavity Synovial fluid Articular cartilage Ligaments |
|
|
Synovial : joint capsule |
Extending from the periosteum of each of the articulating bones is a sheet of connective tissue that encloses the joint cavity |
|
|
Synovial membrane |
This moist ; slippery membrane lines the inside of the joint capsule, where it secrets synovial fluid |
|
|
Joint cavity |
This small space between the bones allows for freedom of movement . - it also contains synovial fluid |
|
|
Synovial fluid |
A slippery, viscous fluid that has the consistency of an egg white - it lubricates the joint , nourishes the cartilage and contains phagocytes to remove debris |
|
|
Articular cartilage |
A thin layer of hyaline cartilage covers the bone surfaces. - in combination with synovial fluid , permits friction - free movement |
|
|
Ligaments |
Tough cords of connective tissue help bind the bones more firmly together |
|
|
**bursae in synovial joints |
Some joints -such as the knee, shoulder, and elbow - contain small sacs filled with synovial fluid called - residing in areas where muscles and tendons pass over bony prominences., the ー facilitate movement and ease friction |
|
|
Types of synovial joints |
1. Ball and socket 2. Pivot 3. Hinge 4 saddle 5 condyloid 6. Gliding |
|
|
Ball and socket joint |
Head of the one bone fits into a cup like socket of another bone to form this joint to offer the widest range of motion of all joints -ex : shoulder , hip |
|
|
Most range |
Ball and socket joint |
|
|
Pivot joint |
Projection from one bone articulates with a ring shaped socket of another bone, allowing the bones to rotate or ____. Ex: dens of second cervical vertebra turns within a ring shaped portion of the first vertebra - allowing the head to rotate Ex: radiounlar joint, head of the radius rotate within a groove of ulna |
|
|
Hinge joint |
Like a hinge on a door , this joints allow only back and forth movement (flexion and extension) - to form this joint , the convex surface of one bone (such as a humerus) fits into a concave depression on another bone (such as ulna) Ex: knee and interphalangeal joints of fingers and toes |
|
|
Saddle joint |
Surfaces from both bones in this joint are shaped like a surface of a ___. - concave in one direction (front rear of curvature of horses saddle). Ex: thumbs |
|
|
Condyloid joint |
Oval convex surface on one bone fit into a similarly shaped depression on another Ex: articulation of distal end of radius with carpal bones of wrist as well. As the joint at the base of fingers - this joints allow flexion and extension as well as side to side movement |
|
|
Gliding joint |
Two bones surface, which are relatively flat , slides over each other . Surround ligaments limit the amount of moment -making it least mobile of all synovial joints Ex: tarsal bones of ankle , carpal bone of wrist and articular processes of vertebrae |
|
|
Movement KS of synovial joints depend on |
Upon the shape of joints , as well as involvement of nearly muscle, tendons ,ligament |
|
|
Flexion |
Involves bending a joint so as to decrease the angle of the joint |
|
|
Extension |
Straightening a joint , increasing the angle between the bones |
|
|
Hyperextension |
Is the extreme extensions of a joint beyond its normally straight position |
|
|
Dorisflexion |
Moving the toes or foot upward |
|
|
Plantar flexion |
Moving the toes or foot downward ( toward the plantar surface). |
|
|
Abduction |
Movement of a body part away from the midline of the body |
|
|
Adduction |
Movement of the body part toward the midline of the body |
|
|
Circumduction |
Distal end of an appendage, such as the arm or leg ,move in a circle |
|
|
Internal rotation |
Occurs when a bone spins toward the body's midline Ex: femur undergoes internal rotation when you turn your foot toward the body's midline |
|
|
External rotation |
Occurs when a bone spins away from the body's midline Ex: femur undergoes external rotation when your turn foot away from the midline of the body |
|
|
Supination |
Movement that turns the palm upward |
|
|
Inversion |
Foot movement that turns the sole medically toward the other foot |
|
|
Protraction |
Moves a part forward |
|
|
Retraction |
Moves a part backward |
|
|
Pronation |
Movement that turns the palm downward |
|
|
Eversion |
Foot moment that turns the sole laterally , away from the other foot |
|
|
Joints most often require medical attention are : |
Shoulder , elbows, knees, hip |
|
|
Shoulder |
Most likely to be dislocation joint |
|
|
Humeroscapular joint |
Shoulder - denoting the articulation of the humerus with the scapula |
|
|
glenohumeral joint |
articulation of the head of the humerus with the glenoid cavity of the scapula |
|
|
ball and socket joint |
Of the shoulder has the greatest range of motion of any joint in the body - shoulder more mobile than stable - shoulder is supported by a number of muscles, tendons, ligaments and bursae |
|
|
Shoulder joint is |
Supported by five principal ligaments and four bursae |
|
|
Shoulder dislocated |
Usually does so inferiorly , resulting a downward driving force -bc the ratator cuff protects the joints except inferiorly |
|
|
Children are more prone too shoulder dislocations bc |
Their shoulders aren't fully ossified. Injuries mostly from jerked off the ground by one arm or from forceful tug on the arm |
|
|
Elbow |
Is a hinge joint consisting of two articulations : humeroulnar joint and humeroradial joint |
|
|
Knee or tibiofemoral joint |
The largest joint in the body , it's also the most complex - contains 13 bursae which serve as a pad around the knee joint |
|
|
Knee: condyles |
Femur perch on the flat upper surface of the tibia |
|
|
Knee: 2 collateral ligaments |
1. Fibula collateral ligament 2. Tibial collateral ligament - keep the knee from rotating when the joint is extended |
|
|
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) |
Cross each other and further stabilize the knee . |
|
|
ACL |
Keeps the knee from hyperextending |
|
|
PCL |
Limits sideways motion |
|
|
Lateral meniscus and medial meniscus |
Two slightly concave pieces of fibrocartilage. - cradle the condyles and absorb shock |
|
|
Which injury more knee or hip |
Knee does bc it used den stops or turn ,making knee injury one must Commons athletic injuries |
|
|
Hip |
- ball and socket joint - more stable than shoulder -hip socket : depression into which the head of femur sits - is much deeper than the socket of the shoulder joint |
|
|
Hip: several ligament help hold the femur in place |
When you stand, the ligaments twist , pulling the head of the femur into the acetabulum |

