![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Synarthroses Joints |
Joints where no movement occurs |
|
|
|
Amphiarthroses Joints |
Joints that have limited movement |
|
|
|
Diarthroses Joints |
Joints that are freely movable |
|
|
|
Fibrous Joints |
Articulating bones are held together by fibrous connective tissue |
|
|
|
Fibrous Joints |
Articulating bones are held together by fibrous connective tissue |
|
|
|
Cartilaginous Joints |
Articulating bones are held together by cartilage |
|
|
|
Synovial Joints |
A connective tissue capsule encloses a fluid filled cavity between the articulating bones |
|
|
|
Coronal suture |
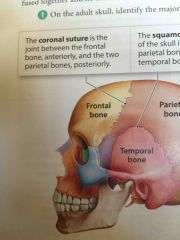
Joint between the frontal bone anteriorly |
|
|
|
Squamous Suture |
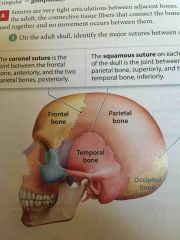
On each side of the skull. The joint between the parietal bone and the temporal bone. |
|
|
|
Squamous Suture |
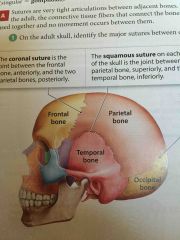
On each side of the skull. The joint between the parietal bone and the temporal bone. |
|
|
|
Lambdoid Suture |
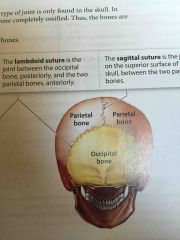
The joint between the occipital bone and the two parietal bones |
|
|
|
Squamous Suture |
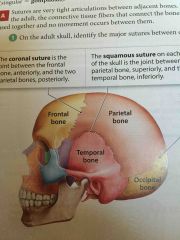
On each side of the skull. The joint between the parietal bone and the temporal bone. |
|
|
|
Lambdoid Suture |
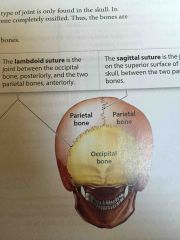
The joint between the occipital bone and the two parietal bones |
|
|
|
Sagittal Suture |
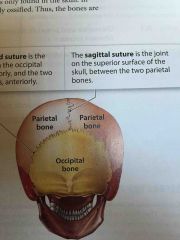
The joint on the superior surface of the skull; between the two parietal bones |
|
|
|
Periodontal Ligaments |
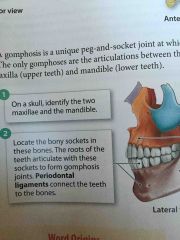
Connect the teeth to the bones |
|
|
|
Interosseous Membranes |

What the bones of the forearm and legs are connected by |
|
|
|
Coracoclavicular Joint |
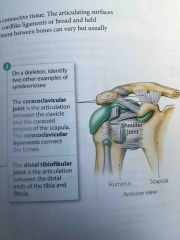
The articulation between the clavicle and the coracoid process of the scapula |
|
|
|
Coracoclavicular Joint |

The articulation between the clavicle and the coracoid process of the scapula |
|
|
|
Distal Tibiofubular Joint |
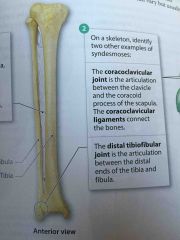
The articulation between the distal ends of the tibia and fibula. |
|
|
|
Intervertebral Discs |
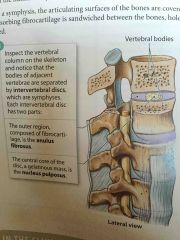
Discs between the bodies of the vertebrae. |
|
|
|
Intervertebral Discs |

Discs between the bodies of the vertebrae. |
|
|
|
Epiphyseal Plate |
Where growth occurs in developing a long bone |
|
|
|
Epiphyseal Line |
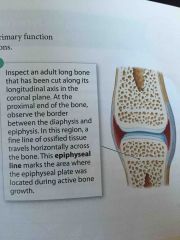
Marks the area where the epiphyseal plate was located during active bone growth |
|
|
|
Gliding Movements |
Occur when articulating surfaces of two bones move back and forth or side to side |
|
|
|
Gliding Movements |
Occur when articulating surfaces of two bones move back and forth or side to side |
|
|
|
Flexion and Extension |

The angle between the articulating bones changes |
|
|
|
Gliding Movements |
Occur when articulating surfaces of two bones move back and forth or side to side |
|
|
|
Flexion and Extension |
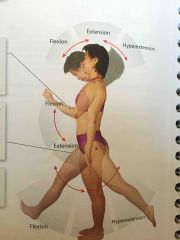
The angle between the articulating bones changes |
|
|
|
Abduction and adduction |
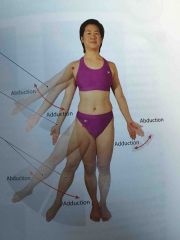
Angular movements that occur only at joints in the limbs |
|
|
|
Gliding Movements |
Occur when articulating surfaces of two bones move back and forth or side to side |
|
|
|
Flexion and Extension |
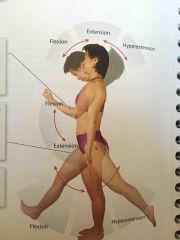
The angle between the articulating bones changes |
|
|
|
Abduction and adduction |
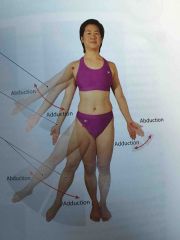
Angular movements that occur only at joints in the limbs |
|
|
|
Circumduction |

A circular motion that results from a combination of angular movements; the distal end of the part being moved describes a circle |
|
|
|
Gliding Movements |
Occur when articulating surfaces of two bones move back and forth or side to side |
|
|
|
Flexion and Extension |
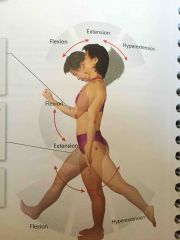
The angle between the articulating bones changes |
|
|
|
Abduction and adduction |

Angular movements that occur only at joints in the limbs |
|
|
|
Circumduction |

A circular motion that results from a combination of angular movements; the distal end of the part being moved describes a circle |
|
|
|
Rotational Movements |

Occur around the long axis of a bone |
|
|
|
Pronation and supination |
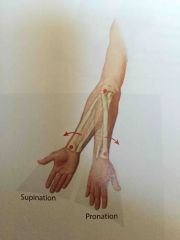
Specifically apply to the rotation of the radius around the ulna at the proximal and distal radioulnar joints |
|
|
|
Special movements |
Unique actions that occur at specific joints |
|
|
|
Opposition |

Occurs when the thumb is brought over to touch another digit. |
|
|
|
Reposition |
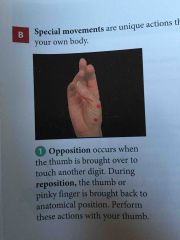
The thumb or pinky finger is brought back to anatomical position |
|
|
|
Reposition |
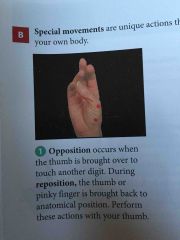
The thumb or pinky finger is brought back to anatomical position |
|
|
|
Eversion |

An action that moves the sole of the foot away from the median plane |
|
|
|
Reposition |

The thumb or pinky finger is brought back to anatomical position |
|
|
|
Eversion |
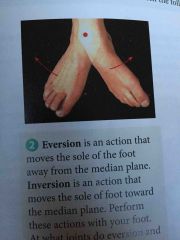
An action that moves the sole of the foot away from the median plane |
|
|
|
Inversion |
An action that moves the sole of foot toward the median plane |
|
|
|
Dorsiflexion |
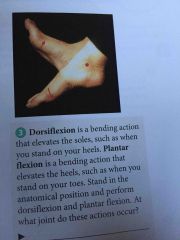
A bending action that elevates the soles, such as when you stand on your heels |
|
|
|
Front (Term) Intercarpal Joints |
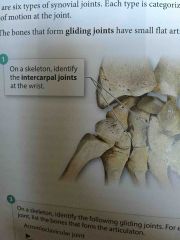
|
|
|
|
Nonaxial joints |
Gliding joints |
|
|
|
Elbow Joint |

Between the capitulum on the humorous and the radial head on the radius. Between the trochlea on the humorous and the trochlear notch on the ulna. |
|
|
|
Uniaxial Joint |
Hinge joints |
|
|
|
Pivot Joints |
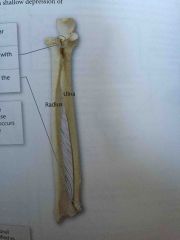
A rounded surface of one bones fits into a shallow depression of another bone |
|
|
|
Atlantoaxial Joint |
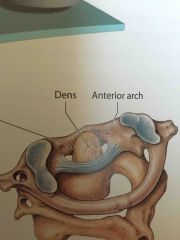
An articulation between the first two cervical vertebrae |
|
|
|
Ellipsoid Joint |
An oval shaped convex surface articulates with shallow elliptical cavity |
|
|
|
Wrist joint |
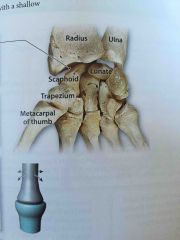
A condyle formed by the scaphoid and lunate bones, articulates with an elliptical cavity. |
|
|
|
What does the elbow joint do? |
The shapes of the articulating surfaces and the strong collateral ligaments allow flexion and extension but prevent other movements |
|
|
|
Annular Ligament |
The ligaments attaches to the anterior and posterior margins of the radial notch and wraps around the radial head |
|
|
|
Carpometacarpal Joint |
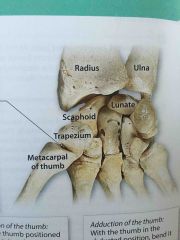
Formed by the articulation between the trapezium and the metacarpal bone of the thumb |
|
|
|
Ball and socket joints |
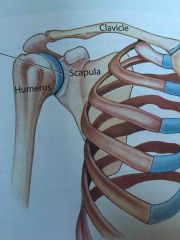
A rounded head articulates with a cup like concavity |
|
|
|
Iliofemoral ligament |
Y-shaped ligament that strengthens the anterior aspect of the hip joint |
|
|
|
Pubofemoral ligament |
This structure is attached to the pubic part of the acetabular rim |
|
|
|
Ischiofemoral Ligament |
Reinforces the posterior aspect of the joint |
|
|
|
Acetabular Labrum |
Forms an incomplete ring around the periphery |
|
|
|
Acromioclavicular Ligament |
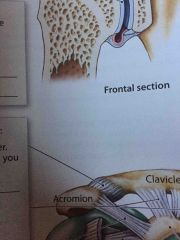
Supports the superior aspect of the shoulder |
|
|
|
What does the elbow joint do? |
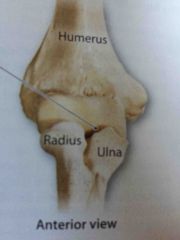
The shapes of the articulating surfaces and the strong collateral ligaments allow flexion and extension but prevent other movements |
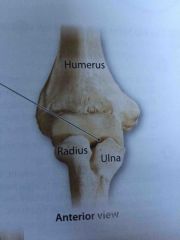
|
|
|
Annular Ligament |
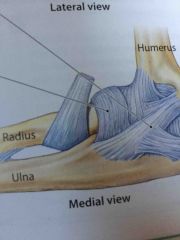
The ligaments attaches to the anterior and posterior margins of the radial notch and wraps around the radial head |
|
|
|
Lateral (radial) collateral ligament |
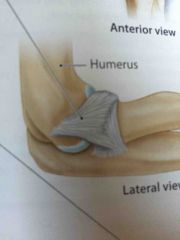
Blends and becomes continuous with the annular ligament. |
|
|
|
Quadriceps Tendon |
Attaches the quadriceps femoris muscle to the patella |
|
|
|
Iliofemoral ligament |
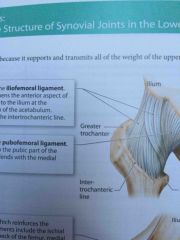
Y-shaped ligament that strengthens the anterior aspect of the hip joint |
|
|
|
Pubofemoral ligament |
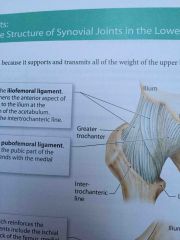
This structure is attached to the pubic part of the acetabular rim |
|
|
|
Ischiofemoral Ligament |

Reinforces the posterior aspect of the joint |
|
|
|
Acetabular Labrum |

Forms an incomplete ring around the periphery |
|
|
|
Lateral and Medial Meniscus |
C shaped fibrocartilage plates that rest on the articular surface of the tibia |
|
|
|
Ligament of the femoral head |

Extends from the transverse acetabular ligament to the fovea capitis, a small depression on the femoral head |
|
|
|
Saddle Joints |
Each articulating surface has a convex and a concave region. The shape of each surface resembles a saddle |
|
|
|
Quadriceps Tendon |
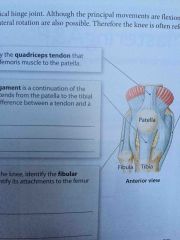
Attaches the quadriceps femoris muscle to the patella |
|
|
|
Patellar Ligament |
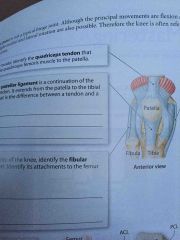
A continuation of the quadriceps tendon. It extends from the Patella to the tibial tuberosity. |
|
|
|
Fibular Collateral Ligament |
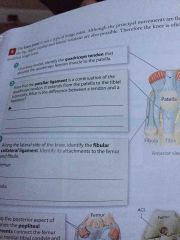
Along the lateral side of the knee. |
|
|
|
Popliteal Ligaments |
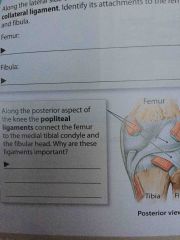
Along the posterior aspect of the knee. Connects the femur to the medial tibial condyle |
|
|
|
Tibial collateral ligament |

Along the medial side of the knee |
|
|
|
Lateral and Medial Meniscus |
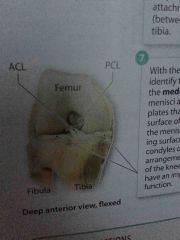
C shaped fibrocartilage plates that rest on the articular surface of the tibia |
|
|
|
Name all four sutures |
Coronal Sagittal Lambdoid Squamous |
|
|
|
Name all four sutures |
Coronal Sagittal Lambdoid Squamous |
|
|
|
What are fontanels? |
Soft spots or spaces that allow for growth. |
|
|
|
Name all four sutures |
Coronal Sagittal Lambdoid Squamous |
|
|
|
What are fontanels? |
Soft spots or spaces that allow for growth. |
|
|
|
Name the 6 cranial bones |
Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Sphenoid Ethmoid |
|
|
|
Name the 8 facial bones |
Nasal Maxilla Zygomatic Mandible Lacrimal Palatine Vomer Inferior nasal concha |
|
|
|
Name the three Auditory Ossicles |
Malleus-hammer Incus-anvil Stapes-stirrup |
|
|
|
What is a hyoid? |
It looks like a horseshoe It is used for speech It is not attached |
|
|
|
What are the 9 things that make up the Typical Structure of the Vetebrae |
Body Vertebral Arch Vertebral Foramen Intervertebral Foramen Transverse Process Spinous Process Superior Articulating Process Inferior Articulating Process Facets |
|

