![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
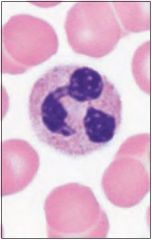
Neutrophil -Phagocyte in blood -Granulocyte -1st to site of infection -Granules help kill |
|
|
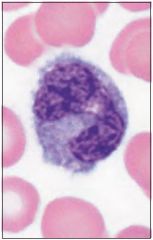
Lymphocyte -Specific immune response. B and T cells -Agranulocyte -B-cell = APC |
|
|
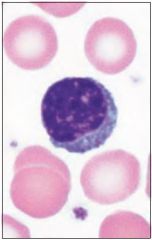
Monocyte -Becomes macrophage - Phagocyte in tissue -Agranulocyte -Largest WBC |
|
|
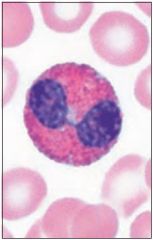
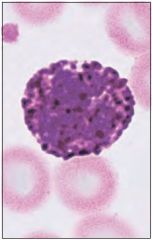
Eosinophil -Fights parasites and worms -Granulocyte -Acidic granules |
|
|
Basophil -Releases inflammatory chemicals -Granulocyte |
|
|
Name the Granulocytes. |
Neutrophil Eosinophil Basophil |
|
|
Name the Agranulocytes |
Lymphocyte Monocyte |
|
|
What are the basic functions of blood? (3) |
1. Distribution -Oxygen and CO2 -Nutrients and metabolic waste -Hormones 2. Regulation -Body temperature -Normal pH (~7.4) -Adequate fluid volume (~5L) 3. Protection -Prevent blood loss -Prevent infection |
|
|
What are the components of Blood? |
Plasma (55%) -- Erythrocytes (RBCs) (45%) --Transport oxygen Buffy Coat (<1%) -Leukocytes (WBCs) --Protect the body -Platelets --Help stop bleeding |
|
|
What are the two parts of the immune system? |
Leukocytes - Specialized immune cells Lymphoid organs and tissues |
|
|
What are the primary lymphoid organs? |
Bone marrow Thymus |
|
|
What are the secondary lymphoid organs? |
Tonsils Spleen Peyer's patches Appendix |
|
|
What are the three parts of the lymphatic system? |
Lymphatic vessels Lymph nodes Lymph |
|
|
What do lymph nodes do? |
Filter lymph Facilitate immune response |
|
|
What does the spleen do? |
Filter blood -Removes pathogens, aged RBCs and platelets -Stores platelets and breakdown products of RBCs -Site for activation of lymphocytes |
|
|
What are lacteals? |
Special lymphatic capillaries in the intestines transport absorbed fat from intestines into the blood. |
|
|
What are the three lines of defense? |
1. Surface barriers (innate) -Skin -Mucous membranes 2. Internal defenses (innate) -Phagocytes -Fever -NK Cells -Antimicrobial proteins -Inflammation 3. Adaptive defenses (adaptive) -B cells -T cells |
|
|
The 2 branches of adaptive defenses? |
Humoral (B-cells) Cellular (T cells) |
|
|
Features of Humoral Branch? |
B lymphocytes Release antibodies Target extracellular invaders Facilitate phagocytosis |
|
|
Features of Cell mediated Branch? |
T lymphocytes (cytotoxic) Release cytotoxic chemicals Target intracellular invaders Cause cell death |

