![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Blood☆ |
• Liquid part of the cardiovascular system.☆
|
|
|
Function of Blood:☆ |
1. To transport materials to & from cells. • O2 & CO2 (Lungs) • Nutrients (GIT) • Hormones (Endocrine) • Waste products (To the kidney/Liver) |
|
|
Function of Blood: ☆ |
2. Regulation of pH & ions: Eliminates deficiencies & excesses of Ca & K, Absorbs Lactic Acid. 3. Restricts fluid losses at injury sites: Enzymes that cause clotting 4. Defense against toxins/pathogens: WBC & Antibodies. 5. Stabilization of body trmparature: Redistributes heat from sleletal muscles. |
|
|
Components of whole blood(LCT)☆ |
• Plasma •Fluid Matrix •water •Plasma protein-in solution • other solution • Formed elements: •All cells,fragments & solids • Suspended in Plasma •Produced by Hematopoiesis. • Myeloid &Lymphoid Stem Cells. |
|
|
Blood☆ |

• Whole Blood=Plasma+Formed elements • Fractionation - Spinning of Blood - Process of sperating whole blood for clinical analysis/use. Into plasma and formed elements. |
|
|
Source of Whole blood☆ |
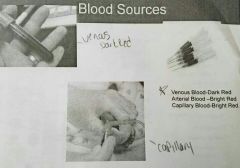
• Venous Blood- Used for most lab examinations/Blood Donation. From vein by phlebotomy. (Dark Red/purple • Arterial Blood- From Arteries, usef for Blood gases & pH. (Bright Red) • Capillary Blood- Used for some tests & for blood from infants. (Bright Red) |
|
|
Three Basic Physical Characteristic of Blood:☆ |
• Temp; 38°C (100.4°F) is above normal body temperature • 5 times as Viscous as water • Slightly alkaline pH (7.35-7.45) Blood volume: 7% body weight(kg) •Male: 5-6L •Female: 4-5L • Diff. Due to size. • Whole blood volume of 70kg man= 4.9L |
|
|
What is the liquid compent on blood?☆ |
• Plasma |
|
|
Plasma☆ |
• Makes up 55% of Whole blood Vol. • More than 90% of plasma is water • Extracellular fluids(ECF) - Interstital fuid(IF) & plasma - Materials in the plasma & IF exchange across capillary walls : Water, Ions, Small solutes. |
|
|
Difference between Plasma & IF☆ |
• Levels of O2 & CO2 - Tissue Cell Metabolism - IF has high CO2 & Low O2 • Concentrations & types of dissolved protiens - Plasma protien do not pass through capillary walls - IF has 5x less PP concentration. |
|
|
Plasma protien |
• Albumins (60%) - Transport substances such as fatty acids, thyroid hormones, & steroid hormones. • Globulins (35%) - Immunoglobulins-antibodies that fight infections - From Transport Globulins: small molecules,hormines lost at kidney - Hormone-binding protiens: Thyroid Binding Globulin,(T3/T4),Transcription, (ACTH) |
|
|
Fibrin |
• Fribrinogen (4%) - Molecules that form clots and produce long, insoluble strands of fibrin,clot framework. • Serum: Plasma minus fibrinogen & clotting protien. *Does not have the ability to clot. |
|
|
3 types of formed Elements☆ |
• Red blood cells(RBCs) or erythrocytes : Transport oxygen- 5million/microL • White Blood Cells (WBCs) or leukocytes : Part of the immune system- 5-10 thousand/microL • Platelets : Cell fragments (clotting)-500 thousand/microL |
|
|
Rule of 5th☆ |
1. Blood vol: 5L Plasma vol: 55% Cells: 45%(pack cells no hematocrit) 2. RBC-5×10^6=5 3. WBC-(5-10)×10^5 4. Platelets-500×10^3 |
|
|
Hemoglobin☆ |
• Binds & transport oxygen & carbon dioxide |
|
|
Red blood cell count:☆ |
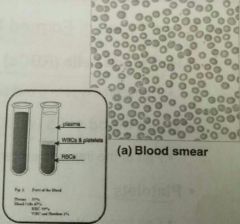
• the number of RBCs in 1microliter of whole blood. • Male: 4.5-6.3 miliion • Female: 4.2-5.5 million • Hematoctit (packed cell volume, PCV): % of RBCs in centrifuged whole blood. • Male: 40-50(47) •Female: 37-47(42) |
|
|
Hematocrit (HCT)☆ 45 |
Conditions Affecting. • Increase • Dehydration • After EPO • Decrease • Blood loss • Improper RBC formation |
|
|
RBC☆ |
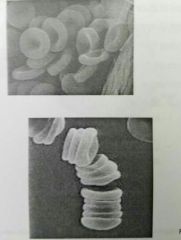
• High suface-to-volume ratio • Quickly absorbs & releases O2 • Disc from stacks called rouleaux •Smooth the flow through narrow blood vessels • Disc bend & flex entering small capillaries. |
|
|
RBC Life Span |
• Lifespan of RBCs is 120 days * Cannot repair themselves - no repair - Anaerobic metabolism- (Glucose from plasma) - Cannot use O2 : must deliver all to body cells |
|
|
Hemoglobin (Hb)☆ 15gms |
• Protien molecule that transport respiratory gasses • 95% of intracellular protiens • Normal hemoglobin: • 14-18g/dL: Male • 12-16g/dL: Female |
|
|
Hemoglobin Structure |
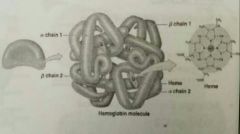
• Four globular protein subunits: • 2 Alpha & 2 Beta chains • Each with one molecule of heme • Each heme contains one iron ion • Iron ions • weak bonds • Associated easily w/ O2 (oxyhemoglobin) - bright red • Dissociate easily from O2 (deoxyhemoglobin) |
|
|
Hemoglobin function☆ |
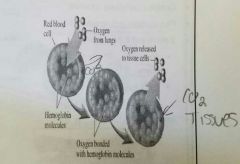
• 98.5% of O2 in Blood stream is bound to Hbg • Hemoglobin releases O2 • Binds carbon Dioxide • carbaminohemoglobin |
|
|
RBC turnover☆ |
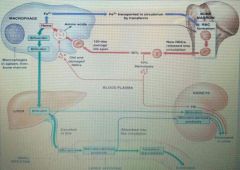
• Microphages of liver,spleen, & bone marrow • Engulf RBCs before membranes rupture (hemolyze) |
|
|
RBC turnover☆ |
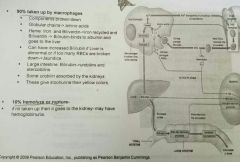
• 90% taken up by macrophages • 10% hemolyze or rupture |
|
|
Know☆ |
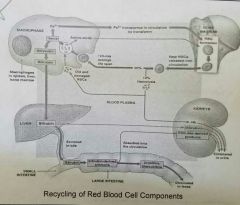
|
|
|
RBC Production |
• Erythropoiesis • vessels od Yolk Sac in embryo • Liver & Spleen in fetus • Occurs only in myeloid tissue (red bone marrow) in adults |
|
|
Hemocytoblasts |
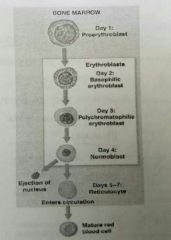
• Stem cells (in myeloid tissue) divide to produce -Myeloid stem cells: become RBCs, some WBCs -Lymphoid stem cells: become lymphocytes • Cells becoming RBC become proerythoblast then Erythroblast - at day 5 (the normiblast) necleus sheds & becomes a reticulocyte. - Enters circul. at day 7, mature RBC at day 8 |
|
|
Regulation of Erythopoiesis |
• Buildind res blood cells requires: -Amino acids -Iron -Vitamin B12 |
|
|
Stimulating hormones |
• Erythropotietin (EPO)-(Kidney) • also called erythropoirsis stimulating hormone • (hypoxia) |
|
|
Blood type☆ |
• Amtigens - RBC surfaces protien that identify cells to immune system • Surface Antigens A,B,Rh,(D) • RBC Plasma membrane |
|
|
Four basic Blood types☆ |
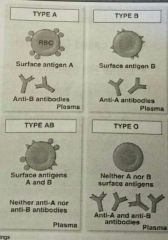
• A (Surface antigen A) • B (Surface antigen B) • AB (Antigen A & B) • O (Neither A nor B) |
|
|
AB+ is what accepter☆ |

• Universal Acceptor |
|
|
O- is what donor☆ |

• Universal Donor |
|
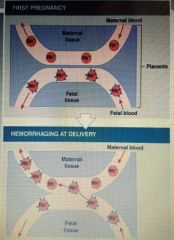
Blood typing☆ |

|
|
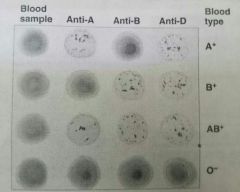
Blood typing☆ |

|
|
|
WBC (Leukocyte) ☆ |
•Have nuclei & organelles • Most WBCs are in : Connective tissue proper & Lymphoid system • Small # in blood 5000-10000 per mL |
|
|
WBC function?☆ |
1. Defend against pathogens 2. Remove toxins & waste 3. Attack abmormal cells |
|
|
WBC 5 types:☆ |
• Neutrophils (white dots) : Phagocytesis, 1st reponders. They die=pus *most abundent • Esinophils (red dots) : Kills parasites(worms) Allergies • Basophils (blue dots) : Release histamime & heparine: anti coaglant • Lymphocytes : 3types: B cell- humoral T cell- cell mediated immunity Natural Killer- immuno logical survailence • Monocytes- move in macrophages, engulf foreign substance(phagocyte) |
|
|
☆ bood |
• RBC originate in Bone marrow • T cells : Thymus • B cells : Bone marrow |
|
|
Granulocytes:☆ |
• Neutrophils • Esinophils • Basophils (inhance inflammation) |
|
|
Agranulocytes☆ |
• Monocytes • Lymphoctes |
|
|
☆WBC dissorder |
• Leukopenia- low WBC count • Leukocytosis- high WBC count • Leukemia- Extremely high WBC count |
|
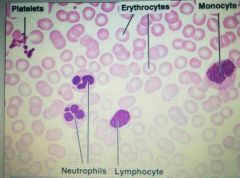
Know |
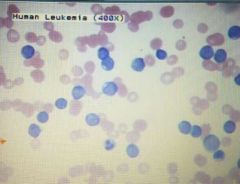
Leukemia |
|

Platelets☆ |
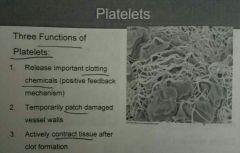
Function |
|
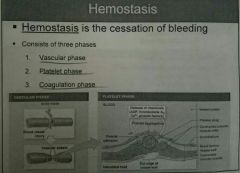
Homeostais☆ |

|
|
|
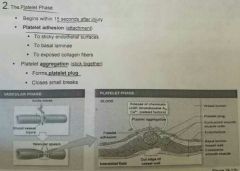
Platelet phase |
|
|
|
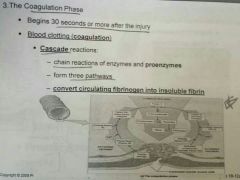
Coagulation phase |
|
|
|
Know |

|
|
|
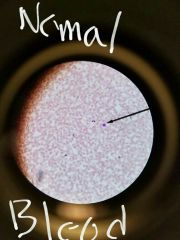
|
|
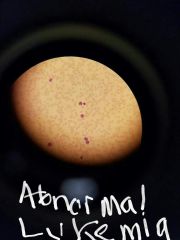
|
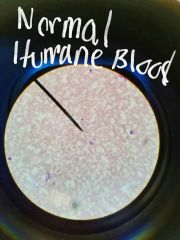
|
|
|
Bone marrow |
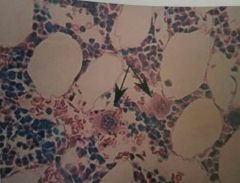
|

